Relative clauses are a type of sentence that helps us provide more information about a noun. They are called relative because they relate the new information to the original noun. In simple terms, a relative clause starts with a relative pronoun, such as who, which, or that, and describes or explains something about the noun it is connected to. They’re like mini-sentences that are connected to a larger sentence with a relative pronoun, such as “who,” “which,” or “that.” In this article, we will define relative clauses, explain their types, discuss their usage, and provide examples to help you understand how to use them effectively. So, let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What is a Relative Clause?
A relative clause, also known as an adjective clause, is a group of words that contains a subject and a verb. It functions as an adjective by providing more information about a noun. This type of clause begins with a relative pronoun (such as who, whom, whose, which, or that) or a relative adverb (such as where, when, or why).
In a relative clause, the relative pronoun or adverb connects the clause to a specific noun or pronoun in the main clause, creating a relationship between the two. The information provided by the relative clause helps identify, describe, or give more details about the noun it modifies.
Here’s a simple example to illustrate:
- Main clause: The book is on the table.
- Relative clause: that you lent me
- Combined sentence: The book that you lent me is on the table.
In this example, the relative clause “that you lent me” gives additional information about the book, specifying which book is being referred to.
Here are some other examples:
- The city where I was born is in Europe.
- The reason why she’s upset is unclear.
- She found the keys that were missing.
- I have a friend whose sister is a doctor.
- The boy who is laughing is my brother.
Types of Relative Clauses
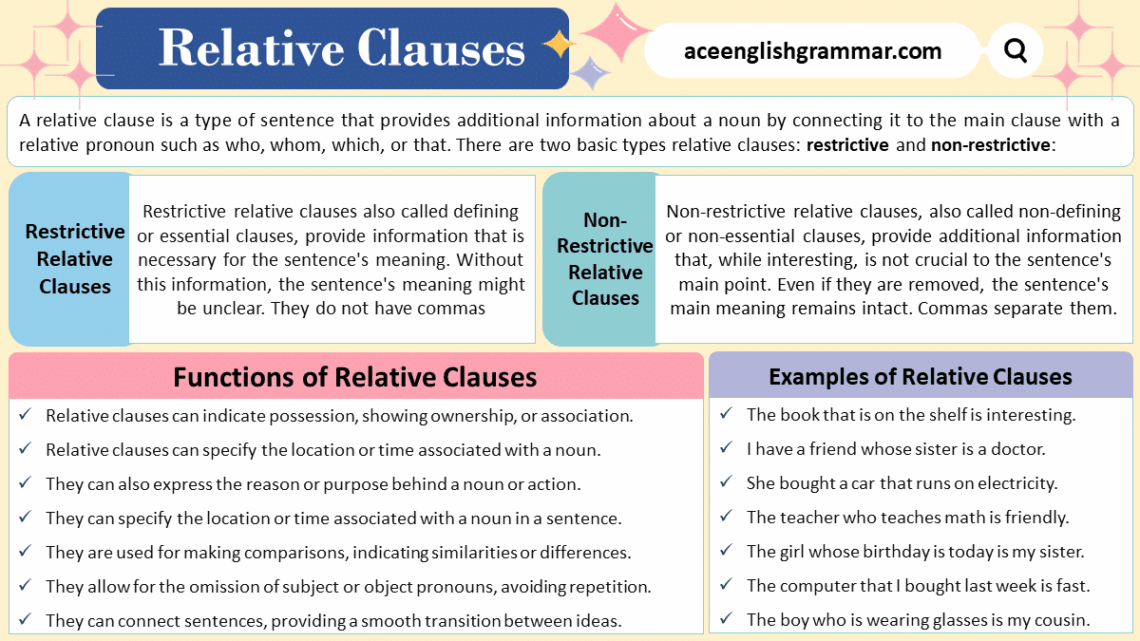
Relative clauses, also known as adjective clauses, provide additional information about a noun in a sentence. There are two basic types of relative clauses: restrictive (defining) and non-restrictive (non-defining).
Restrictive Relative Clauses
Restrictive relative clauses, also called defining or essential clauses, provide information that is necessary for the sentence’s meaning. Without this information, the sentence’s meaning might be unclear. Commas do not separate them.
Examples:
- The girl who won the award is my sister.
- The car that needs repairs is in the garage.
- The house that has a red door is ours.
- The computer that I use for work is new.
- The movie that I saw last night was scary.
Characteristics:
- No commas are used to separate the restrictive relative clause from the rest of the sentence.
- The information in the clause is crucial for identifying the noun.
Non-Restrictive Relative Clauses
Non-restrictive relative clauses, also called non-defining or non-essential clauses, provide additional information that, while interesting, is not crucial to the sentence’s main point. Commas separate them.
Examples:
- My brother, who loves soccer, scored a goal.
- The cake, which I baked yesterday, is delicious.
- The cat, whose fur is soft, likes to be petted.
- My friend, who is a great artist, painted this.
- My laptop, which I bought last year, is now outdated.
Characteristics:
- Commas are used to set off the non-restrictive relative clause from the rest of the sentence.
- The information in the clause adds extra detail but is not necessary for identification.
Functions of Relative Clauses
Relative clauses serve several important functions in a sentence. Let’s explore these functions:
- Identification and Definition:
- Function: Relative clauses help identify or define a specific noun in a sentence, making it clear which person, thing, or place is being referred to.
- Example: The girl who won the race is my sister.
- Additional Information:
- Function: They provide additional information about a noun, giving more details to enrich the description.
- Example: The car, which is parked outside, needs repairs.
- Restrictive Clauses:
- Function: Some relative clauses are restrictive, narrowing down the possible meanings of the noun they modify.
- Example: The students who passed the exam are celebrating.
- Non-Restrictive Clauses:
- Function: Others are non-restrictive, providing extra information without limiting the meaning of the noun.
- Example: My sister, who lives in Paris, is coming to visit.
- Possession:
- Function: Relative clauses can indicate possession, showing ownership or association.
- Example: The man whose car broke down needs assistance.
- Location and Time:
- Function: Relative clauses can specify the location or time associated with a noun.
- Example: The house where I grew up is for sale.
- Reason and Purpose:
- Function: They can express the reason or purpose behind a noun or action.
- Example: I need a tool that can fix this problem.
- Comparisons:
- Function: Relative clauses are used for making comparisons, indicating similarities or differences.
- Example: She chose the dress that matched her shoes.
- Omission of Subject or Object Pronouns:
- Function: Relative clauses allow for the omission of subject or object pronouns, avoiding repetition.
- Example: The person whom I met yesterday is an artist. (Instead of “The person whom I met yesterday is an artist.”)
- Connecting Sentences:
- Function: Relative clauses can connect sentences, providing a smooth transition between ideas.
- Example: She missed the train, which caused her to be late for the meeting.
Relative Pronouns List
Relative pronouns are words that introduce relative clauses, providing more information about a noun in a sentence. They connect the main clause to the relative clause, serving as a bridge to give additional details. Here is a list of common relative pronouns used in relative clauses:
- That
- Who
- Why
- Whom
- Whose
- Which
- Where
- When
Relative Clauses Examples
- The book that is on the shelf is interesting.
- I have a friend whose sister is a doctor.
- The cat that chased the mouse is playful.
- She bought a car that runs on electricity.
- The person who called you is waiting outside.
- The house that has a red door is mine.
- She has a friend who lives next door.
- I love the book that you recommended.
- The cake that Mom baked is delicious.
- The school where I studied is old.
- The person who called you is waiting outside.
- The house that has a blue door is mine.
- This is the restaurant where we had dinner.
- The teacher who teaches math is friendly.
- The girl whose birthday is today is my sister.
- The dog that barks loudly is small.
- The computer that I bought last week is fast.
- The boy who is wearing glasses is my cousin.
- The city where I was born is beautiful.
- The jacket that I bought on sale fits well.
- The pizza that she ordered arrived late.
- The mountain that we climbed was challenging.
Relative Clauses Exercises
1. The person __________ helped us was very kind.
- a) whose
- b) where
- c) when
- d) which
2. I have a friend __________ speaks five languages.
- a) where
- b) when
- c) who
- d) which
3. The book __________ you recommended is fantastic.
- a) whom
- b) where
- c) which
- d) when
4. The country __________ we visited last summer was beautiful.
- a) whose
- b) which
- c) where
- d) when
5. The reason __________ he left early is unclear.
- a) which
- b) whose
- c) why
- d) when
6. The car, __________ is parked outside, belongs to my brother.
- a) whom
- b) which
- c) when
- d) whose
7. The hotel __________ we stayed had a stunning view.
- a) when
- b) where
- c) who
- d) which
8. This is the restaurant __________ serves the best pizza in town.
- a) where
- b) when
- c) which
- d) who
9. The person __________ we met at the party is a famous actor.
- a) whom
- b) which
- c) when
- d) whose
10. The day __________ we arrived was sunny and warm.
- a) where
- b) whose
- c) which
- d) when
Answers:
- a) whose
- c) who
- c) which
- c) where
- c) why
- b) which
- b) where
- a) where
- a) whom
- d) when
FAQs
Q1: What is a relative clause?
A relative clause is a group of words that begins with a relative pronoun (such as who, whom, whose, which, or that) and functions as an adjective. It provides additional information about a noun in a sentence, specifying which person or thing we are talking about.
Q2: What is the purpose of a relative clause?
The primary purpose of a relative clause is to give more information about a noun, making the sentence more precise and descriptive. It helps clarify which person, thing, or place we are referring to and adds depth to the overall meaning of the sentence.
Q3: What are some common relative pronouns?
Common relative pronouns include who, whom, whose, which, and that. These words introduce relative clauses and connect them to the nouns they modify.
Q4: What’s the difference between a restrictive and a non-restrictive relative clause?
A restrictive clause is essential to the sentence’s meaning and doesn’t have commas. A non-restrictive clause provides extra information and is separated by commas.
Q5: What are the common relative pronouns?
Common relative pronouns include:
- Who: Referring to people.
- Whose: Indicating possession.
- Which: Refers to things or animals.
- That: Used for both people and things.
- Whom: Referring to the object of a verb.
You May Also Like:



Leave a Comment