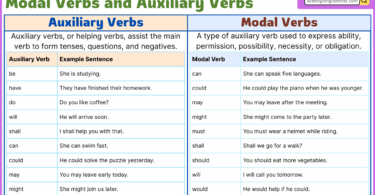
An adverb of time shows when, how long, or how often an action happens. It adds timing to a verb, using words like yesterday, often, or soon. These adverbs help explain the order and frequency of events. Understanding adverbs of time improves sentence accuracy and helps express actions more clearly in daily English. This post simplifies the topic with examples and visuals for better learning.
Table of Contents
What Are Adverbs of Time?
Adverbs of time help us understand when something happens. They tell us about the timing, frequency, or duration of an action. These words answer questions like “When did it happen?” or “How often does it happen?” Some adverbs give exact times—like yesterday, now, or tomorrow. Others describe general time, like soon or later.
For example, in the sentence “She arrived early,” the word early is an adverb of time. It tells us when she arrived.
Below is a list of common adverbs of time with example sentences:
- Now: She is studying French now.
- Yesterday: We went to the park yesterday.
- Tomorrow: We’ll meet tomorrow.
- Soon: The bus will arrive soon.
- Early: I woke up early.
- Late: She arrived late to the party.
- Rarely: I rarely watch TV.
- Later: We can discuss this later.
- Always: He always arrives on time.
- Never: She never misses her morning walk.
Functions of Adverbs of Time
1. Tells Us When Something Happens
These adverbs show the exact time of an action.
Example: I will meet you at the park tomorrow.
2. Tells Us How Often Something Happens
They explain if something happens all the time, sometimes, or just once.
Example: She always brings snacks to the movie night.
3. Tells Us How Long Something Lasts
These adverbs show the duration of an activity.
Example: They played games for hours.
4. Connects Events in Time Order
Some adverbs help connect actions and show what happened first, next, or later.
Example: Afterward, we went for ice cream.
5. Makes the Sentence Clearer
By adding adverbs of time, your sentence becomes more specific and easier to understand.
Example: We’ll start the meeting soon.
Types of Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time are often grouped by what they show — such as when, how long, or how often something happens. Here are the most common and useful types:
1. Simple Adverbs of Time
These words directly point to a specific time when something takes place. They often answer “when” something happened, happens, or will happen.
Examples:
- Now: I am doing my homework now.
- Yesterday: She visited us yesterday.
- Then: We’ll decide then, after the meeting.
- Tonight: We’re staying home tonight.
- Tomorrow: Let’s call them tomorrow.
2. Frequency Adverbs
These adverbs tell us how often an action happens. They answer “how frequently” something occurs and can refer to regular habits or rare events.
Examples:
- Always: He always checks his messages.
- Usually: We usually have dinner at 7.
- Sometimes: I sometimes go for a walk.
- Rarely: She rarely eats junk food.
- Never: I’ve never seen that movie.
3. Duration Adverbs
These words explain how long an action or state continues. They give us a sense of length in time.
Examples:
- Briefly: He paused briefly before speaking.
- All day: They worked all day to finish it.
- For hours: We talked for hours.
- Forever: I’ll remember that moment forever.
- Still: She is still waiting for a reply.
Common Adverbs of Time
- Today: Refers to the current day.
- Soon: Means in a short time from now.
- Always: Signifies at all times.
- Never: Signifies not at any time.
- Tomorrow: Means the day after today.
- Yesterday: Indicates the day before today.
- Now: This refers to the present moment.
- Later: At a subsequent time.
- Yesterday: On the day before today.
- Tomorrow: On the day after today.
- Sometimes: Occasionally, not always.
- Often: Frequently or many times.
- Seldom: Rarely, not often.
- First: Before anything else.
- Last: At the end, After all others.
- Next: Following in order.
- Before: Earlier than a particular time.
- After: Subsequent to a particular time.
- During: Throughout the course of.
- While: At the same time as.
- Today: During the current day.
- Tonight: During the current evening or night.
- Nowadays: In the present period.
- Immediately: Without delay or instantly.
- Until: Up to a particular time.
- Eventually: At some later time.
- Suddenly: Happening quickly and unexpectedly.
- Since: From a specified time until the present.
- Already: Prior to a specified or implied time.
- Always: Without exception or continuously.
List of Adverbs of Time
- Now
- Yesterday
- Today
- Tomorrow
- Later
- Early
- Late
- Soon
- Already
- Still
- Just
- Recently
- Before
- After
- During
- While
- Always
- Currently
- Never
- Often
- Sometimes
- Usually
- Seldom
- Frequently
- Rarely
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly
- Yearly
- Fortnightly
- Annually
- Quarterly
- Early
- Late
- Quickly
- Slowly
- Swiftly
- Lately
- Shortly
- Long
- Short
- While
- Then
- Beforehand
- Suddenly
- Gradually
- Immediately
- Eventually
- Presently
- Constantly
- Continuously
Adverbs of Time Example Sentences
- The phone rang suddenly.
- He finally arrived at the party.
- She has already eaten lunch.
- She rarely eats junk food.
- She always arrives early for class.
- She went to the market yesterday.
- Finish your homework before dinner.
- First, we’ll eat, then we’ll play.
- They often go for a walk in the park.
- Typically, the store closes at 9 p.m.
- I read a book while waiting for the bus.
- Nowadays, people use smartphones.
- We have a family meeting monthly.
- They celebrate their anniversary yearly.
- She finished her homework quickly.
- He finished his homework yesterday.
- They will arrive tomorrow morning.
- Please submit your report before lunch.
- She always takes a walk in the park.
Position of Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time can be placed in different parts of a sentence based on what you want to focus on. Here’s how their position can change the sentence:
1. Before the Main Verb
Placing the adverb here adds time-related detail right after the subject.
Examples:
- She always smiles.
- They will soon leave.
2. At the Beginning of a Sentence
This placement adds emphasis to the time. It’s often followed by a comma.
Examples:
- Yesterday, I went to the park.
- Now, I am studying.
3. At the End of a Sentence
Often used for a natural flow or for stressing when the action happened.
Examples:
- She arrived late.
- We’ll meet tomorrow.
Read More



Leave a Comment