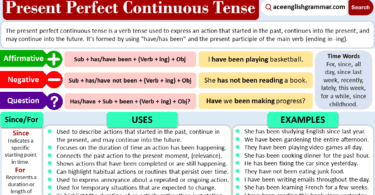
The Present Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that started in the past but are still relevant or have an ongoing effect in the present. This tense connects the past with the present, highlighting completed actions that have significance now. It is formed by using “have” or “has” followed by the past participle of the main verb.
Table of Contents
What is the Present Perfect Tense?
The Present Perfect Tense refers to actions or events that happened at some point in the past but still have importance now. It emphasizes the connection between the past and present. For example:
- I have eaten lunch tells us that lunch was completed at some point, and the result is relevant now (perhaps you’re not hungry anymore).
- She has visited Paris suggests that the experience of visiting Paris has an ongoing significance or impact.
This tense helps express actions that may not be linked to a specific time, but still matter in the current moment.
Structure of Present Perfect Tense
Positive Sentences
The basic structure for positive sentences in the Present Perfect Tense is:
- Subject + have/has + past participle
For example:
- I have completed my homework.
- She has visited the museum.
In these examples, “have” or “has” is combined with the past participle to show that the action is completed and relevant now.
Negative Sentences
In the negative form, add “not” after “have” or “has”:
- Subject + have/has + not + past participle
For example:
- I have not traveled abroad.
- He has not finished his dinner.
These examples emphasize that the action has not occurred up to the present moment.
Interrogative Sentences
To ask questions, invert “have” or “has” with the subject:
- Have/has + subject + past participle?
For example:
- Have you finished your homework?
- Has she visited the Eiffel Tower?
This structure helps inquire about completed actions that are still relevant now.
Use of “Has” and “Have” in Present Perfect Tense
The choice between “has” and “have” depends on the subject of the sentence:
- “Has” is used with singular subjects such as he, she, it, and singular nouns.
- She has completed her project.
- “Have” is used with plural subjects such as I, you, we, they, and plural nouns.
- They have finished the assignment.
Time Expressions in Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense often uses specific time expressions to emphasize the connection between the past action and the present:
- Already: I have already eaten.
- Yet: Has she called yet?
- Just: They have just arrived.
- Ever/Never: Have you ever been to Japan? / I have never tried sushi.
- Recently/Lately: I have recently started a new job.
These time expressions help clarify the timing or relevance of actions to the present.
When to Use the Present Perfect Tense
- Actions Completed with Present Relevance
This tense is used when an action is completed but still affects the present.- I have finished my report (the action is done, but it matters now).
- Life Experiences
It is often used to describe life experiences without specifying exactly when they happened.- She has traveled to many countries.
- Changes Over Time
It can be used to talk about changes that have happened over time.- The city has grown rapidly over the last decade.
- Unfinished Actions
This tense can describe actions that began in the past and are still ongoing.- We have lived here for five years (and we still live here).
- Multiple Actions at Unspecified Times
The Present Perfect is also used for multiple actions that occurred at different times.- I have visited Paris three times.
Rules of Present Perfect Tense
- Formation:
Use “have” or “has” + past participle.- I have studied English for two years.
- Past Participle:
For regular verbs, the past participle is formed by adding “-ed” (e.g., played, worked). Irregular verbs have their own forms (e.g., eaten, gone). - Use with Unspecified Time:
The Present Perfect Tense is often used when the exact time of the action is not mentioned or important.- She has visited New York (but we don’t know exactly when).
- Negatives and Questions:
For negatives, use “not” after “have/has.” For questions, invert “have/has” and the subject.- He has not seen the movie.
- Have they completed the task?
Present Perfect Tense Examples
- I have just finished my dinner.
- She has never been to Japan.
- Have they ever visited the museum?
- We have lived here since 2018.
- They have already left for the airport.
- He has not completed the assignment yet.
Common Mistakes with Present Perfect Tense
- Using Present Perfect with Specific Past Times
Don’t use the Present Perfect Tense with specific past time references (like yesterday or last year).
Mistake: I have seen the movie yesterday.
Correction: I saw the movie yesterday. - Forgetting the Past Participle
Mistake: I have eat dinner.
Correction: I have eaten dinner.