Learning Auxiliary Verbs makes English grammar a lot clearer and less confusing. They help you build different verb tenses and ask questions correctly. By mastering them, you’ll know how to form negatives, questions, and emphatic sentences. This saves you from many small mistakes. You’ll learn the main types and their rules through simple examples. Each example shows how auxiliary verbs work in real sentences. You’ll probably spot errors you didn’t notice before.
Table of Contents
What Are Auxiliary Verbs?
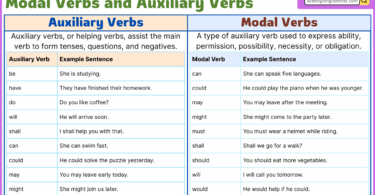
Auxiliary verbs, also known as helping verbs, are verbs that support the main verb in a sentence.

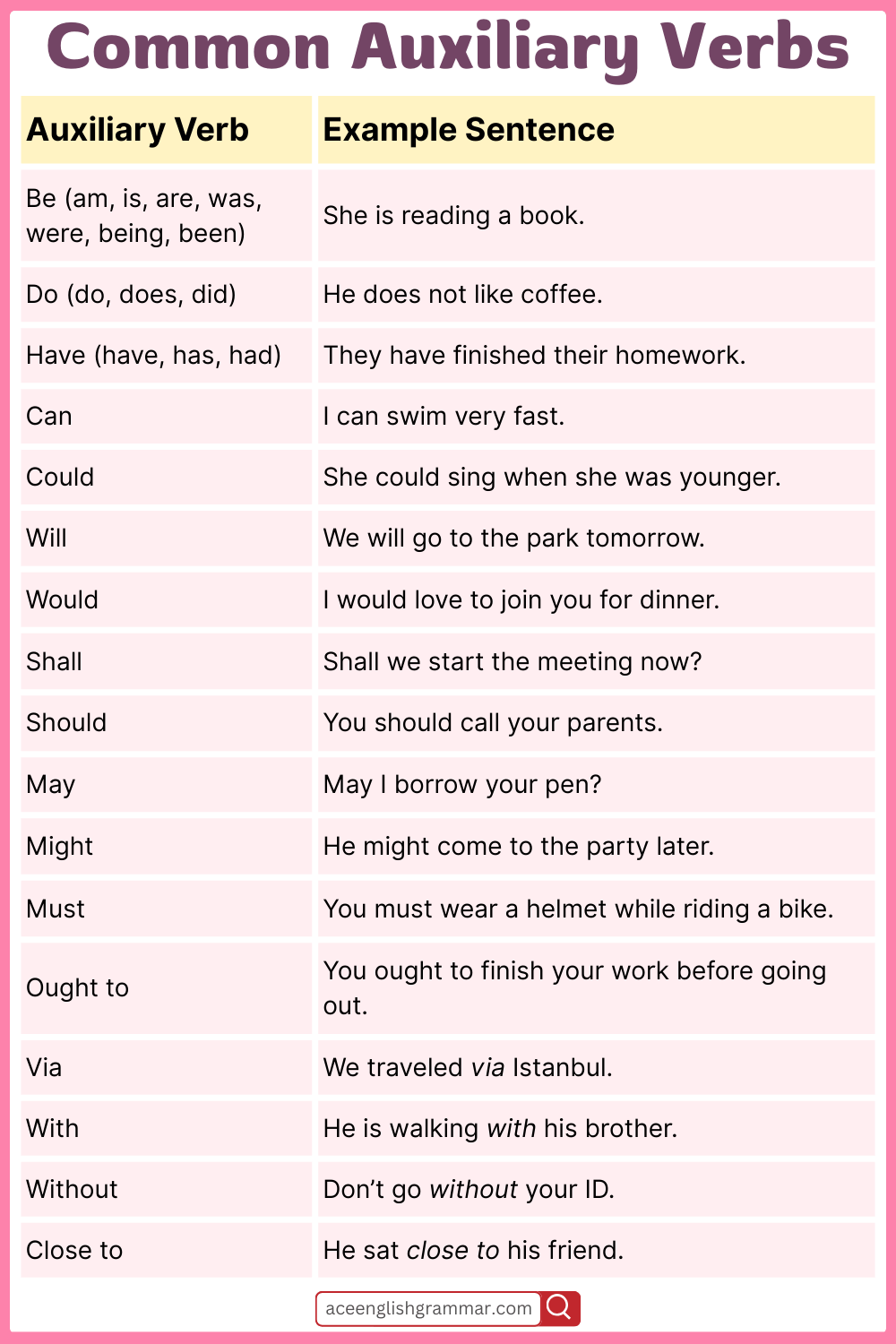
Common Auxiliary Verbs in English
- Be (am, is, are, was, were, being, been)
- Do (do, does, did)
- Have (have, has, had)
- Can
- Could
- Will
- Would
- Shall
- Should
- May
- Might
- Must
- Ought to
Types of Auxiliary Verbs
- Primary Auxiliary Verb
- Modal Auxiliary Verb
- Semi-Auxiliary Verb
1. Primary Auxiliary Verb
These are used to form different tenses, questions, negations, and passive voice. There are three primary auxiliary verbs:
- be (am, is, are, was, were)
- have (have, has, had)
- do (do, does, did)
2. Modal Auxiliary Verb
These express necessity, possibility, permission, ability, or obligation. They do not change for the subject and are followed by the base form of the verb.
- can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, ought to
3. Semi-Auxiliary Verb
These are verbs that function in a similar way to auxiliary verbs but are not considered true auxiliaries. They include have to, get to, used to, going to and more.
Auxiliary Verbs in Different Tenses with Examples
Here’s a chart showing Auxiliary Verbs in different Tenses:
| Tense | Auxiliary Verbs | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | do/does | She does her homework every day. |
| Present Continuous | am/are/is + present participle (-ing) | He is studying right now. |
| Present Perfect | have/has + past participle | They have finished their work. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | have/has been + present participle (-ing) | She has been waiting for an hour. |
| Past Simple | did | I did not go to the party. |
| Past Continuous | was/were + present participle (-ing) | They were playing football yesterday. |
| Past Perfect | had | He had already left when I arrived. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | had been + present participle (-ing) | I had been reading for two hours. |
| Future Simple | will/shall | I will visit you tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous | will be + present participle (-ing) | We will be traveling next week. |
| Future Perfect | will have + past participle | She will have completed the task by 5 PM. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | will have been + present participle (-ing) | They will have been working for 5 years next month. |
Helping Verb vs. Main Verb
| Feature | Helping Verb | Main Verb |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Help form tenses, questions, or negatives | Show the main action or state |
| Examples | am, is, are, do, have, can, might | eat, run, go, see, think |
| Position in Sentence | Always comes before the main verb | Can stand alone in a sentence |
| Example Sentence | She is running. | She runs every morning. |
Auxiliary Verbs Examples
- She is eating dinner.
- I have visited Makkah.
- They will arrive soon.
- We were studying all night.
- She does not like to play outside.
- I am waiting for your reply.
- They did not go to school yesterday.
- You should take care of your health.
- He can speak three languages.
- You might want to check your work again.
- She has finished her project.
- He is planning to visit his family.
- I would love to help you.
- They could be at the park.
- She will join us for dinner.
- I must finish this report by tomorrow.
- We have been waiting for hours.
- He had already left when I called.
- You should see a doctor.
- We will leave after lunch.
- I might go to the gym later.
- She was reading a book when I saw her.
- They were playing football when it started raining.
- I did not enjoy the movie.
- We could meet up this weekend.
- He might be at work.
FAQs
Auxiliary verbs change the meaning by indicating tense, aspect, mood, or voice. For example, “She is studying” shows an ongoing action, while “She has studied” shows a completed action.
Auxiliary verbs help form tenses, questions, and passive voice in English.
No, auxiliary verbs cannot stand alone. They always work with a main verb to form a complete sentence. For example, “She is dancing.” The auxiliary is works with the main verb dancing.
Yes, modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb. They express necessity, ability, permission, or possibility. Examples include can, might, should, and must.
Helping verbs help form different verb tenses and questions, while main verbs express the primary action or state of being. For example, in the sentence “She is reading”, “reading” is the main verb, and “is” is the auxiliary verb.
You might also like