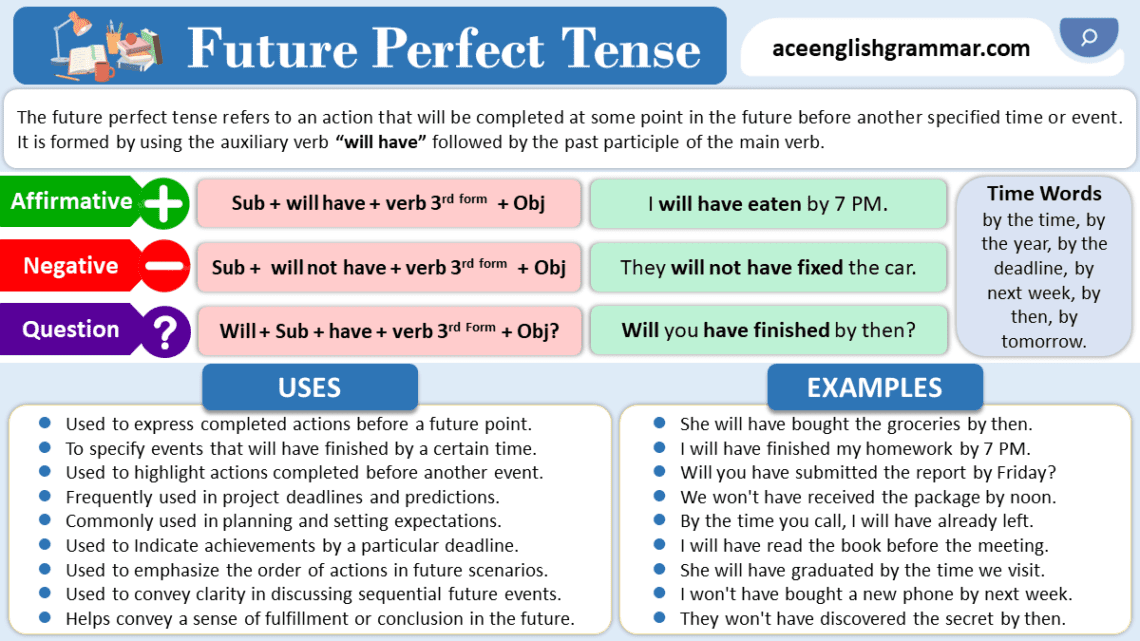
The future perfect tense is used to express actions that will be completed at some point in the future before another specified time or event. The structure is simple: it uses the auxiliary verb “will have” followed by the past participle of the main verb. This tense allows us to discuss actions or events that will be finished before a certain moment in the future.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense combines the idea of completion with a future time frame. It’s useful when we want to talk about something that will be done before a specific point in time in the future.
Example:
- By 8 PM, I will have finished my homework.
In this sentence, “I will have finished” indicates the action of completing the homework, and “by 8 PM” tells us the specific future point by which the action will be done.
In every future perfect tense sentence, there are two points in time:
- The action that will be completed.
- A future time that serves as the reference point.
Structure of the Future Perfect Tense
Positive Form
The positive form is used to indicate an action that will be completed in the future. It’s constructed using:
- Subject + will have + past participle of the verb
For example:
- She will have graduated by next year.
- They will have completed the project by the deadline.
In both sentences, the future perfect tense emphasizes that the action will be finished before the specified time.
Negative Form
The negative form is created by adding “not” after “will,” forming:
- Subject + will not (won’t) have + past participle
This is used to show that an action will not be completed by a specific future time.
For example:
- She won’t have finished the report by tomorrow.
- They will not have started the project before Monday.
These sentences express the lack of completion by a certain future point.
Interrogative Form
To ask questions in the future perfect tense, you invert the subject and “will”:
- Will + subject + have + past participle?
For example:
- Will you have finished the assignment by Friday?
- Will he have arrived by then?
This structure allows you to ask whether something will be completed by a certain time in the future.
Time Words Used with Future Perfect Tense
Certain time expressions help to clarify when the action will be completed:
- By the time
- By tomorrow
- By next week/month/year
- Before
- In a few hours/days
These time markers give the sentence a clear reference point for when the action will be finished.
Examples:
- By the time she arrives, I will have cleaned the house.
- They will have finished their homework by tomorrow evening.
Uses of Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used in a variety of situations:
- Expressing Completed Actions:
It’s useful for talking about actions that will be finished before a specific time.
Example: By next week, we will have completed the project. - Deadlines and Achievements:
It’s commonly used to talk about meeting deadlines or accomplishing goals.
Example: She will have graduated by the end of the year. - Predictions:
The tense is often used for making predictions about what will have happened by a certain time.
Example: By midnight, the storm will have passed.
Rules of the Future Perfect Tense
- Formation:
Combine “will” with “have” and the past participle of the verb.
Example: They will have finished the work by 6 PM. - Subject-Verb Agreement:
“Have” remains constant regardless of the subject.
Example: I will have arrived and They will have arrived. - Negation:
Add “not” after “will” to make a sentence negative.
Example: He will not have finished by then. - Questions:
Invert the subject and “will” to form questions.
Example: Will she have completed the task by 10 AM? - Time Expressions:
Use phrases like “by the time,” “before,” or “by next week” to show when the action will be completed.
Example: By tomorrow, they will have found a solution. - Regular and Irregular Verbs:
For regular verbs, add “-ed” to form the past participle (e.g., work → worked). For irregular verbs, the past participle must be memorized (e.g., go → gone).
Future Perfect Example Sentences
- I will have read the entire book by next week.
- She won’t have finished the project by noon.
- Will they have arrived by the time we leave?
- By the time you call, I will have gone to bed.
- The package will have arrived by Friday.
These sentences show how the future perfect tense highlights actions that will be completed by a particular time in the future.