Punctuation marks are essential tools in English writing. They help us understand the meaning of a sentence clearly. Without punctuation, sentences become confusing or misleading. Learning punctuation marks helps English learners write correctly, communicate clearly, and improve their grammar. This blog post helps learn punctuation marks by explaining their names, uses, rules, and examples that reflect real-life writing. Visuals of each mark are included to support understanding and make learning easier.
Table of Contents
What Are Punctuation Marks in English Grammar?
Punctuation marks are symbols used in writing to organize sentences, clarify meaning, and separate ideas. They show readers where to pause, stop, ask, or feel emotion in a sentence. In English grammar, punctuation helps give structure and meaning to written communication.
- Fatima said, “I will be there at 5.” – The quotation marks show spoken words.
- Do you want tea or coffee? – The question mark shows it is a question.
Each punctuation mark has a specific job. Without them, the reader can easily misunderstand the message.
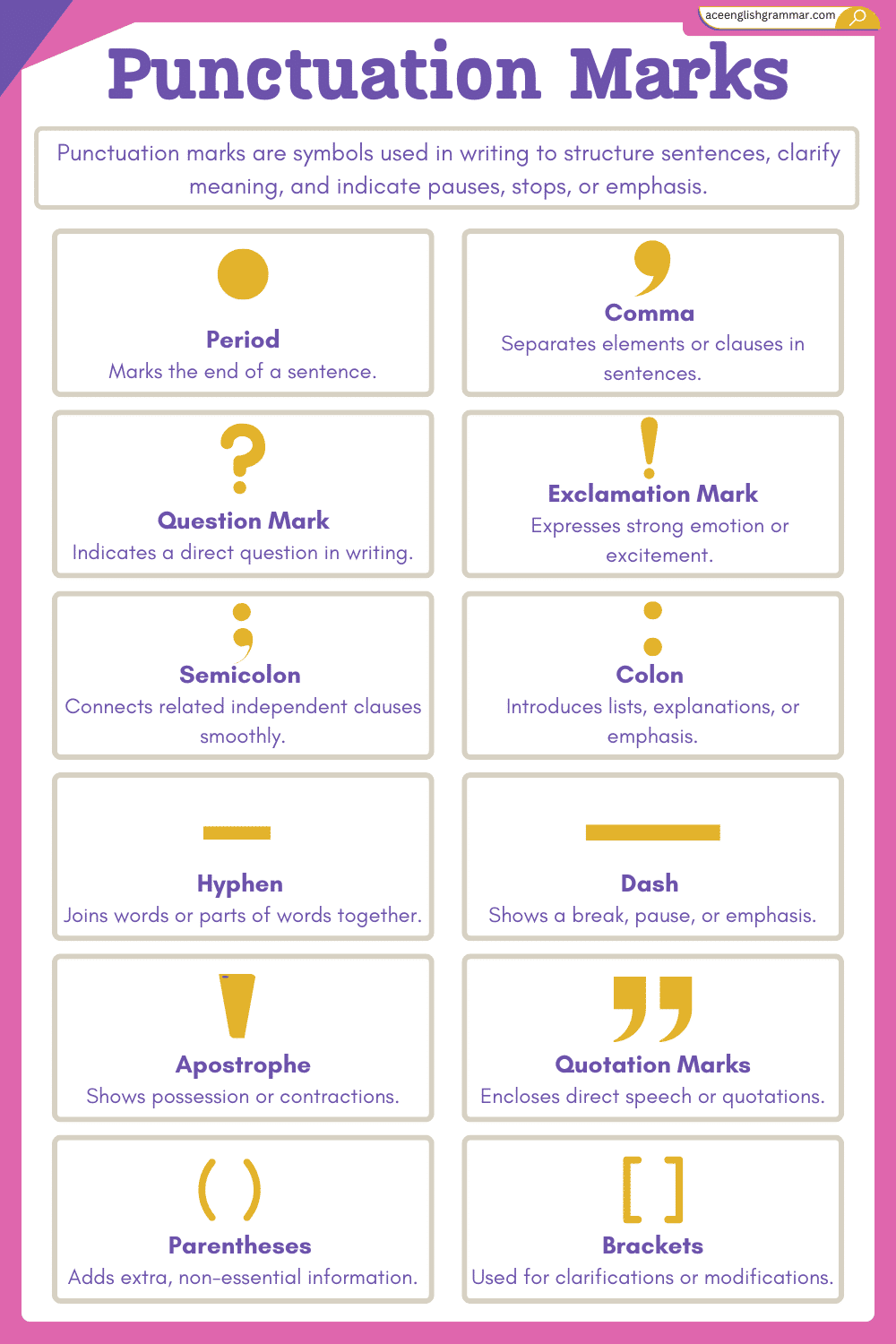
Common Punctuation Marks and their Names
Here are the most common punctuation marks used in English grammar:
- Period or Full Stop
- Comma
- Question Mark
- Exclamation Mark
- Colon
- Semicolon
- Apostrophe
- Quotation Marks
- Hyphen
- Dash
- Parentheses
- Ellipsis
- Slash
- Brackets
Each of these marks has its own unique function in writing.
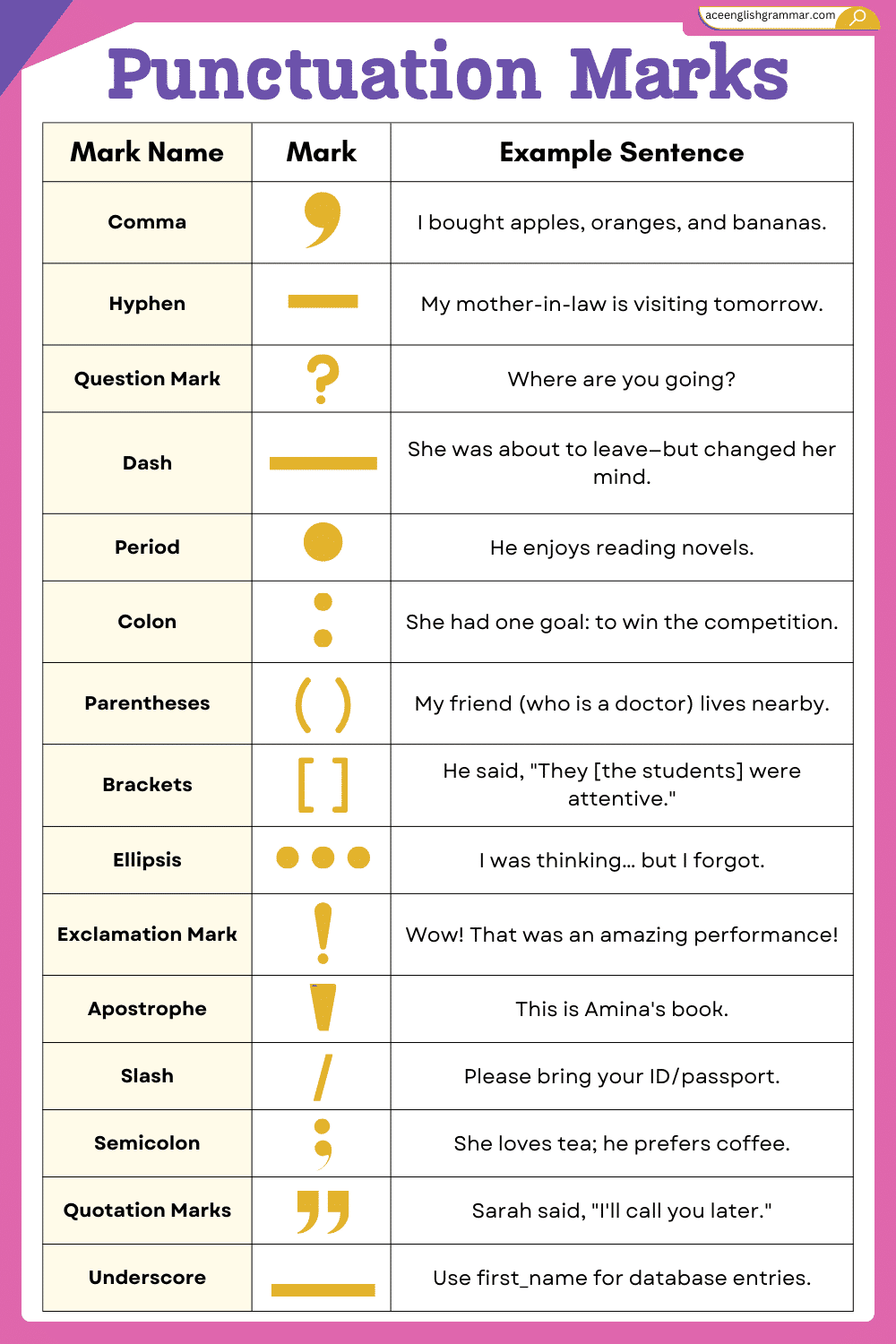
Punctuation Marks and Their Uses
| Punctuation Name | Mark | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Period (Full Stop) | . | Ends a statement or a command |
| Comma | , | Separates items, clauses, or adds a pause |
| Question Mark | ? | Ends a direct question |
| Exclamation Mark | ! | Shows strong emotion or a command |
| Colon | : | Introduces a list, quote, or explanation |
| Semicolon | ; | Connects two related independent clauses |
| Apostrophe | ’ | Shows possession or contraction |
| Quotation Marks | ” “ | Shows spoken words or quotations |
| Hyphen | – | Joins compound words |
| Dash (Em Dash) | — | Adds extra information or an interruption |
| Parentheses | ( ) | Adds extra details or clarification |
| Ellipsis | … | Shows omission or unfinished thought |
| Slash | / | Shows choices or fractions |
| Brackets | [ ] | Adds explanation inside quoted text |
Rules of Punctuation for English Learners
Punctuation rules help you use marks correctly and clearly in sentences. Here are key rules to remember:
- Start every sentence with a capital letter and end it with a period, question mark, or exclamation mark.
- Use a comma to separate items in a list: I need eggs, milk, bread, and sugar.
- Use an apostrophe for possession: Ali’s book is on the table.
- Place quotation marks around spoken words: She said, “Let’s go now.”
- Use a colon before listing items: You need: a pen, notebook, and ruler.
- Use a semicolon to join two related sentences: Amina was tired; she still finished her work.
- Do not confuse a hyphen with a dash; they are used for different purposes.
Following these rules improves your grammar and makes your writing easier to understand.
Difference Between a Hyphen (-) and a Dash (—)
Though they look similar, a hyphen and a dash have different roles:
Hyphen (-):
- Connects two words to form compound words.
- Example: well-known, mother-in-law, twenty-one
Dash (—):
- Separates parts of a sentence.
- Used for sudden breaks, added information, or emphasis.
- Example: He arrived late — as expected — and missed the meeting.
Real Life Examples Using Punctuation Marks
These examples show how punctuation marks appear in everyday writing:
- Period: Hassan is a doctor.
- Comma: I visited Karachi, Lahore, and Multan.
- Question Mark: Did you call Ahmed?
- Exclamation Mark: Wow! That’s amazing!
- Colon: She has three hobbies: reading, swimming, and painting.
- Semicolon: I was tired; I still finished the homework.
- Apostrophe: That’s Fatima’s bag.
- Quotation Marks: “Let’s go home,” said Zoya.
- Hyphen: This is a high-quality bag.
- Dash: He can’t swim — not even a little.
- Parentheses: My sister (the youngest one) is studying medicine.
- Ellipsis: Well… I’m not sure about that.
- Slash: Please bring your ID/passport.
- Brackets: She said, “He [the teacher] helped me a lot.”
Each example helps show how punctuation adds meaning to real sentences.
Why Are Punctuation Marks Important for English Learners?
Understanding punctuation marks is crucial for writing and reading in English. They help:
- Avoid confusion in meaning
- Create smooth sentence flow
- Show pauses, emotions, and clarity
- Strengthen grammar and structure
For learners, punctuation is like a traffic sign — guiding the reader’s pace and direction in every sentence. Correct punctuation makes your writing look professional and easy to read. It also helps in exams, emails, and everyday writing tasks.
FAQs
The 14 punctuation marks include the period, question mark, exclamation mark, comma, semicolon, colon, quotation marks, apostrophe, parentheses, brackets, hyphen, dash, ellipsis, and slash.
Punctuation mark helps clarify meaning, improve readability, and prevent misunderstandings. It structures writing and conveys emotions effectively.
A semicolon connects two independent clauses without a conjunction. Example: “I love to write; it helps me express my thoughts.”
Use parentheses to add extra information that is not essential to the main sentence. Example: “Sarah (my cousin) will visit next week.”
A hyphen connects words (like well-known), while a dash separates ideas or adds emphasis — like this. They are not interchangeable.
Brackets clarify or add information in a quote and Parentheses Insert extra, non-essential details in a sentence.
Read More
