Modal verbs are essential in the English language as they help express different moods and attitudes towards a particular situation. Whether you are asking for permission, giving advice, expressing possibility, or making a suggestion, modal verbs play a crucial role in conveying your message accurately. In this article, we will explore what modal verbs are, their different types, and how to use them effectively in different contexts. So let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What Are Modal Verbs?
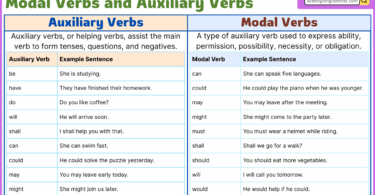
Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary (helping) verbs in English that express the speaker’s attitude or perspective toward the action or state of the main verb. Unlike regular action verbs, which describe actions or states directly, modal verbs express possibilities, necessity, permission, ability, and more. They modify the meaning of the main verb and often indicate the tone and intention of the speaker or writer. Modal verbs are always followed by a base form (infinitive) of the main verb. Some common modal verbs in English include can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must, and ought to.
Here’s a list of the most common modal verbs in English:
Modal Verb | Function | Example Sentence |
| Can | Ability / Possibility | She can speak English fluently. |
| Could | Past Ability / Polite Request | Could you help me? |
| May | Possibility / Permission | It may rain. May I go out? |
| Might | Possibility / Slight Chance | He might come later. |
| Must | Necessity / Strong Obligation | You must finish your homework. |
| Shall | Future Action / Formal Offer | Shall we go to the movies? |
| Should | Advice / Suggestion | You should eat more vegetables. |
| Will | Future Action / Willingness | I will help you. |
| Would | Polite Request / Hypothetical | Would you like some tea? |
| Ought To | Moral Obligation / Duty | You ought to respect your elders. |
Unlike regular verbs, modal verbs have some unique characteristics:
- They do not change their forms (no -s, -ing, -ed) regardless of the subject or tense.
- They are followed by the base form of the main verb. For example, “I can swim,” where “can” is the modal verb, and “swim” is the base form of the main verb.
- They don’t require the use of “do” for questions and negatives (e.g., “Can you swim?” instead of “Do you can swim?”).
- Modal verbs themselves do not have a past tense form. Instead, they use auxiliary verbs like “could,” “might,” or “would” to convey past meanings.
- They do not take an “s” in the third-person singular form. For example, “He can go,” not “He cans go.”
Common Modal Verbs
Here are some of the most frequently used modal verbs, along with their meanings and examples:
Can
Function: “Can” is used to indicate the ability or capacity to do something in the present or future. It signifies that someone has the physical or mental capability to perform an action.
Examples:
- She can speak French fluently.
- Can you help me with this?
Could
Function: “Could” is the past tense of “can” and is used to indicate past ability or a polite request or suggestion in the present or future.
Examples:
- I could swim when I was younger.
- Could you please pass the salt?
May
Function: “May” is used to express permission, possibility, or a polite request. It is often considered more formal and polite than “can.”
Examples:
- You may leave the classroom now.
- It may rain later.
Might
Function: “Might” is used to express a weaker possibility or uncertainty compared to “May.” It can also be used to make polite requests.
Examples:
- I might go to the party tonight.
- It might be a good idea to bring an umbrella.
Must
Function: “Must” is used to express a strong necessity or obligation. It indicates that something is required or imperative.
Examples:
- I must finish my homework before I go out.
- You must see this movie; it’s fantastic!
Shall
Function: “Shall” is less common in modern English but is used for making suggestions, offers, or expressing future actions, especially in British English.
Examples:
- Shall we go for a walk?
- I shall help you with your bags.
Should
Function: “Should” is used to give advice, make recommendations, express obligation, or indicate the likelihood of something happening.
Examples:
- You should eat more vegetables.
- Students should attend class regularly.
Will
Function: “Will” is used to express future actions, predictions, spontaneous decisions, or willingness.
Examples:
- I will meet you at the park tomorrow.
- She will probably win the competition.
Would
Function: “Would” is often used to express hypothetical or polite requests. It is also used in conditional sentences.
Examples:
- Would you like some tea?
- If I were rich, I would travel the world.
Ought To
Function: “Ought to” is used to give advice, strong recommendations, or express moral or social obligations.
Examples:
- You ought to respect your elders. (advice)
- We ought to help those in need. (moral obligation)
Usage of Modal Verbs
Expressing Certainty:
Modal verbs can be used to express varying degrees of certainty. For example, “will” and “must” convey a high level of certainty, while “might” and “could” indicate lower levels of certainty.
Examples:
- Certain: The sun will rise in the morning.
- Less certain: The weather might improve by the weekend.
Asking for Permission:
Modal verbs like “May,” “could,” and “can” are commonly used to request permission or seek approval.
Examples:
- May I use your phone to make a call?
- Could I borrow your book for a day?
Making Suggestions:
Modal verbs such as “shall” and “should” are used to make suggestions or offer ideas.
Examples:
- Shall we go out for dinner tonight?
- You should eat more vegetables.
Expressing Obligation:
Modal verbs like “must” and “ought to” convey a sense of obligation or necessity.
Examples:
- You must complete the assignment by tomorrow.
- You ought to respect your parents.
Talking About Ability:
“Can” and “Could” are used to discuss one’s abilities or capabilities.
Examples:
- She can swim very well.
- I could play the piano when I was a child.
Predicting the Future:
Modal verbs “will” and “would” help us discuss future events or make predictions.
Examples:
- I think it will snow tomorrow.
- If I had more time, I would travel the world.
Expressing Politeness:
“Would” and “Could” are often used to make requests in a polite and indirect manner.
Examples:
- Would you mind turning down the music a bit?
- Could you please pass me the salt?
Talking About Possibility:
“May” and “Might” are used to discuss possibilities and uncertainties.
Examples:
- It may rain this afternoon.
- She might join us for dinner if she’s not busy.
Modal Verbs in Questions
Modal verbs play a significant role in forming questions. When using modal verbs in questions, remember to invert the subject and modal verb:
- Statement: She can swim.
- Question: Can she swim?
Modal Verbs in Negative Sentences
To create negative sentences with modal verbs, simply add “not” after the modal verb:
- Statement: He must attend the meeting.
- Negative: He must not attend the meeting.
Modal Verbs Example Sentences
- He can play cricket.
- It might rain later today.
- I will call you tomorrow.
- Would you like some coffee?
- Shall we go for a walk?
- You ought to apologize for your mistake.
- May I please have some water?
- I will be there at 3 PM.
- Would you mind closing the window?
- Shall we start the meeting?
- You should visit that museum; it’s amazing.
- We must be on time for the flight.
- Could you please pass me the salt?
- May I use your computer for a moment?
- I might go to the party if I finish my work.
- He must be the smartest person in the class.
- She might know the answer.
- You ought to exercise regularly.
Modal Verbs Exercises
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate modal verb (can, could, may, might, will, would, shall, should, must, or ought to) based on the context provided in each sentence.
- I have an important meeting tomorrow, so I ________ prepare my presentation tonight.
- Sarah is very talented; she ________ speak three languages fluently.
- If you have any questions, you ________ feel free to ask me.
- It’s getting late, and I have to wake up early, so I ________ go to bed now.
- If you want to succeed in this course, you ________ study regularly.
- I’m not sure if I ________ be able to attend the party on Saturday; I’ll let you know.
- She ________ be here any moment now; she said she’d arrive by 5 PM.
- You ________ stop at red traffic lights; it’s the law.
- Excuse me, ___________ I use your phone for a moment?
- The weather forecast says it ___________ rain later, so bring an umbrella.
- I promise I ___________ help you with your homework after dinner.
- If you want to lose weight, you ___________ avoid eating junk food.
- I think you _______ apologize for what you said.
- I think he ___________ be at the office by now; he’s usually punctual.
- We ___________ start planning our vacation soon; summer is just around the corner.
Answers:
- Should/Must
- Can
- May/Should
- Should/Must
- Must/Should
- Will
- Might/Will
- Should/Must/Ought To
- May/Can
- Might/Will
- Will
- Should/Must/Have To
- Ought To
- Should
- Must/Should
FAQs about Modal Verbs
Q1: What are modal verbs?
Modal verbs are a group of auxiliary verbs in English that are used to modify the meaning of the main verb in a sentence. They express various shades of meaning, including possibility, necessity, ability, permission, and obligation.
Q2: How many modal verbs are there in English?
There are ten primary modal verbs in English: can, could, may, might, will, would, shall, should, must, and ought to.
Q3: What is the difference between modal verbs and regular verbs?
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that modify the main verb, indicating various nuances of meaning related to possibility, ability, obligation, and permission. Regular verbs, on the other hand, express actions or events that occur in the past, present, or future.
Q4: What is the main function of modal verbs?
The primary function of modal verbs is to indicate the speaker’s attitude toward the action or state expressed by the main verb. They express various degrees of possibility, necessity, ability, permission, and obligation.
Q5: Give some examples of modal verbs.
Here are some example sentences of modal verbs:
- She can speak English fluently. (Ability)
- Could you please pass the keys? (Polite request)
- I think it will rain tonight. (Prediction)
- She might come to the party later. (Uncertain possibility)
- You ought to apologize for what you said. (Advice)
You may also like:



Leave a Comment