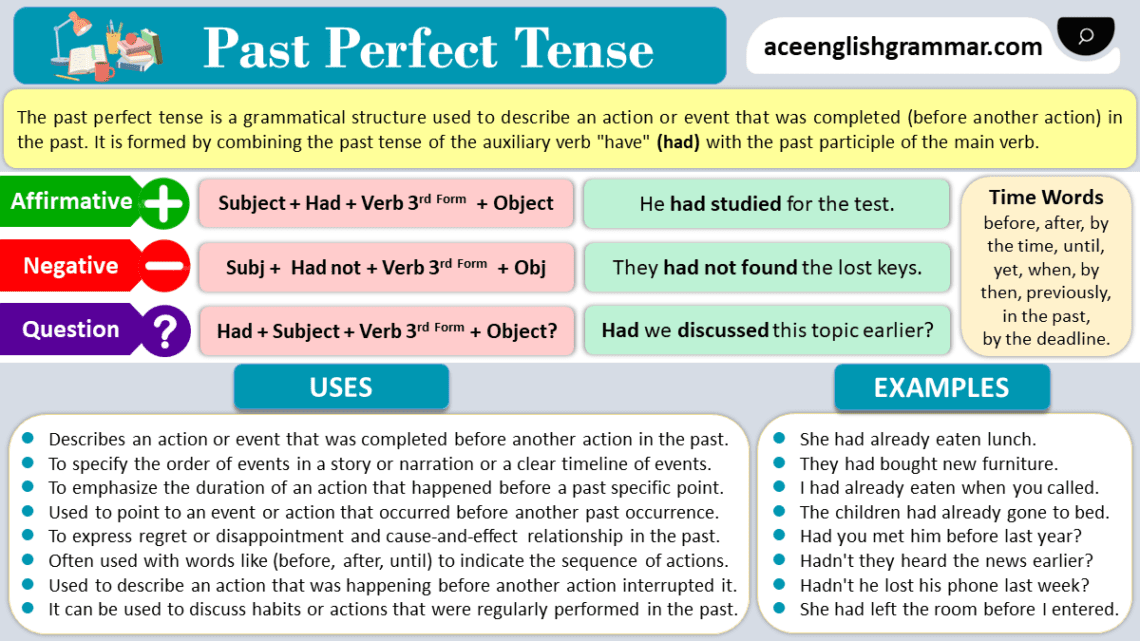
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that were completed before another action in the past. By using “had” followed by the past participle of the main verb, this tense helps clearly show which action happened first when discussing two or more past events.
Table of Contents
What is the Past Perfect Tense?
The Past Perfect Tense is a way of showing that something happened before another action or time in the past. It emphasizes the order of events, indicating which occurred first.
Example:
- “By the time I arrived, she had already left.”
This sentence shows that “leaving” happened before “arriving.”
Structure of the Past Perfect Tense
Positive Sentences:
The structure for positive sentences in the Past Perfect Tense is:
- Subject + had + past participle + object
For example:
- I had finished my homework before dinner.
- They had left before we arrived.
In both sentences, “had” and the past participle of the verb (finished, left) show that these actions were completed before another past action.
Negative Sentences:
To form negative sentences, add “not” after “had”:
- Subject + had + not + past participle + object
For example:
- She had not seen that movie before.
- They had not finished the project by the deadline.
In these examples, “had not” makes it clear that the actions were not completed before the specific point in the past.
Interrogative Sentences (Yes/No Questions):
To form yes/no questions, invert the subject and “had”:
- Had + subject + past participle + object?
For example:
- Had you completed the report before the meeting?
- Had they left before it started raining?
This structure helps to ask about whether an action had been completed before another event in the past.
Interrogative Sentences (Wh-Questions):
When asking wh-questions, use the following structure:
- Wh-word + had + subject + past participle + object?
For example:
- Where had they gone before I called?
- Why had she left so early?
This allows you to ask questions about specific details regarding what happened first in a series of past events.
Time Expressions Used with Past Perfect Tense
Certain time expressions help to make the sequence of events clear when using the Past Perfect Tense. These include:
- Before
- By the time
- Already
- After
- When
- Until
For example:
- By the time he arrived, I had already finished dinner.
- She had left the office before I called.
These time expressions clarify which action occurred first and when it happened.
Uses of the Past Perfect Tense
- Completed Action Before Another Action
The primary use of the Past Perfect is to show that one action happened before another in the past.- He had eaten dinner before we arrived.
- Storytelling
The tense is often used in storytelling to establish the timeline of events and explain what happened first.- She had traveled the world before she moved to New York.
- Expressing Regret or Missed Opportunities
The Past Perfect can be used to express regret about something that didn’t happen.- I wished I had gone to the party.
- Cause and Effect
It helps show cause and effect, explaining how one event led to another.- The ground was wet because it had rained earlier.
Examples of Past Perfect Sentences
- I had finished my homework before I watched TV.
- She had not seen him in years before they met again at the reunion.
- Had you visited Paris before you moved there?
- They had already left by the time we arrived.
- By the time the teacher arrived, the students had cleaned the classroom.
Common Mistakes in Using the Past Perfect Tense
- Using Past Simple Instead of Past Perfect:
Mistake: I finished my homework before I went to bed.
Correction: I had finished my homework before I went to bed.
The Past Perfect should be used to show the first completed action. - Forgetting to Use “Had”:
Mistake: She already eaten before I arrived.
Correction: She had already eaten before I arrived.