Some English verbs don’t need an object to make sense — they stand alone, yet they express full ideas. These are called intransitive verbs. Learning them helps you build clearer sentences and avoid grammar mix-ups. This Intransitive Verbs List shows how they work with movement, time, and even weather.
Table of Contents
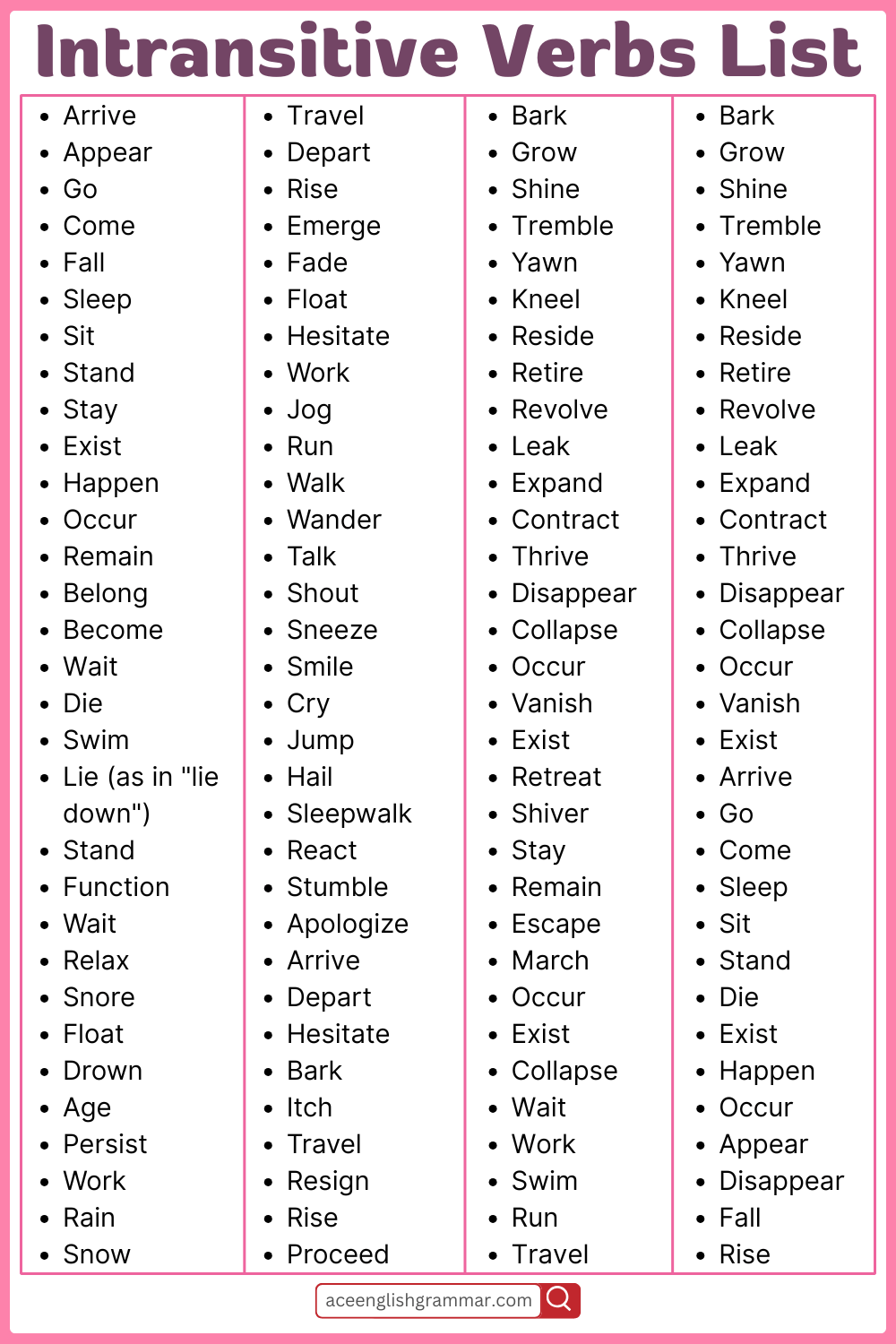
Common Intransitive Verbs List in English
- Arrive
- Go
- Come
- Sleep
- Sit
- Stand
- Die
- Fall
- Appear
- Happen
- Exist
- Laugh
- Cry
- Depart
- Run
- Swim
- Jump
- Rise
- Occur
- Wait
- Walk
- Work
- Grow
- Resign
- Respond
- Stay
- Lie (recline)
- Live
- Escape
- Yawn
- Hesitate
- Wander
- Travel
- Vanish
- Tremble
- Bark
- Cough
- Snore
- Protest
- Explode
- Smile
- Faint
- Retire
- Collapse
- Apologize
- Disappear
- Arrive
- Occur
- Exist
- Wait
Intransitive Verbs for Movement
These verbs describe motion, direction, or position — often used with adverbs or prepositional phrases.
- arrive
- go
- come
- walk
- run
- swim
- travel
- fly
- crawl
- jump
- stand
- lie
- sit
- rise
- fall
- return
- enter
- exit
- stumble
- float
- drift
- slide
- hop
- jog
- climb
Intransitive Verbs with Time or Change
These verbs show change over time — like growth, aging, or shifting states.
- age
- die
- occur
- happen
- begin
- end
- grow
- increase
- decrease
- improve
- worsen
- emerge
- vanish
- appear
- fade
- evolve
- last
- persist
- remain
- stay
- change
- continue
- progress
- recover
- bloom
Intransitive Verbs for Weather and Nature
These describe natural actions or weather conditions and don’t need an object.
- rain
- snow
- hail
- thunder
- storm
- freeze
- melt
- shine
- glow
- erupt
- quake
- tremble
- burn
- flow
- rust
- rot
- fall (leaves, etc.)
- flood
- lightning
- drizzle
100 Intransitive Verbs List with Picture
- Arrive
- Appear
- Go
- Come
- Fall
- Sleep
- Sit
- Stand
- Stay
- Exist
- Happen
- Occur
- Remain
- Belong
- Become
- Wait
- Die
- Swim
- Travel
- Depart
- Rise
- Emerge
- Fade
- Float
- Hesitate
- Work
- Jog
- Run
- Walk
- Wander
- Talk
- Shout
- Sneeze
- Smile
- Cry
- Jump
- Bark
- Grow
- Shine
- Tremble
- Yawn
- Kneel
- Reside
- Retire
- Revolve
- Leak
- Expand
- Contract
- Thrive
- Disappear
- Collapse
- Occur
- Vanish
- Exist
- Lie (as in “lie down”)
- Stand
- Function
- Wait
- Relax
- Snore
- Float
- Drown
- Age
- Persist
- Work
- Rain
- Snow
- Hail
- Sleepwalk
- React
- Stumble
- Apologize
- Arrive
- Depart
- Hesitate
- Bark
- Itch
- Travel
- Resign
- Rise
- Proceed
- Retreat
- Shiver
- Stay
- Remain
- Escape
- March
- Occur
- Exist
- Collapse
- Cough
- Sneer
- Zoom
- Drift
- Exist
- Advance
- Function
- Matter
- Last
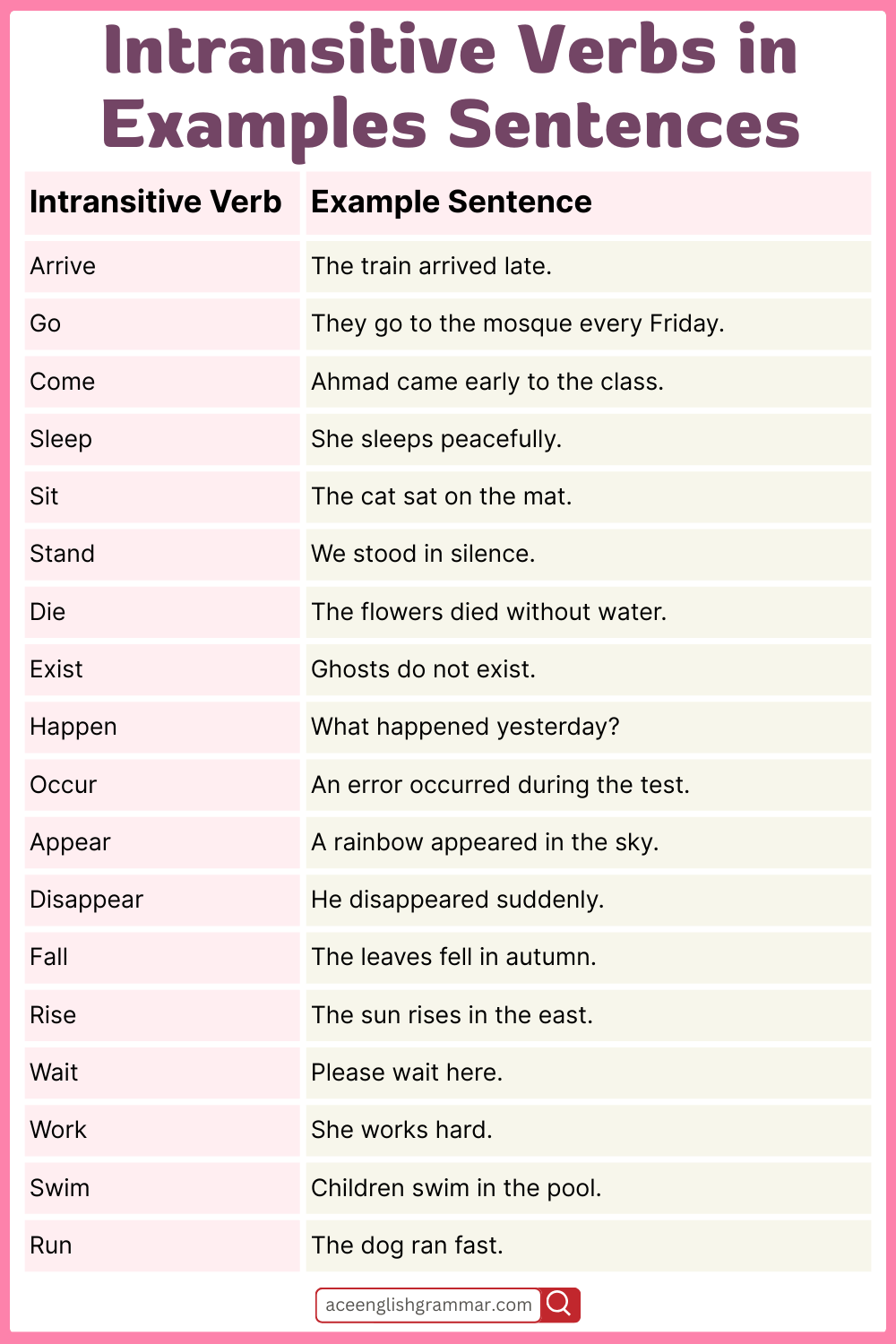
Intransitive Verbs Used in Sentences
These examples show how intransitive verbs work in full sentences. Each verb stands on its own and doesn’t need a direct object.
- He arrived late.
- They went home early.
- She came by bus.
- I walked slowly.
- The baby crawled under the table.
- We swam across the river.
- The plane flew low.
- She ran toward the gate.
- He jumped over the puddle.
- They stood in silence.
- I lay on the grass.
- He sat beside me.
- Prices rose again.
- Leaves fell everywhere.
- She returned yesterday.
- The guests entered quietly.
- He exited quickly.
- The cat stumbled out of bed.
- The balloon floated away.
- Smoke drifted through the air.
- She slid down the hill.
- He hopped into the room.
- They jogged along the trail.
- She climbed slowly.
- He aged well.
- The flower bloomed in spring.
- A problem occurred.
- The meeting began late.
- The light faded slowly.
- It rained all night.
- It snowed for hours.
- Thunder roared above.
- The river flooded.
- He slept deeply.
- They laughed loudly.
FAQs
An intransitive verb is a verb that does not take a direct object. The action ends with the subject or affects the subject itself.
Yes, some verbs can function as both, depending on the sentence.
Example:
Transitive: She runs a business.
Intransitive: She runs every morning.
No, intransitive verbs do not have passive voice because there’s no object to become the subject.
Yes, linking verbs like be, seem, or become are intransitive. They connect the subject to additional information.
Ask “What?” or “Whom?” after the verb. If the answer is missing or doesn’t make sense, it’s likely intransitive.
You might also like


Leave a Comment