Do you struggle with using the right tense in English? You’re not alone. Many learners get confused by the different forms of past, present, and future. Yet, understanding tenses is essential for clear, correct, and confident communication. This blog post covers all 12 tenses in English grammar with structures, rules, and examples to help you master them once and for all.
Table of Contents
What Are Tenses?
Tenses are a way of expressing the time frame of an action or event. They show whether the action has already happened, is happening now, or will happen in the future. In English, there are three primary tenses: past, present, and future. These tenses can be further divided into four aspects: simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous. Let’s explore these tenses one by one.
Types of Tenses
Here are 12 basic types of tenses:
Present Tenses
- Simple Present Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Tenses
- Simple Past Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Future Tenses
- Simple Future Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
1. Simple Present Tense
The Simple Present Tense is used to describe actions that are happening right now, regularly occur, or generally true. It is also used for scheduled events shortly. To form this tense, you typically use the base form of the verb (without any modifications).
Formula: Subject + Base Verb (+s/es for third-person singular) + Object
| Subject | Base Verb | Object |
| We | study | English together. |
Examples:
- She walks to school every day.
- The sun rises in the east.
- The train arrives at 3 PM.
- She writes a letter every day.
- The Earth revolves around the sun.
2. Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is used to describe actions happening at the moment or actions in progress. To form this tense, use a form of “to be” (am, is, are) and add the present participle (verb + -ing).
Formula: Subject + am/is/are + Verb + -ing + Object
| Subject | am/is/are | Verb + -ing | Object |
| We | are | studying | for our exams. |
Examples:
- They are playing basketball now.
- She is reading a book.
- It is raining outside.
- I am writing an article.
- They are playing football in the park.
3. Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is used to connect the past and the present. It describes actions that started in the past and continue into the present, or actions that have just been completed. To form this tense, use “have” or “has” with the past participle.
Formula: Subject + has/have + Past Participle + Object
| Subject | has/have | Past Participle | Object |
| I | have | finished | my homework. |
Examples:
- She has lived in this city for five years.
- I have just bought a new phone.
- She has visited Paris three times.
- The team has won the championship.
- They have already finished their homework.
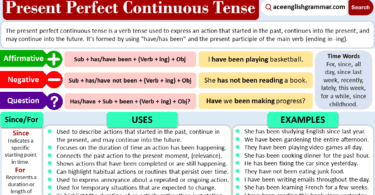
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The present perfect continuous tense is used to describe actions that started in the past, continue into the present, and are expected to continue in the future. To form this tense, use “have been” or “has been” with the present participle.
Formula: Subject + have/has been + Verb + -ing + Object
| Subject | have/has been | Verb + -ing | Object |
| I | have been | studying | English for years. |
Examples:
- She has been working on her thesis for three hours.
- They have been waiting for the bus since morning.
- I have been learning Spanish for a few months.
- They have been playing video games for hours.
- I have been working on this project for weeks.
5. Simple Past Tense
The past simple tense is used to describe completed actions in the past. To form this tense, you usually add “-ed” to regular verbs, while irregular verbs have specific past forms.
Formula: Subject + Past Verb + Object
| Subject | Past Verb | Object |
| I | finished | my homework yesterday. |
Examples:
- They visited Paris last summer.
- She watched a movie yesterday.
- He ate lunch an hour ago.
- They played football after school.
- The train arrived late this morning.
6. Past Continuous Tense
The past continuous tense is used to describe actions that were ongoing at a specific point in the past. To form this tense, use a past form of “to be” (was, were) and add the present participle (verb + -ing).
Formula: Subject + was/were + Verb + -ing + Object
| Subject | was/were | Verb + -ing | Object |
| She | was | sleeping | at midnight. |
Examples:
- I was studying when you called.
- They were having dinner when the power went out.
- They were laughing at a funny movie last night.
- I was reading a book when the phone rang.
- I was working on my project until late at night.
7. Past Perfect Tense
The past perfect tense is used to show that one action happened before another action in the past. To form this tense, use “had” with the past participle.
Formula: Subject + had + Past Participle + Object
| Subject | had | Past Participle | Object |
| I | had | finished | my homework before dinner. |
Examples:
- When I arrived, they had already left.
- She had already left when I arrived.
- She had read the book before watching the movie.
- By the time we got there, the party had ended.
- The train had left before we reached the station.
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The past perfect continuous tense is used to describe actions that were ongoing in the past and were completed at a specific point in the past. To form this tense, use “had been” with the present participle. In other words, it expresses a continuous action that was completed before another past action.
Formula: Subject + had been + Verb + -ing + Object
| Subject | had been | Verb + -ing | Object |
| She | had been | studying | for hours before the exam. |
Examples:
- He had been jogging for an hour when it started raining.
- By the time I arrived, they had been waiting for ages.
- She had been studying all night before the exam.
- We had been playing in the park when it started to rain.
- They had been waiting for the bus for half an hour.
9. Simple Future Tense
The future simple tense is used to talk about actions or events that will happen in the future. To form this tense, you can use “will” or “shall” with the base form of the verb.
Formula: Subject + will/shall + Base Verb + Object
| Subject | will/shall | Base Verb | Object |
| He | will | call | you later. |
Examples:
- I will call you later.
- She shall arrive tomorrow.
- They will meet at the park.
- I think it will rain tomorrow.
- Will you join us for dinner tonight?
10. Future Continuous Tense
The future continuous tense is used to talk about actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future. To form this tense, use “will be” or “shall be” with the present participle.
Formula: Subject + will/shall + be + Verb + -ing + Object
| Subject | will/shall | be | Verb+ -ing | Object |
| I | will | be | studying | tonight. |
Examples:
- At 8 AM, I will be enjoying a cup of coffee.
- They will be traveling to Europe next week.
- She shall be working late tomorrow.
- We will be celebrating his birthday next week.
- We will be watching a movie tonight at 8 PM.
11. Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used to describe an action that will be completed before a specific point in the future. To form this tense, use “will have” or “shall have” with the past participle.
Formula: Subject + will/shall + have + Past Participle + Object
| Subject | will/shall | have | Past Participle | Object |
| She | will | have | completed | the project by Friday. |
Examples:
- By this time tomorrow, I will have finished my presentation.
- They will have completed their project by next month.
- She shall have graduated by June.
- She will have completed her project by Friday.
- By the time you arrive, I will have finished cooking.
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The future perfect continuous tense is used to express the duration of an action that will have been ongoing before a specific future point. In other words, it describes a continuous action that will be completed before another future action.
Formula: Subject + will have been + Verb + -ing + Object
| Subject | will have been | Verb + -ing | Object |
| They | will have been | playing | games all day. |
Examples:
- By midnight, I will have been studying for 3 hours.
- He will have been practicing guitar for a week.
- She will have been working here for a year next month.
- She will have been working on the project for a week by Friday.
- They will have been playing music all day at the party.
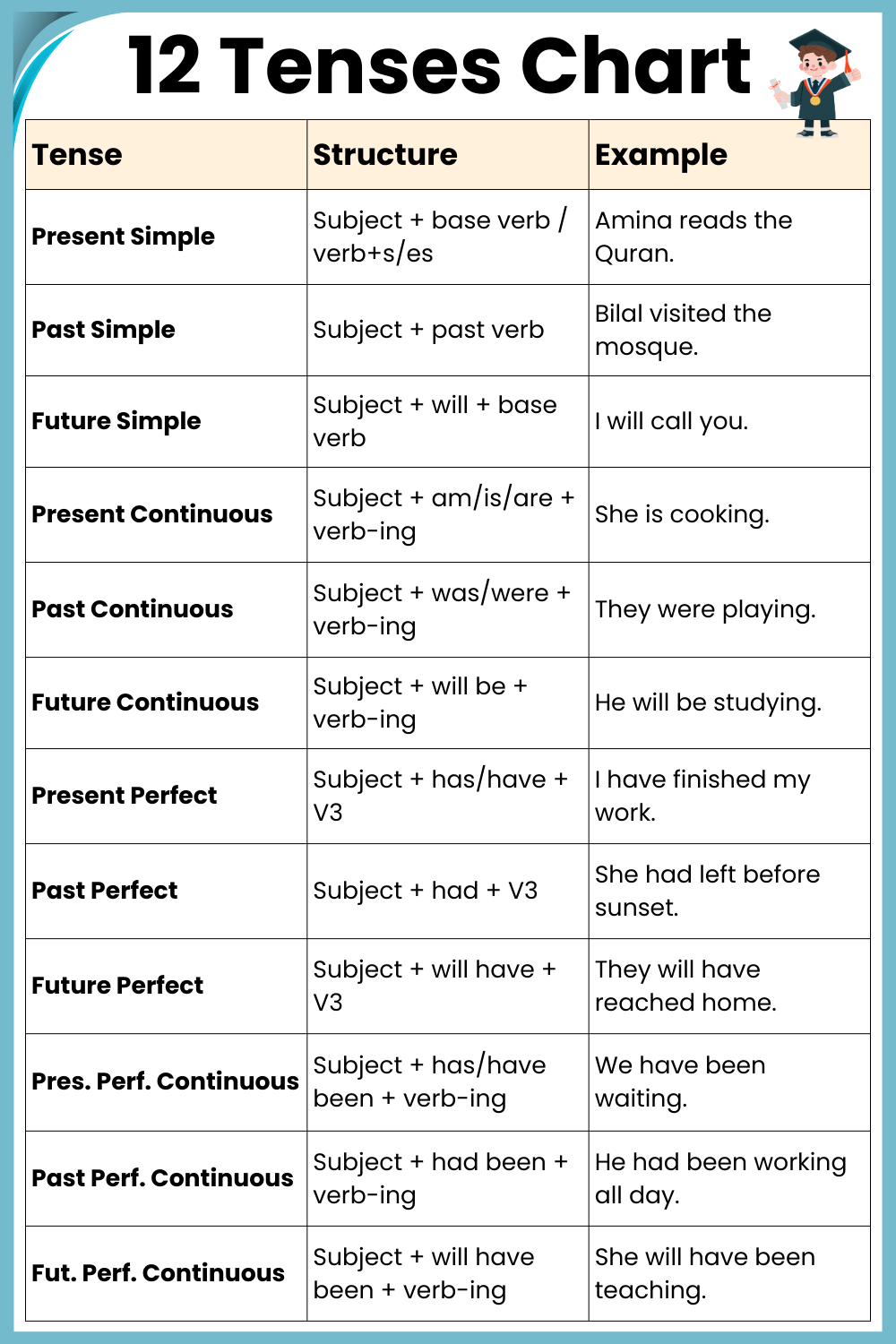
Complete Chart of 12 Tenses in English
| Tense | Structure | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Present Simple | Subject + base verb / verb+s/es | Habits, routines, general truths | Amina reads the Quran every day. |
| 2. Past Simple | Subject + past verb | Completed actions in the past | Bilal visited the mosque yesterday. |
| 3. Future Simple | Subject + will + base verb | Future actions or decisions | I will call you tomorrow. |
| 4. Present Continuous | Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing | Actions happening now | She is cooking dinner. |
| 5. Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + verb-ing | Ongoing actions in the past | They were playing cricket. |
| 6. Future Continuous | Subject + will be + verb-ing | Ongoing actions at a future time | He will be studying at 9 PM. |
| 7. Present Perfect | Subject + has/have + past participle (V3) | Past action with present result or experience | I have finished my homework. |
| 8. Past Perfect | Subject + had + past participle (V3) | Action completed before another past action | She had left before I arrived. |
| 9. Future Perfect | Subject + will have + past participle (V3) | Action completed before a specific future point | They will have reached by 8 PM. |
| 10. Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + has/have been + verb-ing | Action started in past and still continuing | We have been waiting since 10 AM. |
| 11. Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had been + verb-ing | Continuous past action before another past point | He had been working for hours. |
| 12. Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will have been + verb-ing | Action continuing up to a future point | She will have been teaching for 5 years. |
Conclusion
Learning all 12 tenses may seem overwhelming, but once you understand their patterns and usage, speaking and writing become much easier. Tenses give time context to our sentences, making communication clearer and more effective. Keep practicing with real-life examples, and soon you’ll use tenses naturally and confidently.
FAQs
There are 12 main tenses, divided equally into Present, Past, and Future.
The Simple Present Tense is used for habits and routines.
Present Perfect focuses on the result (I have written the letter), while Present Perfect Continuous focuses on duration (I have been writing the letter).
We use it when one past action happened before another (She had gone before he came).
Use Simple Future for general plans or Future Continuous for specific times (I will be meeting him at 6 PM).
Read More



Leave a Comment