Want to make your sentences more descriptive? That’s where adjectives come in! These words, like beautiful, large, and intelligent, help describe nouns and pronouns, making your speech and writing more expressive. Without them, sentences can feel bland and unclear. This blog post helps learn adjectives with definitions, essential rules, and examples to improve your English skills.
Table of Contents
What is an Adjective?
An adjective is a word that describes or gives more information about a noun or pronoun. It tells about quality, quantity, size, color, or condition.
- Ali has a big house.
Functions of Adjectives
- Describe Nouns: Adjectives give information about attributes like size, color, shape, etc.
- Indicate Quantity or Number: They specify how many or how much of something exists (e.g., few, many).
- Answer Specific Questions: They address questions like “What kind?”, “How many?”, “Which one?”, and “How much?”
- Comparison: Adjectives compare nouns, showing superiority (e.g., tallest), equality (as smart as), or inferiority (less expensive).
- Create Imagery: They enhance sentences by providing vivid descriptions.
Formation of Adjectives
- Suffix Addition: By adding suffixes to nouns or verbs (e.g., happy → happiness, colorful → color).
- Comparative and Superlative Forms: Adjectives can show comparisons (e.g., big → bigger → biggest).
- Compound Adjectives: Combining two or more words (e.g., black-and-white, well-behaved).
Types of Adjectives
| Adjective Type | Description | Example |
| Descriptive Adjective | Provide details about a noun’s qualities (e.g., color, size) | The blue sky is clear today. |
| Quantitative Adjective | Indicate quantity or number | I ate three slices of pizza. |
| Demonstrative Adjective | Specify which noun is being referred to (e.g., this, that) | Pass me that book, please. |
| Possessive Adjective | Show ownership (e.g., my, your, his) | It’s my favorite movie. |
| Interrogative Adjective | Ask questions about a noun (e.g., which, whose) | Whose book is this? |
| Exclamatory Adjective | Express strong emotions (e.g., amazing, wonderful) | What an incredible performance! |
| Relative Adjective | Introduce relative clauses (e.g., who, which, that) | This is the house which I want to buy. |
| Comparative and Superlative | Compare two or more things (e.g., better, best) | Her drawing is better than mine. |
| Proper Adjective | Derived from proper nouns to indicate origin or association | She served Italian pasta for dinner. |
| Numeral Adjective | Indicate the number or order of nouns (cardinal and ordinal numbers) | She has three cats. |
| Compound Adjective | Formed by combining words (e.g., well-known, high-pitched) | It’s a well-written essay. |
| Participial Adjective | Derived from verbs (e.g., boring, broken) | She found a fascinating book. |
| Emphasizing Adjective | Add intensity to a noun (e.g., absolute, utter) | He was utterly shocked by the news. |
| Indefinite Adjective | Refer to a non-specific amount or group (e.g., some, few) | Some people enjoy spicy food. |
| Predicate Adjective | Follow linking verbs and describe the subject | She seems happy today. |
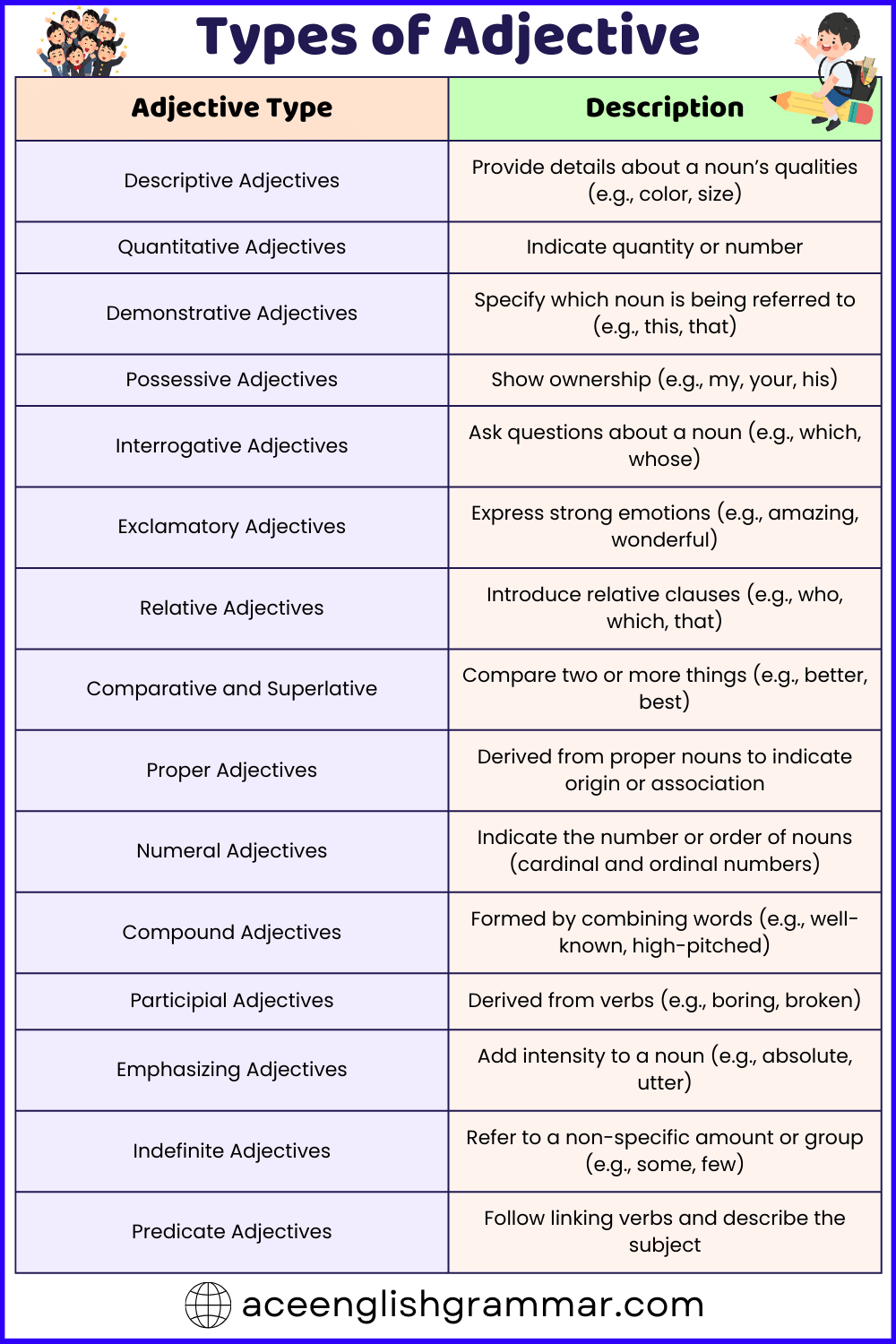
Learn about the different types of adjectives in English, including descriptive, demonstrative, and more.
Degrees of Adjective
Adjective can express varying degrees of comparison:
- Positive Degree: Describes a quality without comparison (fast).
- Comparative Degree: Compares two things (faster).
- Superlative Degree: Indicates the highest degree among three or more (fastest).
Order of Adjectives
When using multiple adjectives to describe a noun, they generally follow a specific order:
Opinion → Size → Age → Shape → Color → Origin → Material → Purpose.
- Example: A beautiful, large, old, round, red Italian leather handbag.
Placement of Adjective
Adjectives usually come before the noun they describe (e.g., a red car, an expensive watch). However, they can also come after a linking verb for emphasis (e.g., the car was fast, the sky is blue).
Common Mistakes with Adjectives
- Confusing Adjectives with Adverbs: Adjectives modify nouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs (e.g., quick [adjective] vs. quickly [adverb]).
- Avoiding Double Comparatives: Do not use “more” or “most” with comparative and superlative adjectives (e.g., “more better” is incorrect).
- Irregular Comparisons: Some adjectives do not follow regular comparative patterns (e.g., good → better → best).
Example Sentences with Adjectives
- The red apple is delicious.
- His blue eyes sparkled with joy.
- The bright sun warmed my skin.
- She wore a beautiful dress to the party.
- His brilliant idea saved the project.
- The strange noise kept me awake at night.
List of Common Adjectives
- Happy
- Sad
- Angry
- Funny
- Serious
- Brave
- Timid
- Bright
- Dark
- Loud
- Quiet
- Tall
- Short
- Fast
- Slow
- Beautiful
- Ugly
- Kind
- Cruel
- Honest
- Dishonest
- Strong
- Weak
- Big
- Small
- Warm
- Cold
- Delicious
- Salty
- Bitter
- Healthy
- Sick
- Friendly
- Hostile
- Clean
- Dirty
- Adventurous
- Famous
- Unknown
- Joyful
- Sincere
- Vibrant
- Dreary
- Flexible
- Stiff
- Loyal
- Reliable
- Wise
- Educated
- Responsible
FAQs
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun, giving details about size, color, shape, or emotions.
Examples include happy, tall, bright, small, strong, cold, and beautiful.
Adjectives make sentences more descriptive and clear by adding details. (Example: She wore a red dress.)
Yes, adjectives can appear before or after a noun. (Example: The sky is blue.)
Descriptive: (big, soft, dark)
Quantitative: (many, few, some)
Demonstrative: (this, that, those)
Possessive: (my, his, their)
Interrogative: (which, what, whose)
Comparative & Superlative: (bigger, biggest)
Adjective describe nouns (a fast car).
Adverb describe verbs (He runs quickly.)
Yes, adjective like happy, sad, excited, and nervous describe emotions.
She has a beautiful, long, red dress.
Comparative: Compares two things (Ali is taller than Ahmed.)
Superlative: Compares three or more (Ali is the tallest in the class.)
Yes, words like red, blue, green, and yellow are adjectives when describing nouns. (Example: The blue sky.)
Conclusion
Adjective is essential in English because they make sentences more descriptive, clear, and engaging. They help us express qualities, quantities, emotions, and comparisons effectively. By understanding different types of adjectives and their usage, learners can improve their writing and speaking skills. Mastering adjective will allow you to communicate ideas more vividly and accurately in English.
Read More