Many English learners struggle when describing two actions that happened in the past. The Past Perfect Tense helps clarify which action occurred first. This blog post helps learn the definition, structure, and usage clearly and effectively.
Table of Contents
What is the Past Perfect Tense?
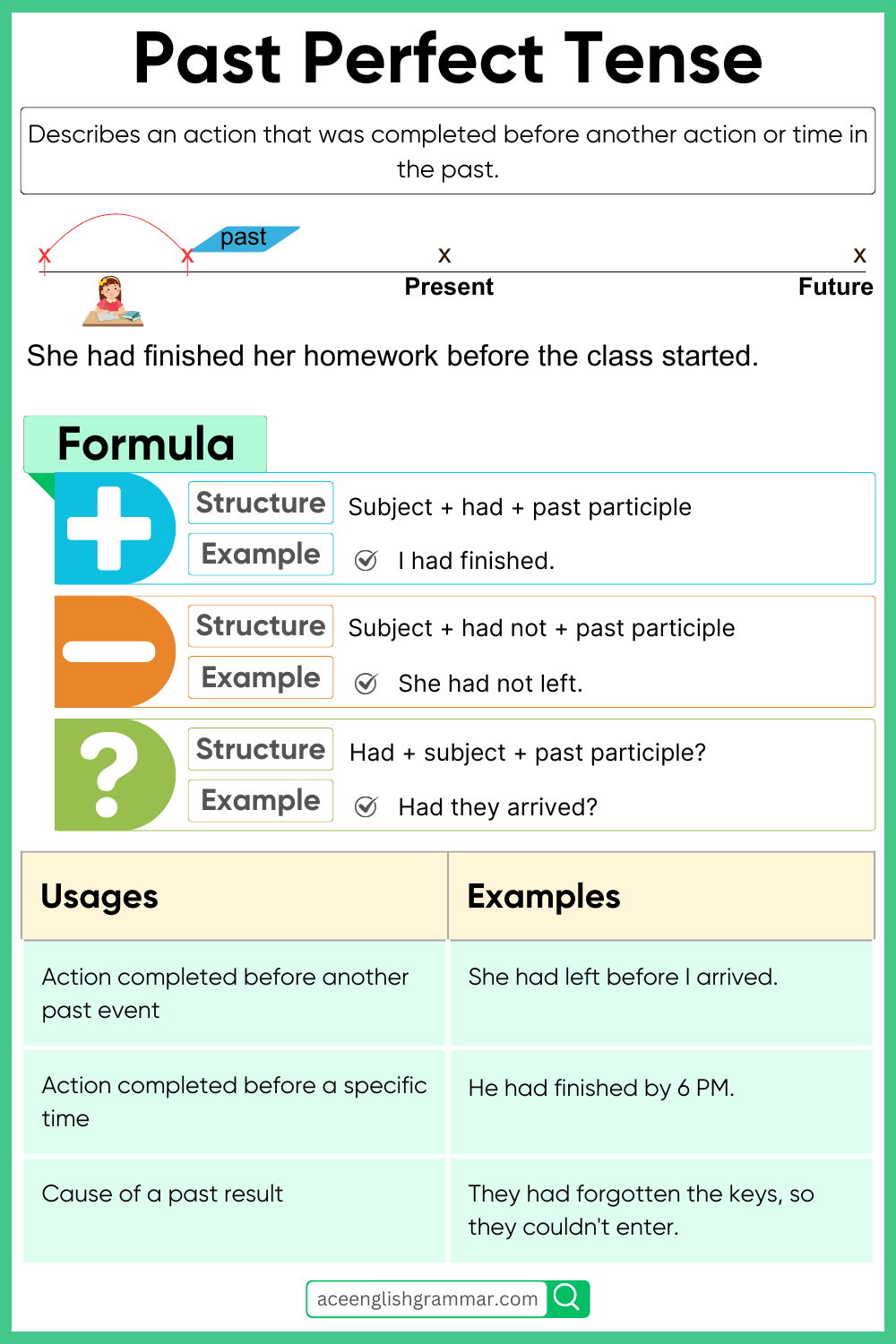
The Past Perfect Tense is a way of showing that something happened before another action or time in the past. It emphasizes the order of events, indicating which occurred first.
Example:
- “By the time I arrived, she had already left.”
This sentence shows that “leaving” happened before “arriving.”
Structure of the Past Perfect Tense
Positive (+)
The structure for positive sentences in the Past Perfect Tense is:
- Subject + had + past participle + object
For example:
- I had finished my homework before dinner.
- They had left before we arrived.
In both sentences, “had” and the past participle of the verb (finished, left) show that these actions were completed before another past action.
Negative (-)
To form negative sentences, add “not” after “had”:
- Subject + had + not + past participle + object
For example:
- She had not seen that movie before.
- They had not finished the project by the deadline.
In these examples, “had not” makes it clear that the actions were not completed before the specific point in the past.
Interrogative (?)
To form yes/no questions, invert the subject and “had”:
- Had + subject + past participle + object?
For example:
- Had you completed the report before the meeting?
- Had they left before it started raining?
This structure helps to ask about whether an action had been completed before another event in the past.
Interrogative (Wh-Questions)
When asking wh-questions, use the following structure:
- Wh-word + had + subject + past participle + object?
For example:
- Where had they gone before I called?
- Why had she left so early?
This allows you to ask questions about specific details regarding what happened first in a series of past events.
When Do We Use the Past Perfect Tense?
1. To show which action happened first in the past
- I had eaten before Bilal arrived.
- She had left before the call came.
2. To explain the reason for a past situation
- He was tired because he had worked all day.
- They were upset because they had lost the match.
3. To describe unreal or imaginary past situations (in conditionals)
- If she had studied, she would have passed.
- I would have helped if I had known earlier.
Time Expressions Often Used with Past Perfect
| Time Expression | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Before | I had prayed before dinner. |
| After | She left after she had packed her bag. |
| By the time | By the time he arrived, I had left. |
| Already | They had already eaten when we came. |
| Just | He had just finished the task. |
Past Perfect vs Present Perfect Tense
Here’s a comparison table for Past Perfect vs Present Perfect Tense — clear, concise, and great for learners:
| Feature | Past Perfect Tense | Present Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Describes an action completed before another action in the past. | Describes an action that happened at an unspecified time before now or started in the past and continues. |
| Structure | Subject + had + past participle (V3) | Subject + has/have + past participle (V3) |
| Time Reference | Refers to before a past event | Refers to before now / up to now |
| Signal Words | before, after, by the time, already (in past context) | just, already, yet, ever, never, since, for |
| Example 1 | Amina had left before the class started. ✅ | Amina has left the room. ✅ |
| Example 2 | They had eaten dinner when we arrived. ✅ | They have eaten dinner. ✅ |
| Incorrect Use | He had gone to the store just now. ❌ | I have done it before he came. ❌ |
| Common Use | Used to show sequence in past events | Used to show past experience or ongoing result |
Examples of Past Perfect Tense
Affirmative (+)
- I had performed Wudu before prayer.
- She had written the letter.
- They had arrived late.
- We had forgotten the keys.
- Aisha had cleaned the room.
Negative (–)
- I had not read the book.
- She had not reached the school.
- They had not completed the test.
- He had not met the teacher.
- We had not checked the result.
Interrogative (?)
- Had you studied before the exam?
- Had she left early?
- Had they finished the work?
- Had Bilal called you?
- Had we discussed the matter?
Common Mistakes and Corrections
- I had went to the market. ❌
- I had gone to the market. ✅
- She hadn’t saw him. ❌
- She hadn’t seen him. ✅
- Had you gave him the money? ❌
- Had you given him the money? ✅
- They had leave the city. ❌
- They had left the city. ✅
- We had wrote the essay. ❌
- We had written the essay. ✅
Past Perfect Tense Exercises
Fill in the blanks:
- Bilal ______ (leave) before the guests arrived.
- We ______ (not eat) anything since morning.
- ______ she ______ (visit) the new school?
- They ______ (complete) the work before deadline.
- I ______ (never see) that place before.
Answers:
- had left
- had not eaten
- Had, visited
- had completed
- had never seen
FAQs
Subject + had + past participle (V3)
Use it to describe an action that was completed before another action or point in the past.
Yes, “had” is the helping verb for all subjects in past perfect tense.
Yes, especially when the context makes the order of actions clear or implied.
No, “had been” is used in Past Perfect Continuous, which shows duration—not just completion.
Read More



Leave a Comment