Linking words, also known as transition words or connectors, are defined as words or phrases that connect clauses, sentences, paragraphs, and ideas, and convey the intended meaning more clearly and effectively. These words not only make the text readable but also help the readers to understand the writer’s perspective. We can use these words to express ideas, contrast, comparison, order, cause and effect, time, and many other functions. Linking words is an essential part of writing to “link” all your ideas in a way that helps create a smooth flow and connections between different parts of a text. In this article, we will take a comprehensive look at what linking words are, their functions with examples, and how to use them effectively. So, let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What are linking words?
Linking words are words or phrases that we use to link or connect different parts of a text. They help make the writing smoother and show how different ideas are related to each other. Linking words makes it easier for readers to understand the flow of information and how one idea leads to another. Linking words can be used to indicate contrast, similarity, cause and effect, time, addition, conclusion, and more. Examples of linking words include “and,” “but,” “because,” “however,” “also,” “for example,” “therefore,” and so on.
For instance:
- She is happy. (The linking verb “is” connects the subject “She” to the complement “happy.”)
- The cake tastes delicious. (Here, “tastes” links the subject “The cake” to the complement “delicious.”)
- She wanted to go shopping; however, it started raining. (Here linking word “However” indicates a contrast between her desire to go shopping and the unexpected rain, helping the reader understand the change in the situation.)
Why use linking words?
Linking words are essential for effective writing because they:
- Improve flow and coherence
- Help establish relationships between ideas
- Make writing smoother to read
- Create clear transitions between paragraphs
- Enhance reader comprehension and understanding
- Linking words can help to emphasize and clarify important points
How to use Linking Words?
Here are some basic rules for the placement and usage of linking words:
- Before using linking words, make sure you understand what they mean and how they are used. For example,
- Some words are used to add new ideas such as, (“furthermore” or “moreover”) while others are used to show contrast or contradiction, (“however” or “nevertheless”) etc.
- Choose the appropriate linking word based on the context, for example,
- (“Additionally” for adding, “For example” for illustrating)
- Place linking words at the beginning or middle of sentences for smooth transitions.
- Use a comma after starting a sentence with a linking word, for example,
- However, I decided to give it a try.
- Add commas around the linking word if placed in the middle, for example,
- In this case, however, the outcome was unexpected.
- Coordinating Conjunctions (and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet) connect equal parts (independent clauses), use a comma before them. for example,
- I like apples, but he prefers oranges.
- Subordinating Conjunctions (although, because, since, while, when) introduce dependent clauses, use commas when dependent clause precedes the main clause. for example,
- Although it was raining, we went for a walk. (Comma before main clause)
- No comma if subordinate clause follows main clause. for example,
- We went for a walk although it was raining. (No comma)
- Maintain parallel structure (similar grammar) when using multiple linking words in a list. for example,
- She likes reading, to cook, and watching movies. ❎
- She likes reading, cooking, and watching movies.✅
Common Linking words:
Linking words, also known as transition words or connectors, help to connect ideas and improve the flow of sentences. Here are some commonly used linking words:
- Addition:
- I like pizza, and my sister likes pasta.
- Contrast:
- She is tall, but her brother is short.
- Comparison:
- My dog is fluffy, just like a teddy bear.
- Cause and Effect:
- He studied hard, so he aced the exam.
- Result:
- It was raining, therefore we stayed indoors.
- Time:
- First, next, we will have breakfast.
- Emphasis:
- Indeed, certainly, he is the best player on the team.
- Conclusion:
- In conclusion, to sum up, we had a great day.
- Similarity:
- My sister also enjoys playing the piano.
- Contradiction:
- I like ice cream, while she prefers cake.
- Illustration:
- For example, such as, apples are fruits.
- Sequence:
- First, then, we will go to the park.
- Clarification:
- In other words, that is to say, it’s too hot outside.
- Alternative:
- You can choose tea, or you can have coffee.
- Condition:
- If it rains, we will stay indoors.
- Concession:
- Even though it’s late, we can finish the project.
- Purpose:
- I bought a new laptop to improve my work efficiency.
- Summary:
- To sum it up, in short, exercise is important for health.
- Restatement:
- The recipe is easy to follow, in essence, just mix and bake.
20. Enumeration:
- There are many reasons to exercise: firstly, it improves health; secondly, it boosts mood.
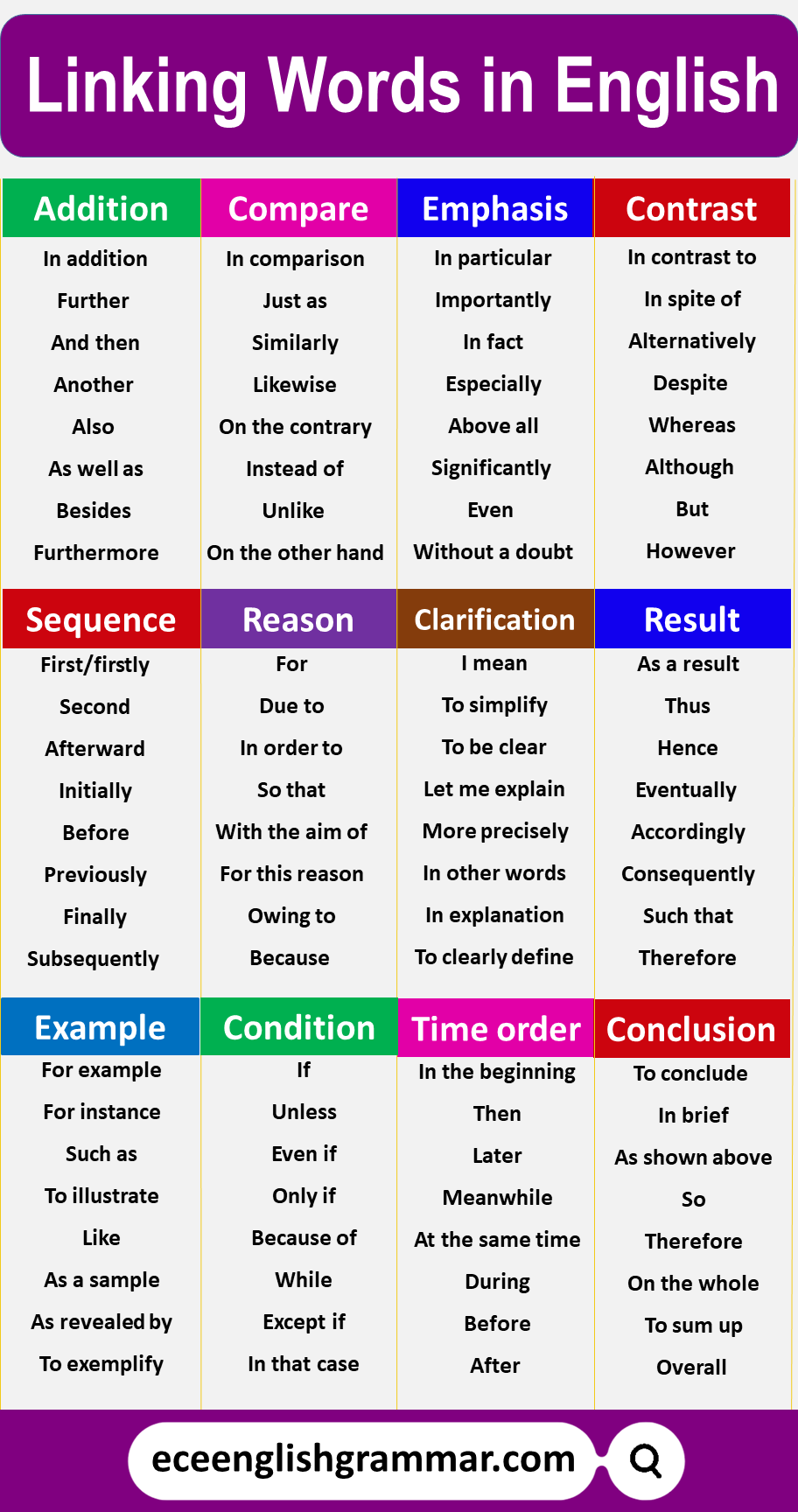
linking words
Functions of linking words
Different linking words serve different purposes/functions:
Addition
Linking words like “and,” “also,” “besides,” “furthermore,” and “moreover” are used to introduce additional information or ideas that are related to the previous point. Common linking words for addition include: and, also, as well as, additionally, furthermore, moreover, in addition, besides, not only…but also, etc.
- Example: I love both chocolate and vanilla ice cream.
Contrasting Ideas
Words such as “but,” “however,” “although,” and “on the other hand” help introduce a contrasting idea or point that is different from what was previously mentioned. Examples of contrastive linking words are: but, however, on the other hand, yet, and, although, nevertheless, in contrast, whereas, although, and even though, etc.
- Example: He wanted to go out. However, it started raining heavily.
Cause and Effect
Linking words indicate the relationships between cause and effect. They help explain why something happened or the consequences of an action. Common cause-and-effect linking words are; because, so, therefore, due to, resulting in, consequently, therefore, thus, hence, etc.
- Example: He missed the bus; consequently, he arrived late.
Comparison
These words help you show similarities or likenesses between ideas. They allow you to compare and contrast different concepts. Examples include; like, similarly, in the same way, and compared to, likewise, just as, just like, in contrast, on the contrary, unlike, etc.
- Example: The first book was good, but the second one was even better.
Time Sequence
Linking words help arrange ideas chronologically or in a specific order. They guide readers through a sequence of events or steps. Common time sequences linking words are; first, next, then, finally, meanwhile, after, before, afterward, subsequently, eventually, etc.
- Example: First, we went shopping. Then, we had lunch at a cafe.
Example/Illustration
Linking words are used to provide examples that clarify or support the main point. They make your ideas more concrete and relatable. Examples of these words include “for example,” “such as,” “specifically,” and “in particular” etc.
- Example: There are many outdoor activities you can try, such as hiking, biking, and camping.
Conclusion/Summary
Linking words are used to provide examples that clarify or support the main point. They make your ideas more concrete and relatable. Examples of these words include “for example,” “such as,” “specifically,” and “in particular.” etc.
- Example: To sum up, regular exercise has numerous health benefits.
Emphasis
These words can be used to emphasize a point or to highlight its significance. They guide readers to pay attention to specific information. Examples are “especially,” “notably,” “indeed,” and “importantly.”
- Example: The view from the top of the mountain was truly breathtaking.
Clarification
These words aid in clarifying or restating an idea to ensure readers understand it correctly. They help avoid confusion. Examples include “in other words,” “that is,” “to put it differently,” and “namely.”
- Example: “The concept is a bit complex. In other words, it might take some time to fully understand.”
Expressing Purpose
Linking words like “in order to,” “so that,” and “for the purpose of” indicate the purpose or intention behind a certain action or statement.
- Example: He worked overtime for extra money.
Sequence/Order
Words like “firstly,” “next,” “then,” “finally,” and “in conclusion” help to organize and sequence ideas in a logical order.
- Example: First, we went to the park. Then, we had a picnic.
Condition:
Linking words like “if,” “unless,” “provided that,” and “in case” introduce conditions or circumstances under which something else will happen. They show that one thing depends on another.
- Example: If it rains, we will stay indoors.
Examples Sentences of linking Words
- I enjoy both swimming and hiking.
- She is not only smart but also diligent.
- We can go to the park or visit the museum.
- He prefers tea over coffee.
- The weather is cold yet clear.
- I have finished my homework, so I can play now.
- She likes pizza, while he prefers pasta.
- I studied hard; consequently, I passed the exam.
- He is a doctor because he studied medicine.
- The team won although they were the underdogs.
- Either we go now or we’ll miss the train.
- I bought a new phone as my old one was broken.
- I need to finish my work before I go to bed.
- She is both kind and generous.
- He cooks well; however, he doesn’t enjoy it.
- Furthermore, the movie was boring.
- Nevertheless, I decided to try it.
- The car is expensive; yet, it is worth the price.
- He is tired because he worked all day.
- Hence, I need a day off.
- It’s raining; therefore, we can’t go to the beach.
- I’ll call you when I arrive.
- He wanted to join us; however, he had other plans.
- Otherwise, we will miss the flight.
- Since it’s your birthday, I bought you a gift.
List of Linking Words
Addition
- Additionally
- Along with
- Also
- Another
- And then
- Apart from this
- As well as
- As well as that
- Besides
- Coupled with
- Finally
- First
- Further
- Furthermore
- In addition
- Then
- In addition to this
- Moreover
- In the same fashion
- Not only…but also
- Not to mention
- Similarly
- Together with
- What’s more
- Plus
Contrast
- Alternatively
- By contrast
- In spite of
- Although
- As opposed to
- Contrarily
- Contrary to
- Conversely
- Despite
- Differing from
- Even so
- However
- In contrast to
- In opposition
- Instead
- Nevertheless
- Nonetheless
- Whereas
- While
- Yet
- Nor
- Notwithstanding
- On the other hand
- Rather
- Though
- Unlike
- Up against
Showing Cause and Effect
- Because
- Since
- Therefore
- As a result
- Consequently
- Thus
- Hence
- Due to
- Owing to
- For this reason
- On account of
- Resulting from
- Under the circumstances
- In consequence of
- As a consequence
- The outcome is that
- The effect of this
- This has led to
- Such that
- Such is the case
- Accordingly
- Eventually
Comparison
- In comparison
- In the same way
- Correspondingly
- Just as
- Likewise
- Similarly
- Compared to/with
- As well as
- Equally
- Along with
- In a similar fashion
- By contrast
- Conversely
- On the contrary
- Same as
- Unlike
- Instead of
- While
- Nevertheless
- In spite of
- Yet
- Nonetheless
- At the same time
- In contrast to
- On the other hand
Time sequence
- First
- First of all
- Initially
- At first
- In the beginning
- To start with
- Next
- Then
- Subsequently
- Later
- Following that
- Meanwhile
- Simultaneously
- Concurrently
- At the same time
- In the meantime
- While
- During
- Throughout
- After
- Before
- Prior to
- Afterwards
- Eventually
- Finally
Example/Illustration
- For example
- For instance
- Such as
- Like
- Including
- To illustrate
- In particular
- Specifically
- Namely
- As an illustration
- To demonstrate
- As shown by
- In the case of
- One example is
- As evidence
- In other words
- As a case in point
- To put it differently
- As revealed by
- A good example of this is
- In a similar manner
- This can be seen when
- As a specific instance
- To exemplify
- As a sample
- In one instance
- As proof
- Let’s consider
- As an example of
- To clarify
Conclusion/Summary
- All things considered
- As demonstrated above
- In brief
- As shown above
- So
- As you can see
- By and large
- Given these points
- In a word
- Briefly
- In any event
- As noted
- In conclusion
- Generally speaking
- In short
- To end
- In the end
- In the final analysis
- On the whole
- Overall
- Therefore
- To conclude
- In summary
- To sum up
- In essence
- To summarize
Emphasis
- Ultimately
- Clearly
- Clearly, then
- Importantly
- Most importantly
- Notably
- Significantly
- Indeed
- In fact
- Undoubtedly
- Without a doubt
- Absolutely
- Positively
- Unquestionably
- In particular
- Especially
- Primarily
- Chiefly
- Above all
- It’s worth noting
- It should be emphasized that
- It’s important to highlight
- A key point to remember
- Of course
- Naturally
- To stress
- Also
- To highlight
- It’s important to note
- Even
- To draw attention to
- It cannot be overstated
- To repeat
- Truly
Clarification
- I mean
- In explanation
- To be clear
- In other words
- Let me explain
- To put it clearly
- Simply stated
- That is to say
- To break it down
- More precisely
- To clearly define
- Allow me to clarify
- To put it in another way
- Simply put
- To simplify
Expressing Purpose, Reason
- Because of
- Therefore
- For the purpose of
- Given that
- Granted that
- In view of
- Owing to
- With this purpose
- Provided that
- Seeing that
- With this in mind
- In fact
- In order to
- As a result
- With this intention
- So that
- With the aim of
Sequence/Order
- First/ firstly
- Second/ secondly
- Third/ thirdly
- Afterward
- Finally
- Initially
- Following
- Previously
- Before
- Subsequently
- To start with
Condition
- If
- Unless
- Although this may be true
- As
- Because of
- Even if
- In that case
- On the condition that
- Only if
- Since
- Then
- When
- Whenever
- While
- Except if
Choice
- Option 1 or Option 2
- Either… or…
- Whether… or…
- Preferably… or…
- In either case…
- Or
- Alternatively
- While… In comparison…
- Rather
- Select between… or…
- Choose either… or…
Restatement
- I mean
- Expressed simply
- In a nutshell
- Otherwise stated
- Put in another way
- In other words
- That is to say
- To put it differently
- In simple terms
- What I mean by this is
- To rephrase
- In short
Generalize information
- In general
- Generally speaking
- On the whole
- Overall
- Broadly
- By and large
- In most cases
- In the majority of instances
- As a rule
- For the most part
- In a general sense
- Without exception
- Universally
- Across the board
- Without distinction
- In a broader context
- Typically
- Commonly
- Without specific regard to
- In a global perspective
- Without pinpointing
FAQs
Q1. What are linking words?
Linking words, also known as transition words or connectors, are words or phrases that create a connection between ideas, sentences, or paragraphs in a text.
Q2. What is the importance of using linking words?
Connecting words help to create cohesion and coherence in writing, making it easier for readers to understand the relationships between different ideas.
Q3. Why are linking words important in writing?
Linking words help writers to make their writing coherent and logical. They allow the writer to smoothly transition from one idea to the next, which helps keep the reader engaged and ensures that the writing flows logically.
Q4. What are some commonly used linking words?
Some commonly used linking words include and, but, or, because, since, therefore, however, furthermore, in addition, and despite.
Q5. What is the difference between conjunctions and linking words?
Conjunctions are a type of linking word that connects two clauses within a sentence. Linking words, on the other hand, connect different sentences or paragraphs within a text.
Q6. Give some example sentences of linking words.
Here are example sentences of linking words:
- He prefers tea over coffee.
- The weather is cold yet clear.
- She is both kind and generous.
- Hence, I need a day off.
- I’ll call you when I arrive.
You May Also Like:



Leave a Comment