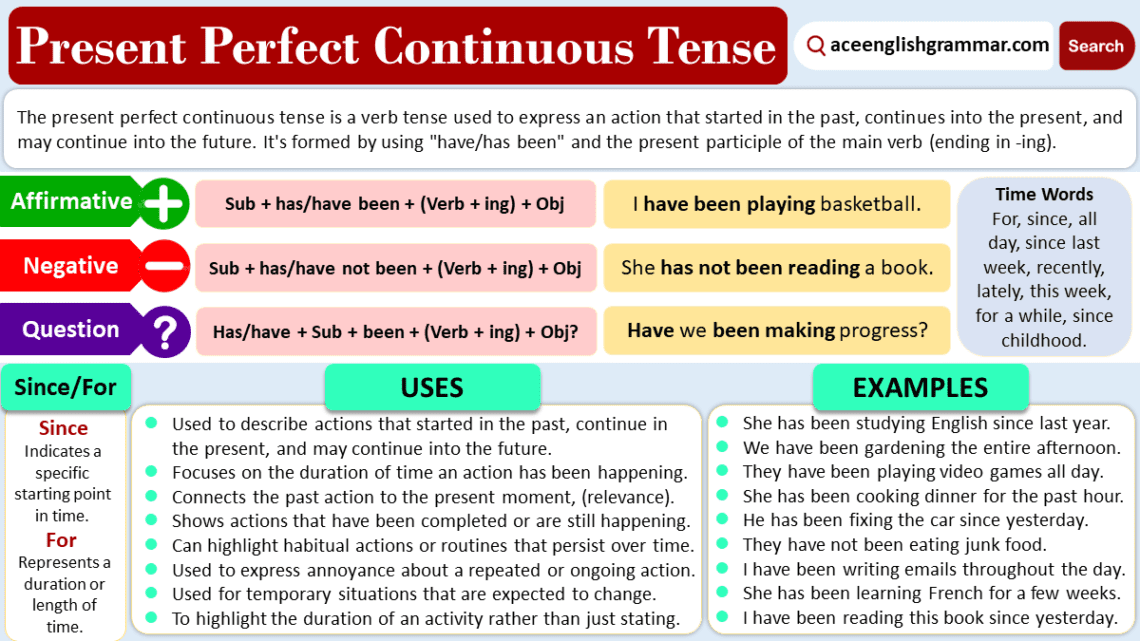
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense combines the features of both the Present Perfect and Present Continuous tenses. It expresses actions that started in the past and are still happening or have just recently stopped, with an emphasis on the duration of the activity. This tense is formed using “have” or “has,” followed by “been” and the verb in its “-ing” form.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous tense indicates that something began in the past, continues in the present, and may carry on into the future. It is useful for showing the duration of an action or event, which is often emphasized with words like “since” or “for.”
For example:
- I have been studying English for two hours.
This sentence tells us the action (studying) began two hours ago and is still ongoing at the time of speaking.
Structure of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Positive Form
To form positive sentences in this tense, use “has” or “have” + “been” + the present participle (verb + ing).
- I have been learning Spanish for six months.
This shows that the action of learning Spanish started six months ago and is still happening. - She has been working at the company since 2019.
This indicates that her work began in 2019 and continues in the present.
Negative Form
To form the negative, insert “not” after “have” or “has.”
- We have not been watching TV this week.
Here, the action of watching TV hasn’t been happening during this specific period. - He has not been attending the meetings regularly.
This expresses that he has not been attending meetings continuously.
Interrogative Form
In questions, “have” or “has” comes before the subject, followed by “been” and the verb in its “-ing” form.
- Have you been exercising lately?
This asks whether the action of exercising has been happening recently. - Has she been cooking dinner all afternoon?
This inquires about whether she has spent the afternoon cooking.
Use of “Since” and “For” in Present Perfect Continuous Tense
“Since” and “for” help express the duration of the action.
- Use “since” to indicate the starting point of the action, referring to a specific time.
- I have been studying English since January.
This shows that the action began in January and continues now.
- I have been studying English since January.
- Use “for” to show the duration of the action, referring to a period of time.
- They have been waiting for two hours.
This highlights the length of time the action has been happening.
- They have been waiting for two hours.
When to Use the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Ongoing Actions
This tense emphasizes actions that started in the past and continue in the present.- She has been working here for five years.
This suggests the action is still happening.
- She has been working here for five years.
- Duration of Actions
It is particularly helpful when you want to emphasize the amount of time something has been happening.- I have been reading this book for a week.
- Temporary Situations
The tense can also indicate temporary actions or states.- He has been staying with us while his house is being repaired.
- Recent Activities
It can also describe actions that were recently completed but have effects in the present.- I am tired because I have been running.
- Expressing Concern or Annoyance
Sometimes, this tense is used to express concern or irritation about a continuous action.- You have been making a lot of noise!
Common Time Expressions with the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Certain words are often used with this tense to clarify the duration or timeframe of the action:
- For
- Since
- All day
- Recently
- Lately
- This week
- For a while
- Since last Monday
These time expressions help indicate how long something has been happening.
Rules for Forming the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Formation:
Use “have/has” + “been” + the present participle (verb + ing).- She has been reading for hours.
- Subject-Verb Agreement:
Use “has” for singular subjects (he, she, it) and “have” for plural subjects (I, you, we, they).- He has been working late.
- Emphasis on Duration:
The tense focuses on actions that started in the past and continue into the present.- We have been cleaning the house since morning.
- Use of “Since” and “For”:
“Since” points to the start time, while “for” indicates the duration.- They have been playing soccer since noon.
Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Sentences
- I have been learning English for two years.
- She has been cooking dinner for the last hour.
- They have been working on the project since Monday.
- We have been waiting for the bus for 30 minutes.
- He has been studying since this morning.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Questions
When forming questions, we start with “have” or “has” before the subject, followed by “been” and the present participle.
- Have you been studying for the exam?
- Has she been working on the report all day?
- Have they been practicing for the game?
You May Also Like