Many English learners struggle with plural noun, leading to confusion in speaking and writing. Imagine saying, “I have two book” instead of “I have two books.” Small mistakes like this can make sentences sound incorrect. Learning plural noun is essential for proper grammar. In this guide, you’ll understand what plural nouns are, the different types, and how to use them correctly with examples. For better understanding and deeper knowledge, learn Types of nouns.
Table of Contents
What is a Plural Noun?
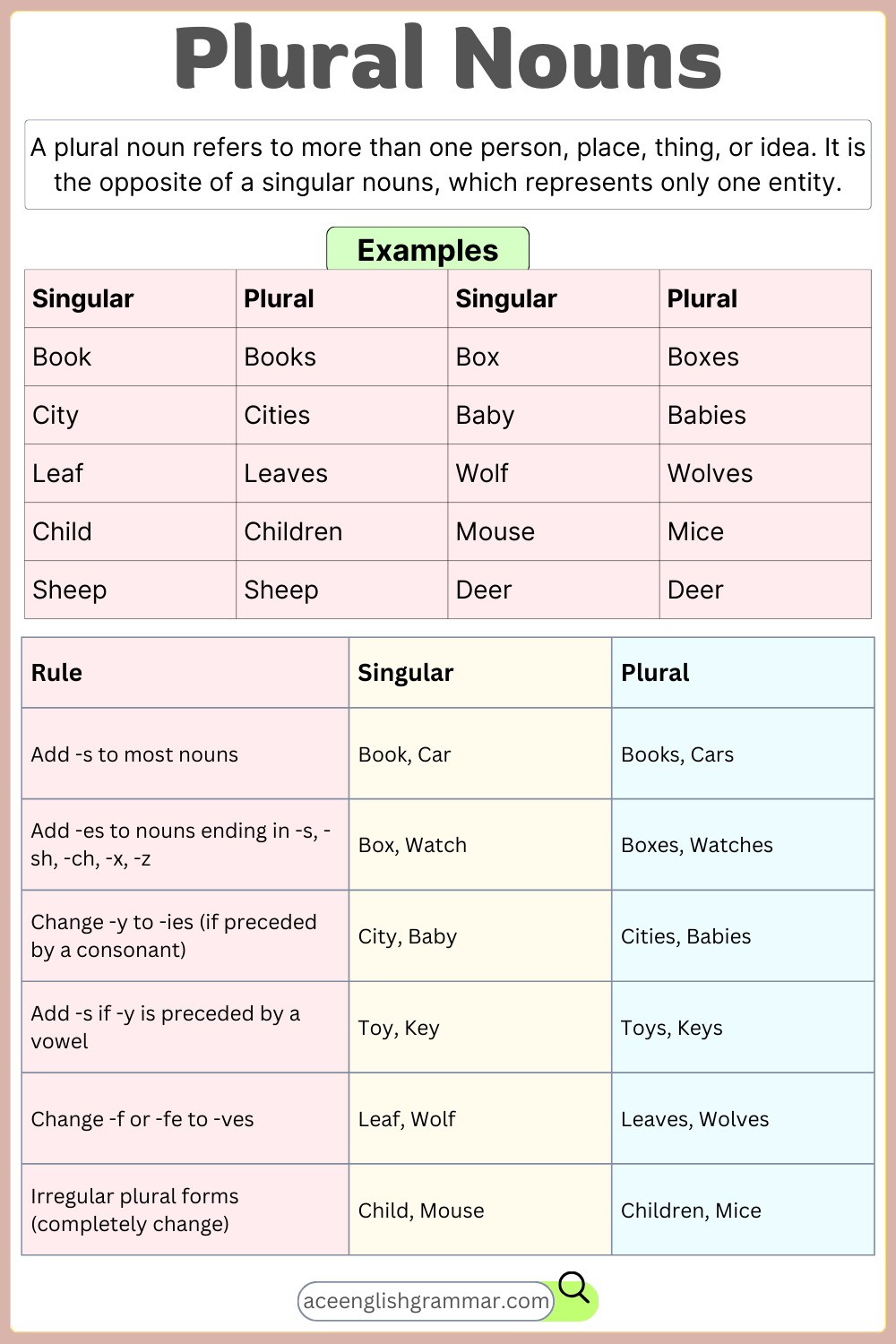
A plural noun refers to more than one person, place, thing, or idea. It is the opposite of a singular nouns, which represents only one entity.
- People: teachers, doctors, students
- Places: mosques, markets, cities
- Things: books, chairs, computers
- Ideas: thoughts, emotions, beliefs
Each of these words represents more than one entity, making them plural nouns.
Types of Plural Nouns
Plural noun can be divided into different types based on how they are formed:
1. Regular Plural Noun
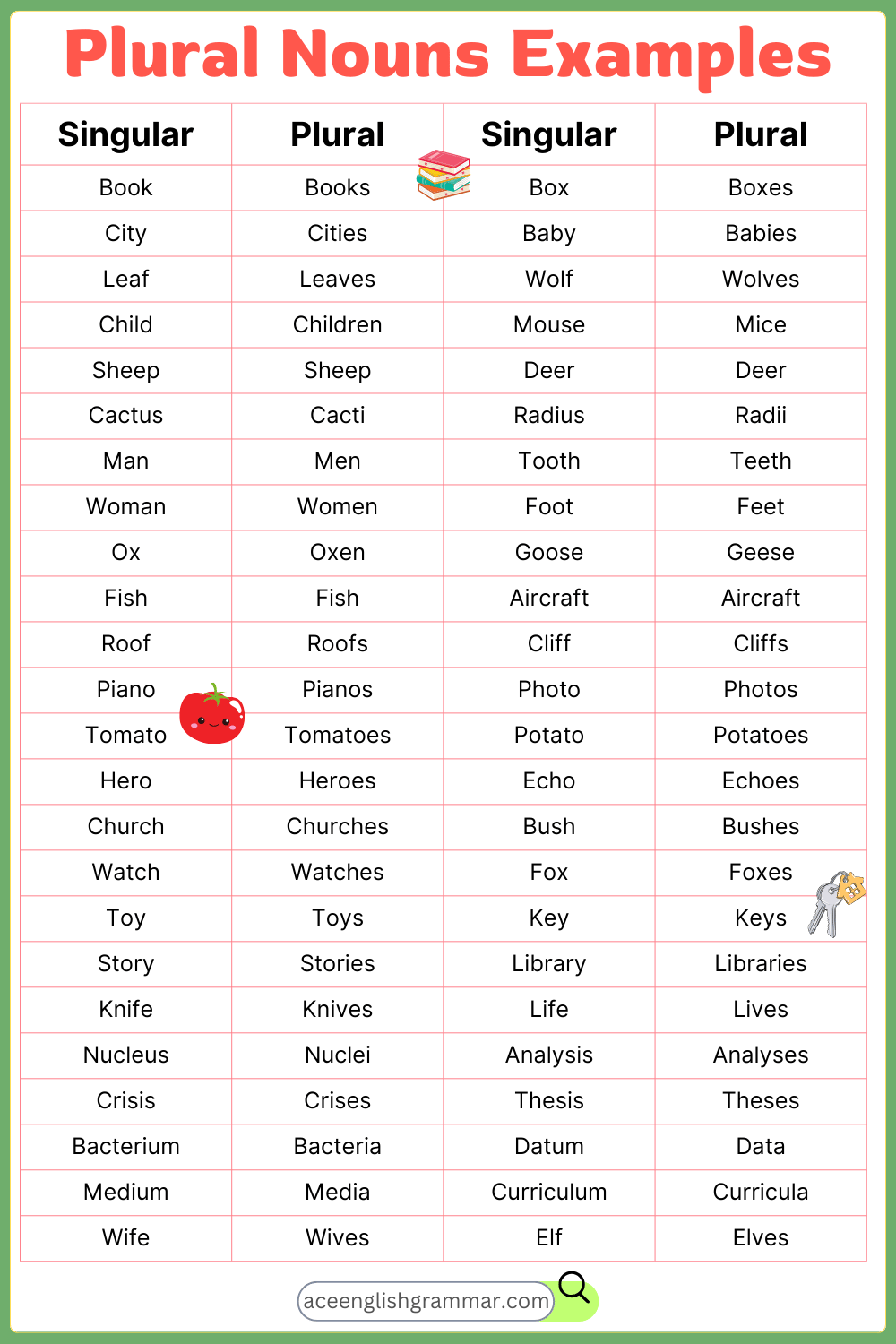
Most nouns form their plural by simply adding -s or -es to the singular noun.
- Add -s to most nouns:
- Book → Books
- Car → Cars
- Dog → Dogs
- Add -es to nouns ending in -s, -sh, -ch, -x, or -z:**
- Box → Boxes
- Bush → Bushes
- Watch → Watches
Some nouns do not follow the regular rules and change completely in their plural form.
2. Irregular Plural Noun
- Child → Children
- Man → Men
- Mouse → Mice
- Tooth → Teeth
These words undergo spelling changes instead of just adding -s or -es.
3. Nouns with the Same Singular and Plural Form
Certain nouns remain unchanged in both singular and plural forms. These are often names of animals or certain objects.
- Sheep → Sheep
- Deer → Deer
- Fish → Fish
- Aircraft → Aircraft
The context of the sentence helps determine whether the noun is singular or plural.
4. Plural Nouns Ending in -y
If a singular noun ends in -y, the plural form depends on the letter before -y:
- If a consonant precedes -y, change -y to -ies:
- City → Cities
- Baby → Babies
- Story → Stories
- If a vowel precedes -y, simply add -s:
- Toy → Toys
- Day → Days
- Key → Keys
5. Plural Nouns Ending in -f or -fe
For some nouns ending in -f or -fe, the -f changes to -ves in the plural form.
- Leaf → Leaves
- Wolf → Wolves
- Knife → Knives
- Life → Lives
However, some nouns just take -s without changing -f or -fe (e.g., roof → roofs).
Rules for Using Plural Noun
1. Most Singular Nouns Add “-s” to Form the Plural
- Car → Cars
- House → Houses
2. Add “-es” to Singular Nouns Ending in -s, -x, -z, -sh, or -ch
- Bus → Buses
- Watch → Watches
3. Change -y to -ies if Preceded by a Consonant
- City → Cities
- Lady → Ladies
4. Some Plural Nouns Have Irregular Forms
- Man → Men
- Goose → Geese
5. Some Nouns Stay the Same in Both Forms
- Sheep → Sheep
- Deer → Deer
Common Examples of Plural Noun in Sentences
- Ahmed and Aisha are good students.
- The books are on the table.
- The cars are parked outside.
- Children love playing in the park.
- The mosques are beautifully designed.
- I bought some apples from the market.
- Women are leading in many fields today.
- The wolves howled at night.
- The babies are sleeping peacefully.
- Cities around the world are growing fast.
- The glasses are on the shelf.
- There are many buses on the road.
- The foxes ran through the forest.
- He owns three watches.
- The leaves are turning yellow in autumn.
- The men are working on a project.
- I saw two mice in the kitchen.
- Geese migrate during the winter.
- The sheep are grazing in the field.
- Toys make children happy.
Plural Noun vs. Uncountable Noun
Distinguishing between plural noun and uncountable noun helps in proper grammar usage and sentence structure.
| Aspect | Plural Nouns | Uncountable Nouns |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refers to more than one of something | Refers to something that cannot be counted individually |
| Example | Books, cars, chairs | Water, rice, advice |
| Formation | Add -s, -es, or change form | Do not have plural forms |
Regular vs. Irregular Plural Noun
Understanding regular and irregular plural noun is key to using correct word forms in sentences. Knowing these rules helps avoid mistakes and improves both written and spoken communication.
| Type | Definition | Examples |
| Regular Plural Nouns | Formed by adding -s or -es | Book → Books, Box → Boxes |
| Irregular Plural Nouns | Change completely or remain the same | Man → Men, Sheep → Sheep |
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- ❌ She have two pen.
- ✅ She has two pens. (Use plural form and correct verb)
- ❌ The childs are playing.
- ✅ The children are playing. (Use irregular plural form)
- ❌ I bought three water.
- ✅ I bought three bottles of water. (Water is uncountable)
FAQs
A plural noun refers to more than one person, place, thing, or idea. Examples include cats, students, books, and cars.
Most singular nouns become plural by adding -s or -es, but some change completely, like child → children and man → men.
No, some nouns are uncountable, such as water, rice, and advice. These do not have plural forms and require words like “some” or “a piece of.”
Regular plural noun follow simple rules (book → books), while irregular plural noun change form (mouse → mice).
Download PDF
This PDF covers the definition of plural noun, key grammar rules, and examples to help learners understand how to form and use plural nouns correctly. Perfect for beginners looking to strengthen their English skills. Download now for easy learning!
Conclusion
Understanding plural noun is crucial for clear communication in English. Learning their rules, types, and common mistakes helps improve accuracy. Keep practicing, and soon, using plural nouns correctly will become natural. Grammar is the foundation of strong language skills!
Read More