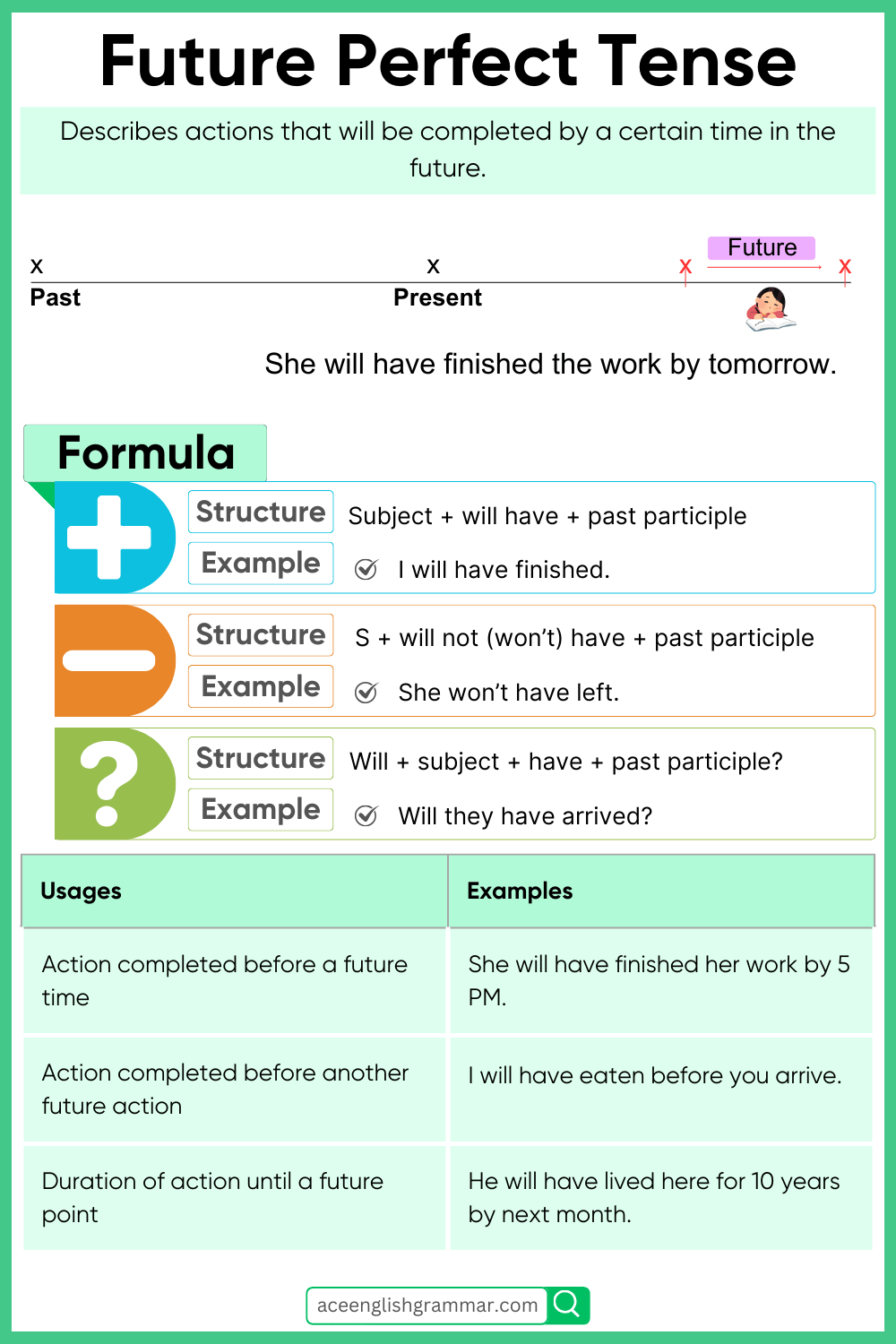
The future perfect tense is used to express actions that will be completed at some point in the future before another specified time or event. The structure is simple: it uses the auxiliary verb “will have” followed by the past participle of the main verb. This tense allows us to discuss actions or events that will be finished before a certain moment in the future.
Table of Contents
What is Future Perfect Tense?
The future perfect tense combines the idea of completion with a future time frame. It’s useful when we want to talk about something that will be done before a specific point in time in the future.
- By 8 PM, I will have finished my homework.
Structure of the Future Perfect Tense
Positive Form(+)
The positive form is used to indicate an action that will be completed in the future. It’s constructed using:
- Subject + will have + past participle of the verb
For example:
- She will have graduated by next year.
- They will have completed the project by the deadline.
In both sentences, the future perfect tense emphasizes that the action will be finished before the specified time.
Negative(-)
The negative form is created by adding “not” after “will,” forming:
- Subject + will not (won’t) have + past participle
This is used to show that an action will not be completed by a specific future time.
For example:
- She won’t have finished the report by tomorrow.
- They will not have started the project before Monday.
These sentences express the lack of completion by a certain future point.
Interrogative Form(?)
To ask questions in the future perfect tense, you invert the subject and “will”:
- Will + subject + have + past participle?
For example:
- Will you have finished the assignment by Friday?
- Will he have arrived by then?
This structure allows you to ask whether something will be completed by a certain time in the future.
When Do We Use the Future Perfect Tense?
1. To show that an action will be completed before a future time or event
- I will have written the article before you arrive.
- She will have cooked dinner by the time the guests come.
2. To talk about the duration of an action up to a point in the future
- By next year, we will have lived here for a decade.
- He will have worked in this company for 20 years.
Time Expressions Used with Future Perfect Tense
| Time Expression | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| By tomorrow | He will have left by tomorrow. |
| By next week | They will have built the wall by next week. |
| By 5 PM | I will have done my homework by 5 PM. |
| Before (event) | We will have eaten before the match starts. |
| In two days | She will have recovered in two days. |
Rules of the Future Perfect Tense
- Formation:
Combine “will” with “have” and the past participle of the verb.
Example: They will have finished the work by 6 PM. - Subject-Verb Agreement:
“Have” remains constant regardless of the subject.
Example: I will have arrived and They will have arrived. - Negation:
Add “not” after “will” to make a sentence negative.
Example: He will not have finished by then. - Questions:
Invert the subject and “will” to form questions.
Example: Will she have completed the task by 10 AM? - Time Expressions:
Use phrases like “by the time,” “before,” or “by next week” to show when the action will be completed.
Example: By tomorrow, they will have found a solution. - Regular and Irregular Verbs:
For regular verbs, add “-ed” to form the past participle (e.g., work → worked). For irregular verbs, the past participle must be memorized (e.g., go → gone).
Examples of Future Perfect Tense
Affirmative (+)
- I will have written three chapters by tomorrow.
- She will have cleaned the kitchen before noon.
- They will have arrived by the time we reach.
- We will have completed the syllabus.
- You will have seen the results.
Negative (–)
- I will not have reached home by 10.
- She will not have completed the task.
- They will not have called you.
- He will not have understood it by then.
- We will not have solved the issue.
Interrogative (?)
- Will you have finished the meal?
- Will she have started the class?
- Will they have built the mosque?
- Will Ahmed have returned home?
- Will we have completed everything?
Common Mistakes and Corrections
- She will have finishes the work. ❌
- She will have finished the work. ✅
- We will have wrote the letter. ❌
- We will have written the letter. ✅
- Will he has gone by then? ❌
- Will he have gone by then? ✅
- I will have buy a car. ❌
- I will have bought a car. ✅
- They will not has arrived. ❌
- They will not have arrived. ✅
Exercises on Future Perfect Tense
Fill-in-the-Blanks
- Zainab ______ (finish) her project by Friday.
- We ______ (not arrive) by 9 PM.
- ______ they ______ (complete) the exam?
- He ______ (read) five books this week.
- I ______ (learn) the dua by then.
Answers:
- will have finished
- will not have arrived
- Will, have completed
- will have read
- will have learned
FAQs
Subject + will have + past participle (V3)
To show that an action will be completed before a specific future time or event.
Future simple talks about actions in the future; future perfect focuses on actions completed before a future time.
Yes, they are commonly used in Future Perfect Tense to mark the future deadline or event.
“Going to have” is not typically used for future perfect; “will have” is preferred for this tense.
Read More




Leave a Comment