Many English learners struggle transitive and intransitive verbs. Using them correctly helps form grammatically complete sentences without confusion. In this blog, you’ll learn the a comprehensive intransitive verbs list with examples to strengthen your grammar.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Intransitive Verbs
An intransitive verb is a verb that does not take a direct object. The action stays with the subject or is followed by an adverb or complement—not a noun receiving the action.
- Fatima sleeps peacefully.
(“Sleeps” is intransitive—there’s no object receiving the action.)
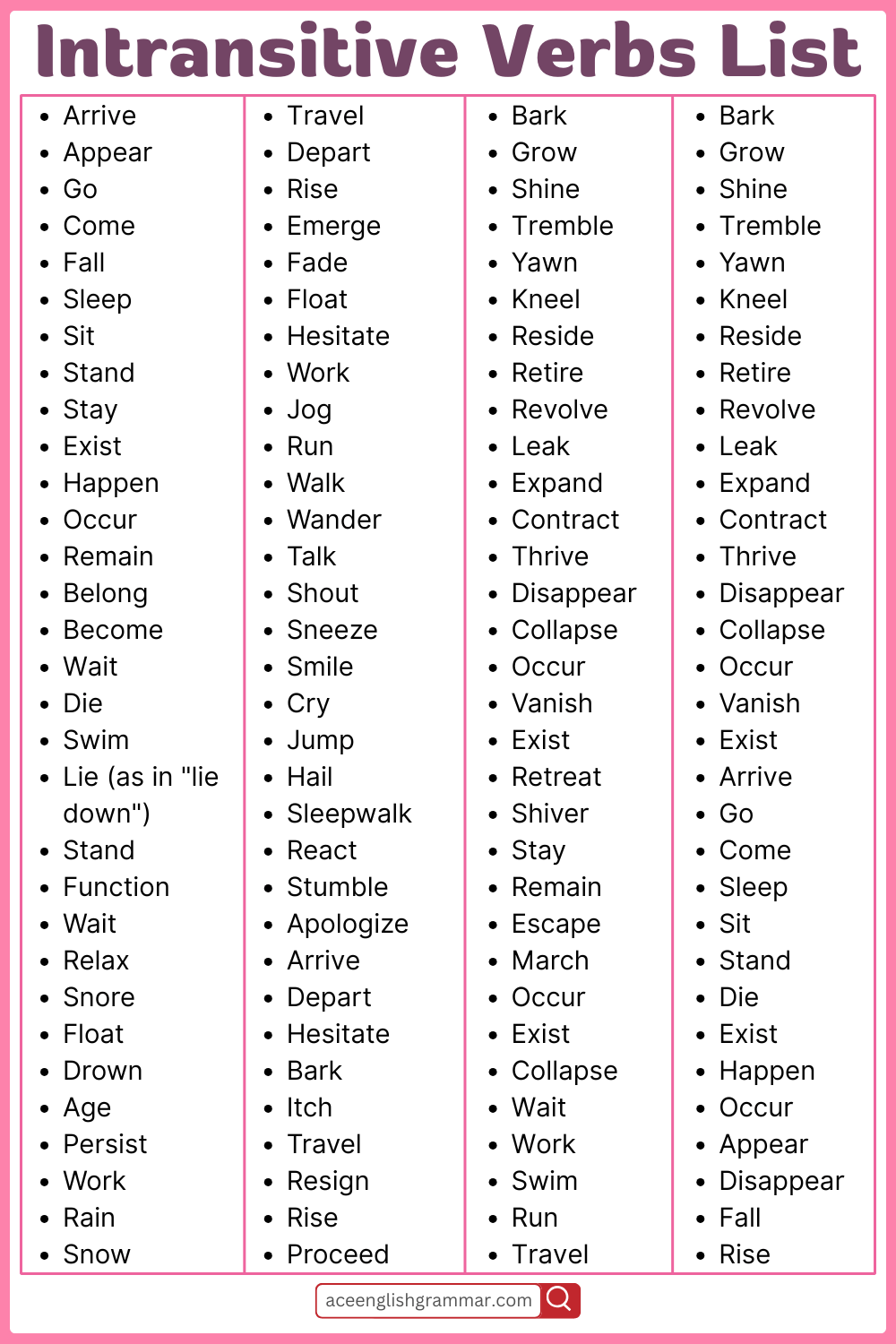
Intransitive Verbs List
- Arrive
- Appear
- Go
- Come
- Fall
- Sleep
- Sit
- Stand
- Stay
- Exist
- Happen
- Occur
- Remain
- Belong
- Become
- Wait
- Die
- Swim
- Travel
- Depart
- Rise
- Emerge
- Fade
- Float
- Hesitate
- Work
- Jog
- Run
- Walk
- Wander
- Talk
- Shout
- Sneeze
- Smile
- Cry
- Jump
- Bark
- Grow
- Shine
- Tremble
- Yawn
- Kneel
- Reside
- Retire
- Revolve
- Leak
- Expand
- Contract
- Thrive
- Disappear
- Collapse
- Occur
- Vanish
- Exist
- Lie (as in “lie down”)
- Stand
- Function
- Wait
- Relax
- Snore
- Float
- Drown
- Age
- Persist
- Work
- Rain
- Snow
- Hail
- Sleepwalk
- React
- Stumble
- Apologize
- Arrive
- Depart
- Hesitate
- Bark
- Itch
- Travel
- Resign
- Rise
- Proceed
- Retreat
- Shiver
- Stay
- Remain
- Escape
- March
- Occur
- Exist
- Collapse
- Cough
- Sneer
- Zoom
- Drift
- Exist
- Advance
- Function
- Matter
- Last
Most Common Intransitive Verbs List
Most frequently used intransitive verbs list that help build natural and fluent sentences in English.
- Arrive
- Go
- Come
- Sleep
- Sit
- Stand
- Die
- Exist
- Happen
- Occur
- Appear
- Disappear
- Fall
- Rise
- Wait
- Work
- Swim
- Run
- Travel
- Walk
- Stay
- Yawn
- Shiver
- Sneeze
- Laugh
- Cry
- Talk
- Smile
- Frown
- Grow
- Live
- Jump
- Bark
- Bleed
- Hesitate
- Resign
- Collapse
- Tremble
- Wander
- Depart
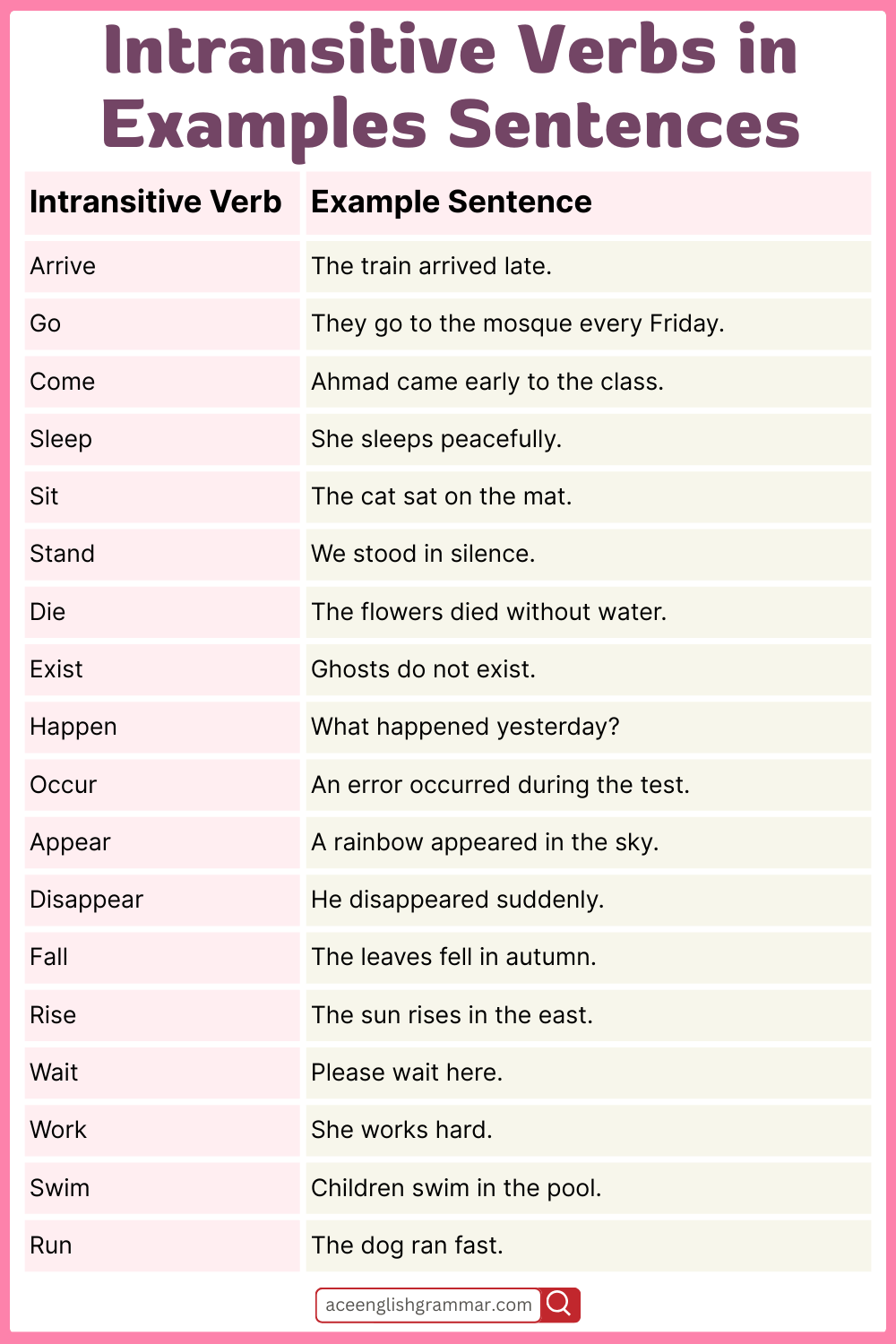
Intransitive Verbs in Examples Sentences
| Intransitive Verb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Arrive | The train arrived late. |
| Go | They go to the mosque every Friday. |
| Come | Ahmad came early to the class. |
| Sleep | She sleeps peacefully. |
| Sit | The cat sat on the mat. |
| Stand | We stood in silence. |
| Die | The flowers died without water. |
| Exist | Ghosts do not exist. |
| Happen | What happened yesterday? |
| Occur | An error occurred during the test. |
| Appear | A rainbow appeared in the sky. |
| Disappear | He disappeared suddenly. |
| Fall | The leaves fell in autumn. |
| Rise | The sun rises in the east. |
| Wait | Please wait here. |
| Work | She works hard. |
| Swim | Children swim in the pool. |
| Run | The dog ran fast. |
| Travel | They travel often. |
| Walk | He walks every morning. |
FAQs
An intransitive verb is a verb that does not take a direct object. The action ends with the subject or affects the subject itself.
Yes, some verbs can function as both, depending on the sentence.
Example:
Transitive: She runs a business.
Intransitive: She runs every morning.
No, intransitive verbs do not have passive voice because there’s no object to become the subject.
Yes, linking verbs like be, seem, or become are intransitive. They connect the subject to additional information.
Ask “What?” or “Whom?” after the verb. If the answer is missing or doesn’t make sense, it’s likely intransitive.
Conclusion
Understanding intransitive verbs helps improve your grammar and sentence clarity. These verbs stand on their own without needing an object, often expressing movement, states, or existence. Mastering them will strengthen both your writing and speaking skills. Keep practicing with real-life examples and notice how intransitive verbs make your sentences more natural and fluent.
You might also like