The Present Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that are happening right now or are in progress at the moment of speaking. It is formed by using the present tense of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) and the -ing form of the main verb. For instance, “I am studying” or “They are playing football” are examples of this tense, indicating ongoing actions.
Table of Contents
What is Present Continuous Tense?
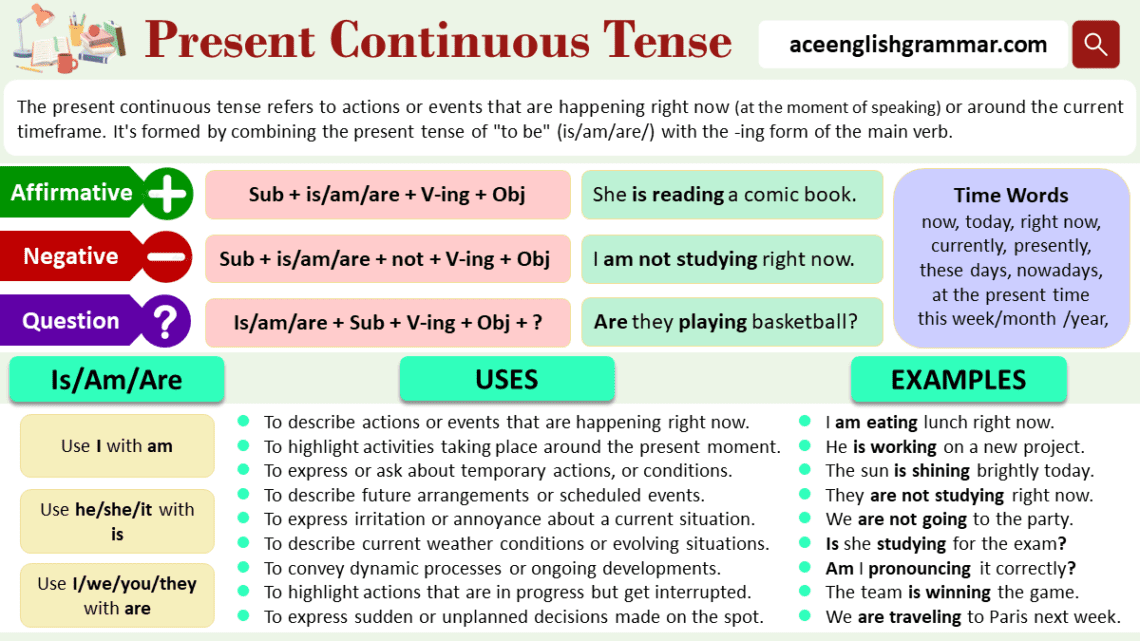
The Present Continuous Tense expresses actions or events occurring at this very moment. It combines the present tense of the verb “to be” with the present participle (verb + -ing), allowing us to indicate that something is in progress.
The verb “to be” is used as follows:
- am for “I”
- are for “you, we, they”
- is for “he, she, it”
For example:
- “She is running” — here, “is” is the present form of “to be,” and “running” is the main verb in its -ing form.
The Present Continuous Tense is useful for expressing:
- Ongoing actions: “I am eating dinner.”
- Temporary situations: “He is staying at a hotel.”
- Future arrangements: “We are meeting tomorrow.”
Structure of the Present Continuous Tense
Positive Sentences
To form positive sentences, the structure is:
- Subject + am/are/is + present participle (-ing form)
Examples:
- I am reading a book.
- She is studying for her exams.
- They are watching a movie.
These sentences indicate that the actions are happening now or are ongoing.
Negative Sentences
For negative sentences, use “not” after the verb “to be”:
- Subject + am/are/is + not + present participle
Examples:
- I am not working today.
- They are not attending the meeting.
- She is not writing the letter.
These sentences emphasize that the action is not happening at the moment.
Interrogative Sentences
To ask questions, invert the subject and “to be”:
- Am/are/is + subject + present participle?
Examples:
- Are you reading a book?
- Is he studying for the exam?
- Are they coming to the party?
These questions ask whether an action is in progress at the moment.
Wh-Questions
To ask for specific information, begin with a wh-word (what, where, why, etc.):
- Wh-word + am/are/is + subject + present participle?
Examples:
- What are you doing?
- Where is she going?
- Why are they leaving?
These forms are used to ask about specific actions happening right now.
Time Words in Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous often uses time expressions to highlight that the action is happening right now or around the current time. Common time words include:
- Now
- At the moment
- Right now
- Currently
- These days
For instance:
- I am watching TV right now.
- She is working on her project at the moment.
Uses of Present Continuous Tense
- Ongoing Actions
This tense is primarily used to describe actions happening right now.- They are playing football.
- Temporary Situations
It can express situations that are temporary but ongoing.- He is staying at his friend’s house for the weekend.
- Future Plans or Arrangements
It is also used to describe definite future plans or arrangements.- I am meeting my friends tomorrow.
- Expressing Irritation or Annoyance
The Present Continuous can express irritation, especially when used with adverbs like always or constantly.- She is always complaining.
Rules of Present Continuous Tense
- Formation:
Combine “am,” “is,” or “are” with the present participle (verb + -ing).- He is reading a book.
- Negative Form:
Add “not” after “am,” “is,” or “are.”- I am not studying right now.
- Interrogative Form:
Invert the subject and “am/are/is” to form questions.- Are you going to the party?
- Spelling Rules for -ing Form:
- For verbs ending in “e,” drop the “e” and add -ing: write → writing.
- For one-syllable verbs with a consonant-vowel-consonant pattern, double the final consonant before adding -ing: run → running.
Present Continuous Example Sentences
- I am reading a novel.
- They are playing basketball in the park.
- She is cooking dinner.
- We are not going to the concert.
- Are you studying for the exam?
These sentences capture actions happening now, in progress, or planned for the near future.