In English grammar, verbal sentences play a crucial role in effective communication. They are sentences that contain a verb, which is typically the central part of the sentence structure. Understanding verbal sentences is essential for learners who want to master sentence construction and improve their grammar skills. This article will break down the concept of verbal sentences, their structure, and provide examples to help you grasp this topic easily.
Table of Contents
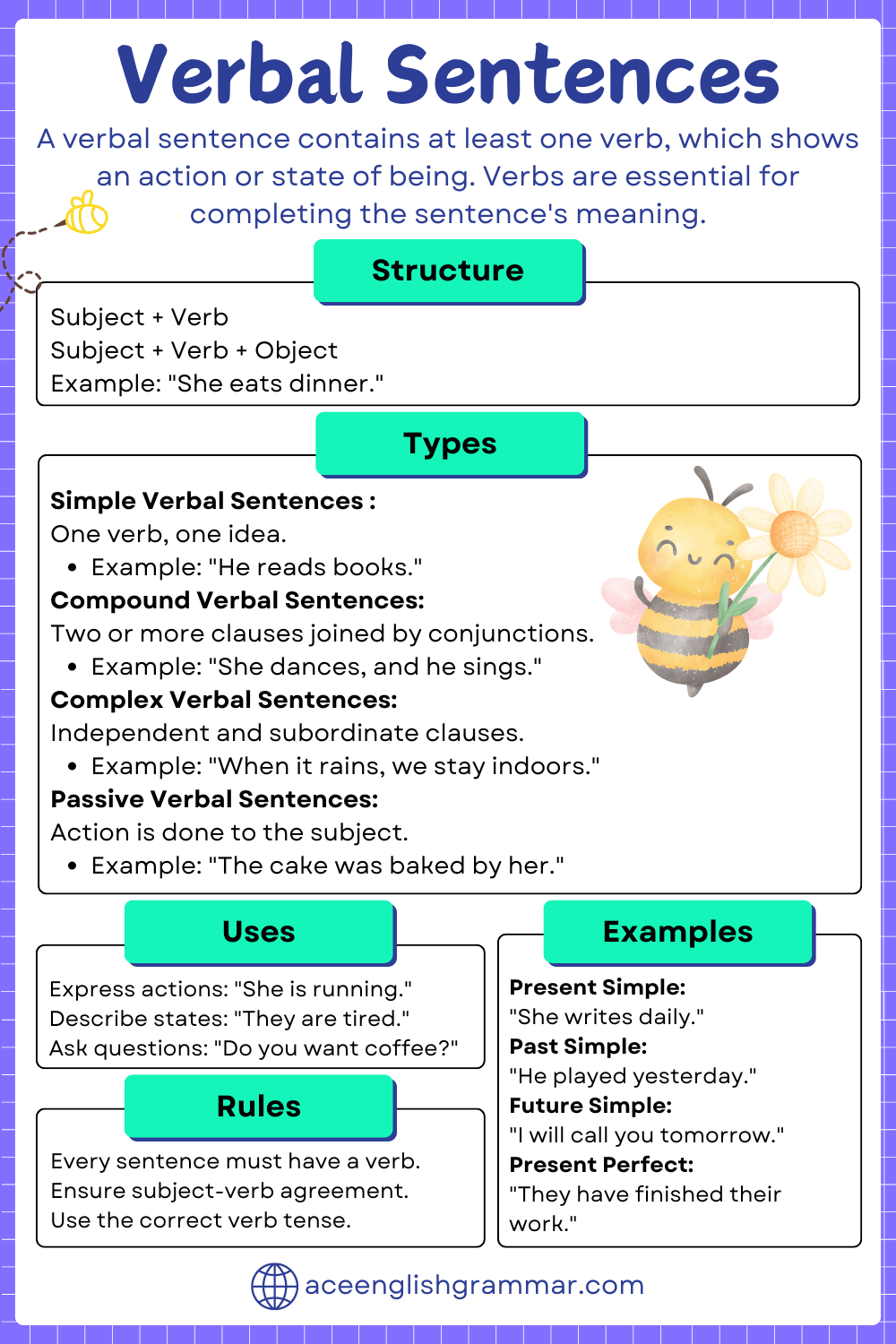
What Are Verbal Sentences?
A verbal sentence is a sentence that contains at least one verb. Verbs are the action words in a sentence that describe what the subject is doing or express a state of being. Without a verb, a sentence is incomplete. In English, most sentences are verbal sentences, as they rely on verbs to convey meaning and action.
Example of Verbal Sentences:
- “She runs every morning.”
- “They are studying for the exam.”
- “He was late to the meeting.”
In all of these examples, the verbs (runs, are studying, was) carry the meaning and make the sentence complete.
Structure of Verbal Sentences
The structure of a verbal sentence generally follows the Subject + Verb + Object pattern, but it can vary depending on the sentence type (active, passive, etc.). Verbs can appear as main verbs or auxiliary verbs, but they are always necessary to form a complete sentence.
Basic Formula:
- Subject + Verb
- Subject + Verb + Object
Examples:
- “She eats dinner at 7 pm.”
- “They are playing soccer in the park.”
Types of Verbal Sentences
Verbal sentences can be divided into different types based on the verb forms and sentence structures.
1. Simple Verbal Sentences:
A simple sentence contains a single verb and expresses one complete idea.
- “He reads books.”
2. Compound Verbal Sentences:
A compound sentence consists of two or more clauses connected by coordinating conjunctions (and, but, or).
- “She dances, and he sings.”
3. Complex Verbal Sentences:
A complex sentence has an independent clause and one or more subordinate clauses.
- “When it rains, we stay indoors.”
4. Passive Verbal Sentences:
In passive sentences, the action is done to the subject, and the verb form typically includes a form of “to be” + past participle.
- “The cake was baked by my sister.”
Uses of Verbal Sentences
Verbal sentences are essential in every form of communication, from everyday conversations to academic writing. They are used to:
- Express Actions:
- “She is running in the park.”
- Describe States or Conditions:
- “They are tired after the trip.”
- Provide Information:
- “The class starts at 8 am.”
- Ask Questions:
- “Do you want coffee?”
Rules for Constructing Verbal Sentences
- Every sentence must contain a verb: Without a verb, the sentence will be incomplete.
- Ensure subject-verb agreement: The verb must agree in number and tense with the subject. For example, “She runs” is correct, while “She run” is incorrect.
- Use the correct verb tense: Depending on the time frame, the verb tense should match. For example, “He was eating” (past continuous) or “He will eat” (future simple).
Examples of Verbal Sentences
- Present Simple: “She writes every day.”
- Present Continuous: “They are watching a movie.”
- Past Simple: “He played football yesterday.”
- Future Simple: “I will call you tomorrow.”
- Present Perfect: “We have finished our homework.”
Read More