A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun to avoid repetition and make sentences smoother. Words like he, she, it, they, and we are common examples. Many English learners struggle with different types of pronouns, such as personal, possessive, reflexive, and demonstrative pronouns. Understanding pronouns is essential for clear and effective communication. This blog post helps learn pronouns with definitions, types, and examples to improve your grammar skills.
Table of Contents
What is Pronoun?
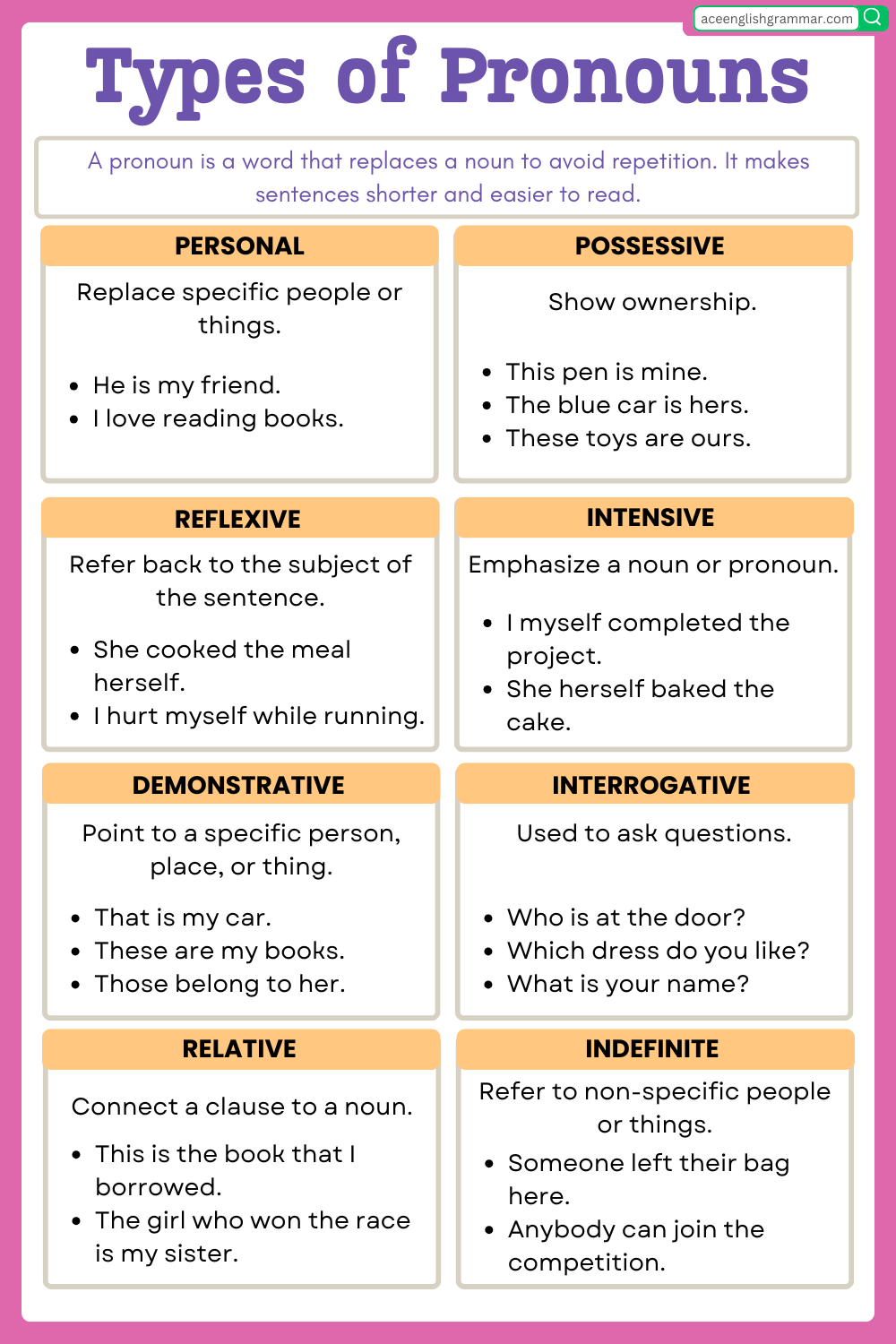
A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun to avoid repetition. It makes sentences shorter and easier to read.
Examples:
- Ali is my friend. → He is my friend.
- The book is on the table. → It is on the table.
- Sara and I went to the park. → We went to the park.
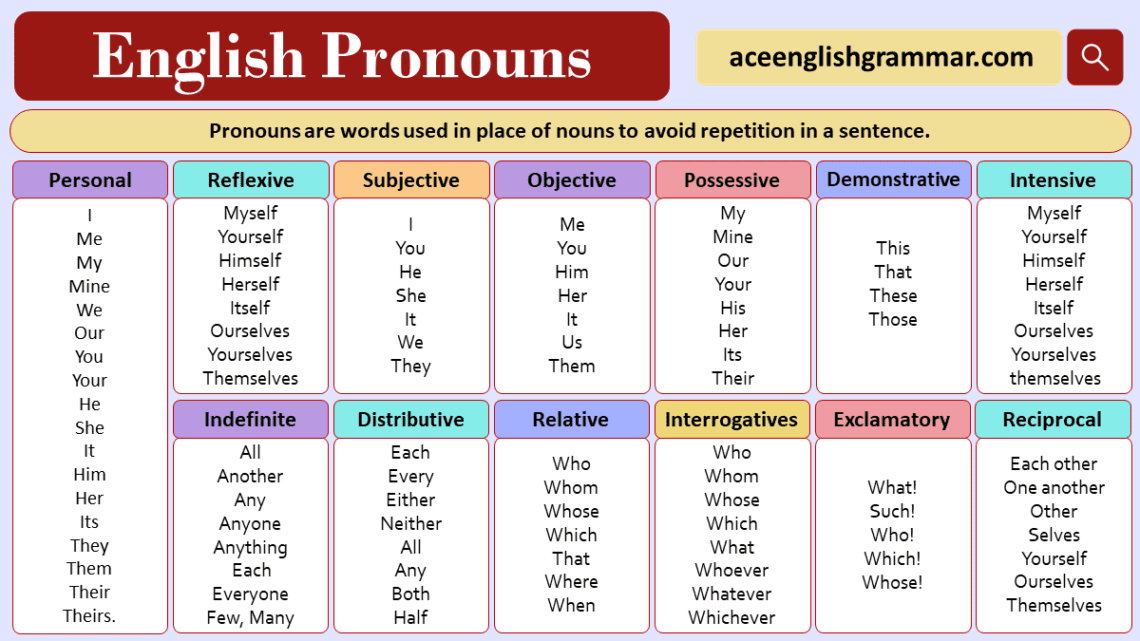
Types of Pronouns
Pronouns are categorized into several types, each serving a specific function in a sentence:
1. Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns replace specific nouns and come in three forms:
- First Person: Refers to the speaker (I, me, we, us).
- Example: I love reading.
- Second Person: Refers to the person spoken to (you).
- Example: Can you pass me the salt?
- Third Person: Refers to others or things spoken about (he, she, it, they).
- Example: He is my friend. They live next door.
2. Possessive Pronoun
Possessive pronoun indicate ownership: my, mine, our, ours, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, their, theirs.
- Example: This book is mine. Is this yours?
3. Reflexive Pronoun
Reflexive pronoun point back to the subject performing the action: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
- Example: I bought a new dress for myself.
4. Demonstrative Pronoun
Demonstrative pronoun identify specific things: this, that, these, those.
- Example: This is my favorite song.
5. Interrogative Pronoun
Interrogative pronoun is used to ask questions: who, whom, whose, which, what.
- Example: Who is at the door?
6. Indefinite Pronoun
Indefinite pronoun refer to nonspecific people or things: all, any, anyone, everyone, few, many, nobody, none, some, someone.
- Example: Everybody enjoyed the party.
7. Relative Pronoun
Relative pronoun introduce relative clauses that describe nouns: who, whom, whose, which, that.
- Example: The person who called will visit tomorrow.
8. Reciprocal Pronoun
Reciprocal pronoun show mutual action between individuals: each other, one another.
- Example: They love each other.
9. Intensive Pronoun
Intensive pronoun emphasize the subject: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
- Example: I will do it myself.
10. Exclamatory Pronoun
Exclamatory pronoun express strong emotion: what, who.
- Example: What a beautiful day!
11. Distributive Pronoun
Distributive pronoun refer to people or things individually: each, either, neither.
- Example: Each of the students received a certificate.
12. Objective Pronoun
Objective pronoun serve as objects in a sentence: me, you, him, her, it, us, them.
- Example: The teacher gave us a challenging assignment.
13. Subjective Pronoun
Subjective pronoun act as the subject in a sentence: I, you, he, she, it, we, they.
- Example: He is coming to the party.
Rules for Using Pronouns
- Match pronouns with the noun’s gender and number: he (male), she (female), they (plural).
- Use subjective pronouns (I, you, he) as the subject of the sentence and objective pronouns (me, him, her) as the object.
- Reflexive pronoun reflect back on the subject: She hurt herself.
- Demonstrative pronouns (this, those) point to specific things: This is delicious.
- Interrogative pronouns (who, what) form questions: Who is coming?
- Indefinite pronoun (everyone, anything) refer to general items: Everyone is invited.
- Relative pronoun (who, that) link clauses: The dog that barks.
- Intensive pronoun emphasize: She herself completed the task.
Example Sentences of Pronoun
- I went to the store.
- She loves to read books.
- We completed the project on time.
- They will join us for dinner.
- Is this book yours?
- Those are my shoes, not hers.
- The house is theirs.
- I cut myself while cooking.
- She found herself lost in the city.
- What a fantastic performance!
How can I avoid common pronoun mistakes?
- Ensure pronouns match the gender and number of the noun.
- Use subjective pronouns as the subject and objective pronouns as the object.
- Avoid unclear references where the pronoun’s noun is unclear.
FAQs
A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun to avoid repetition and make sentences smoother.
The main types include personal, possessive, reflexive, demonstrative, interrogative, indefinite, relative, reciprocal, intensive, exclamatory, distributive, objective, and subjective pronouns.
Subjective pronouns (I, he, she, we, they) act as the subject of a sentence.
Objective pronouns (me, him, her, us, them) function as the object of a sentence.
Possessive pronoun (mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs) stand alone. Example: This book is mine.
Possessive adjective (my, your, his, her, our, their) modify a noun. Example: This is my book.
Reflexive pronoun (myself, yourself, himself, etc.) refer back to the subject.
Example: She taught herself how to swim.
Demonstrative pronoun (this, that, these, those) point to specific things.
Example: This is my favorite song.
An indefinite pronoun refers to non-specific people or things, such as someone, everyone, anything, none.
Example: Everyone enjoyed the party.
Conclusion
Pronoun is an essential in English grammar as they make sentences concise and prevent repetition. Understanding different types of pronouns—such as personal, possessive, reflexive, and indefinite—helps in constructing clear and grammatically correct sentences. Proper usage of pronouns enhances both spoken and written communication, ensuring clarity and coherence.
By mastering pronoun rules and avoiding common mistakes, learners can improve their English fluency. Keep practicing with examples and apply pronouns correctly to enhance your grammar skills!
Read More