Learning Modal and Auxiliary Verbs makes your English grammar strong and flexible. These verbs help you build tenses, questions, and express ability or permission. You’ll learn when to use modals like can and must alongside other auxiliaries. Each section explains rules with simple examples. This knowledge helps you fix common mistakes. By the end, you’ll know how to mix helping verbs confidently.
Table of Contents
What Are Modal Verbs?
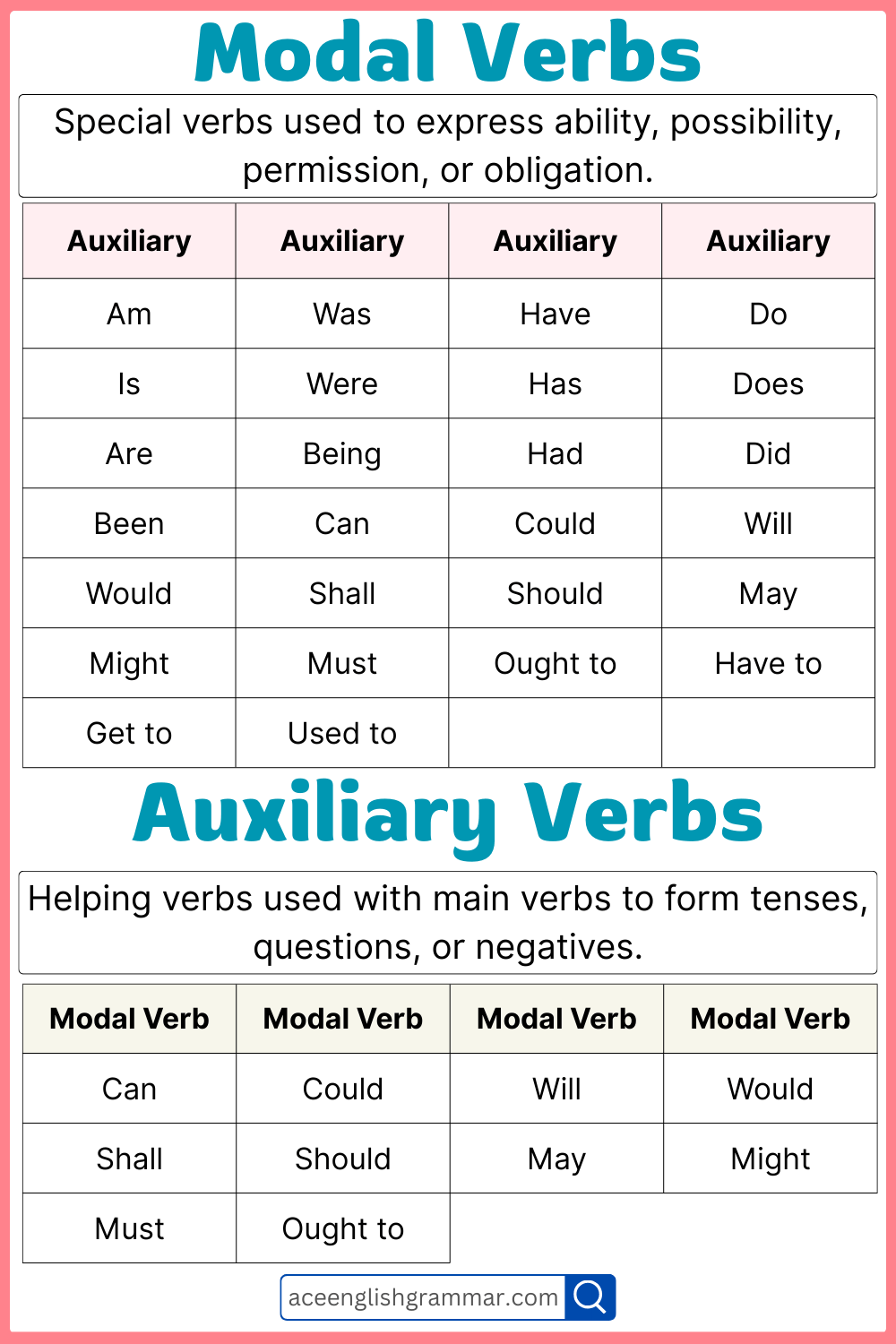
Modal verbs are special helping verbs that show ability, possibility, permission, or necessity. Common modal verbs include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would.
Modal Verbs List
- Can
- Could
- Will
- Would
- Shall
- Should
- May
- Might
- Must
- Ought to
- Need to
- Have to
- Used to
- Be going to
- Be able to
- Be supposed to
- Be allowed to
- Be meant to
- Be likely to
- Dare
What Are Auxiliary Verbs?
Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb used to express ability, permission, possibility, necessity, or obligation. These verbs do not change form for different subjects and are followed by the base form of the main verb.
List of Auxiliary Verbs in English
Primary Auxiliary Verbs
Used to form tenses, voice, and questions.
- Be
- Am
- Is
- Are
- Was
- Were
- Being
- Been
- Have
- Has
- Had
- Having
- Do
- Does
- Did
Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Express ability, possibility, permission, or obligation.
- Can
- Could
- Will
- Would
- Shall
- Should
- May
- Might
- Must
- Ought to
Semi-Modal Verbs
Not always classified as pure auxiliaries but commonly used as helping verbs.
- Need (as in “need not go”)
- Dare (as in “dare not speak”)
- Used to
- Have to
- Be going to
Difference Between Modal and Auxiliary Verbs
| Feature | Modal Verbs | Auxiliary Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Show possibility, necessity, or ability | Help form tenses, questions, or negatives |
| Examples | can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would | be, do, have |
| Used with | Always used with the base form of a verb | Followed by main verb or another auxiliary |
| Change form | Do not change with subject or tense | Often change with subject and tense |
| Stand alone? | Cannot stand alone as full verbs | Can be full verbs (e.g., have, do) |
| Meaning | Add meaning about mood, intent, or possibility | Help structure a sentence grammatically |
| Examples in use | She must go. / He can swim. | She is going. / He has eaten. |
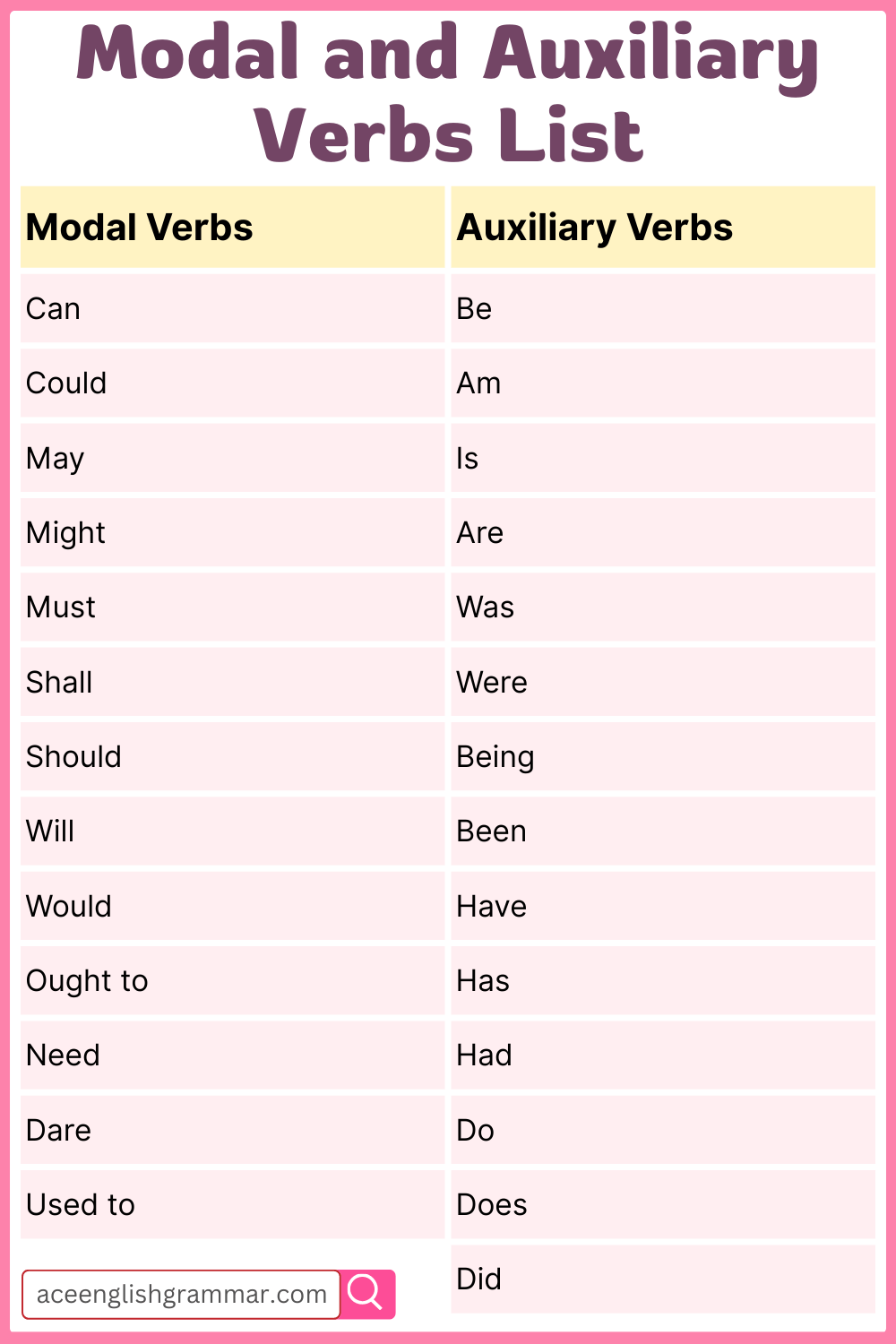
Modal and Auxiliary Verbs List
| Modal Verbs | Auxiliary Verbs |
|---|---|
| Can | Be |
| Could | Am |
| May | Is |
| Might | Are |
| Must | Was |
| Shall | Were |
| Should | Being |
| Will | Been |
| Would | Have |
| Ought to | Has |
| Need | Had |
| Dare | Do |
| Used to | Does |
| Did |
Modal and Auxiliary Verbs in Examples Sentences
Modal Verbs in Sentences:
- You should finish your homework before going out.
- He can swim very well.
- They might come to the party later.
- We must leave immediately to catch the train.
- You could try a different approach to solve the problem.
- I would like to visit you next week.
- She may join us for dinner tonight.
- He will help you with your project.
- They should apologize for their behavior.
- I can speak three languages.
Auxiliary Verbs in Sentences:
- She is playing soccer right now.
- We have finished our work for the day.
- He was reading a book when I called him.
- They are studying for their final exams.
- I am writing an email to my friend.
- They were waiting for the bus when it started to rain.
- He does his homework every evening.
- She has already eaten lunch.
- We did our chores before going out.
- I have been working here for two years.
FAQs
Auxiliary verbs help form tenses, questions, and negatives, such as “be,” “have,” and “do.” Modal verbs express possibility, necessity, or permission, such as “can,” “may,” and “must.”
No, modal verbs do not change form for different subjects. For example, “He can swim” and “I can swim” both use “can” without any change.
Auxiliary verbs help form questions by inverting the subject and the auxiliary verb. For example: “She is coming.” → “Is she coming?”
You might also like