Phrasal verbs are an essential and often challenging part of the English language. They consist of a main verb and one or more particles (prepositions or adverbs) that together create meanings different from the main verb alone. Understanding these verbs can make your language more expressive and dynamic. This guide will explain what phrasal verbs are, their types, examples, and how to use them effectively.
Table of Contents
What Are Phrasal Verbs?
A phrasal verb is a combination of a main verb and one or more small words (particles) that changes the meaning of the main verb. These combinations are widely used in both informal and formal English and help express actions, states, and concepts in a more nuanced way.
- Turn on: “Turn” means to change direction or position, but “turn on” means to activate something.
- Give up: “Give” alone means to provide, but “give up” means to stop trying.
Phrasal verbs are categorized by their transitivity, separability, and idiomatic meanings.
Common Types of Phrasal Verbs
1. Transitive Phrasal Verbs (Require an Object)
These phrasal verbs need a direct object to complete their meaning. They can be separable or inseparable.
Separable Transitive Phrasal Verbs: The object can be placed between the verb and the particle.
- She turned off the lights or She turned the lights off.
Inseparable Transitive Phrasal Verbs: The object must follow the particle.
- He ran into a friend (cannot say “ran a friend into”).
2. Intransitive Phrasal Verbs (No Object Needed)
Phrasal verb stand alone and do not require a direct object.
- She woke up early.
3. Phrasal Nouns
Some phrasal verbs can transform into nouns by adding an article, often used in formal writing.
- The takeoff was smooth (from “take off”).
4. Idiomatic Phrasal Verbs
These phrasal verbs have idiomatic meanings that aren’t always predictable from the words alone.
- Hold on: Can mean to wait (Please hold on for a moment) or to grip tightly (Hold on to the rail).
Phrasal Verbs with Multiple Meanings
Some phrasal verbs can have different meanings depending on context. For example:
Take off can mean:
- To remove something (She took off her coat).
- To depart (The plane took off on time).
Phrasal Verb Example Sentences
Here are examples of phrasal verb in various contexts:
- Don’t forget to turn off the lights before leaving.
- I woke up at 7:00 a.m. today.
- Can you turn down the music, please?
- He tried to cheer her up with a joke.
- She had to put off her vacation because of work.
Common Particles and Their Meanings
The particle in a phrasal verb often affects the verb’s meaning. Understanding these patterns can help:
Up: Often implies an increase or completion.
- Wake up early tomorrow.
- Speed up the project.
Down: Often indicates a decrease or stopping.
- The rain started to die down.
Out: Can mean revealing or making something public.
- She came out with the truth.
In: Usually indicates inclusion or confinement.
- Bring the groceries in.
On: Implies continuation.
- Carry on with the meeting.
Off: Usually means deactivation or cessation.
- Turn the lights off.
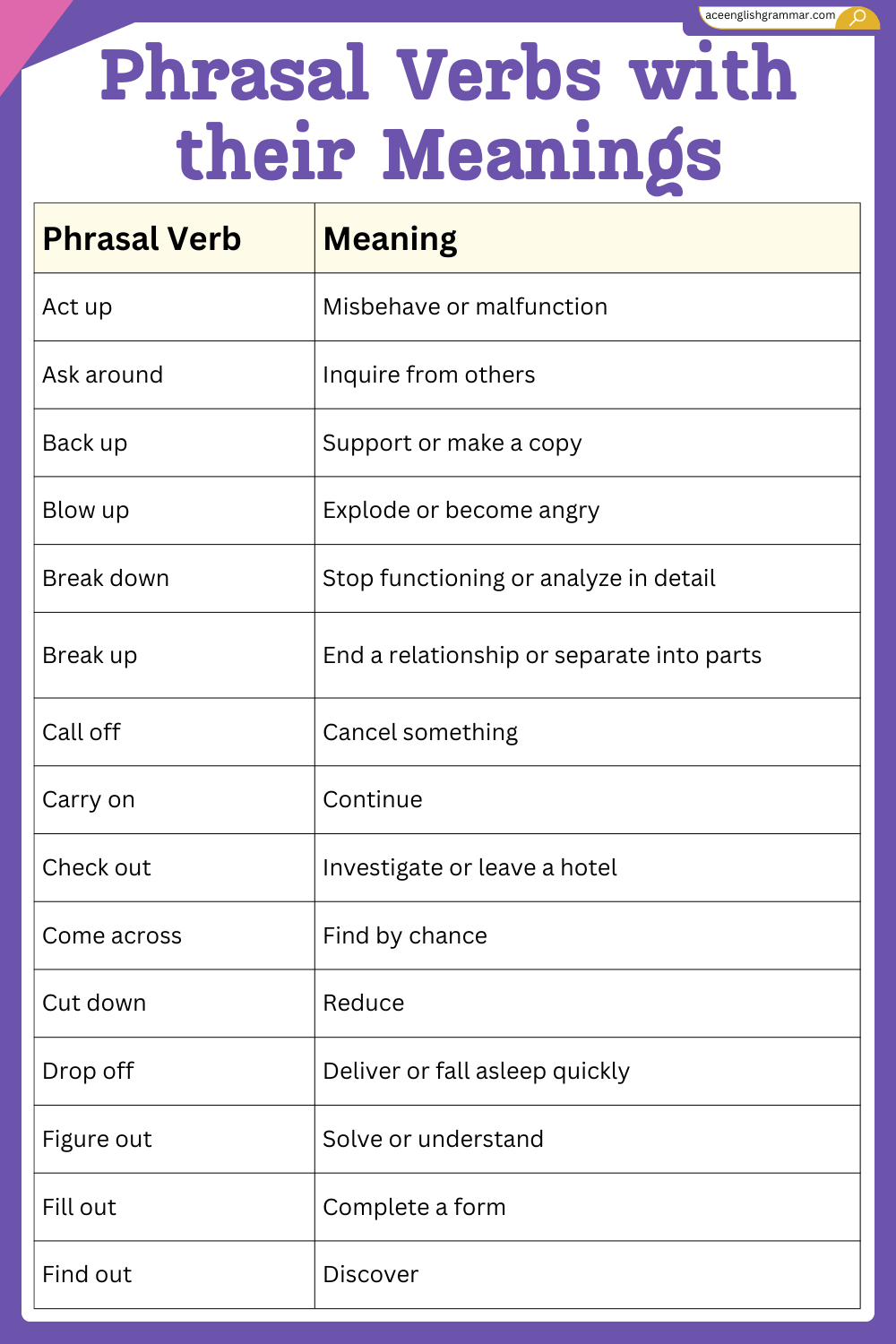
50 Common Phrasal Verbs and Their Meanings
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Act up | Misbehave or malfunction |
| Ask around | Inquire from others |
| Back up | Support or make a copy |
| Blow up | Explode or become angry |
| Break down | Stop functioning or analyze in detail |
| Break up | End a relationship or separate into parts |
| Call off | Cancel something |
| Carry on | Continue |
| Check out | Investigate or leave a hotel |
| Come across | Find by chance |
| Cut down | Reduce |
| Drop off | Deliver or fall asleep quickly |
| Figure out | Solve or understand |
| Fill out | Complete a form |
| Find out | Discover |
| Get along | Have a good relationship |
| Give up | Quit or stop trying |
| Hang out | Spend time socially |
| Hold on | Wait or grip tightly |
| Keep up | Maintain or stay informed |
| Look for | Search for something |
| Pick up | Lift or acquire |
| Point out | Indicate |
| Put off | Postpone |
| Put on | Wear or organize |
| Set up | Arrange or establish |
| Show up | Arrive unexpectedly |
| Take off | Remove clothing or depart |
| Talk over | Discuss |
| Throw away | Discard |
| Turn down | Reject or lower volume |
| Turn off | Deactivate |
| Walk out | Leave or protest |
| Turn up | Arrive unexpectedly or increase |
| Wake up | Stop sleeping |
| Work out | Exercise or solve |
| Back out of | Withdraw from a commitment |
| Bring down | Lower or reduce |
| Call on | Visit or request help |
| Come along | Make progress |
| Cut out | Remove or stop |
| Do without | Manage without something |
| Get over | Recover from an illness or setback |
| Wipe out | Remove completely |
| Go over | Review |
| Hang up | End a phone call |
| Run into | Meet unexpectedly |
| Settle down | Establish a stable routine |
| Show off | Display proudly |
Transitive vs. Intransitive Phrasal Verbs
1. Transitive Phrasal Verb (Require an Object)
A transitive phrasal verb needs a direct object to complete its meaning. Without an object, the sentence would be incomplete.
- Give up → Ayesha gave up smoking. (Object: smoking)
- Turn down → Bilal turned down the offer. (Object: the offer)
- Put off → They put off the meeting. (Object: the meeting)
- Look after → Fatima looks after her sister. (Object: her sister)
- Call off → They called off the wedding. (Object: the wedding)
2. Intransitive Phrasal Verb (Do Not Require an Object)
An intransitive phrasal verb does not need an object to make sense; it stands alone in a sentence.
- Break down → My car broke down on the way.
- Take off → The plane took off at 5 PM.
- Run out → The milk ran out yesterday.
- Grow up → Hamza grew up in Karachi.
- Show up → They showed up late.
FAQs
A phrasal verb is a combination of a verb and a particle (preposition or adverb) that creates a meaning different from the original verb.
Transitive phrasal verb need an object (e.g., She gave up smoking).
Intransitive phrasal verb do not need an object (e.g., The plane took off).
Yes, some phrasal verbs can function as both, depending on the context.
Break up (intransitive): They broke up last year.
Break up (transitive): The teacher broke up the fight.
Some common transitive phrasal verbs include turn down, put off, call off, look after, and give up.
Common intransitive phrasal verbs include break down, take off, run out, grow up, and show up.
Conclusion
Phrasal verb is an essential part of English communication, adding depth and variety to the language. Understanding transitive and intransitive phrasal verb helps in using them correctly in sentences. While transitive phrasal verbs require an object, intransitive ones do not. Mastering these verbs will improve both spoken and written English fluency. Keep practicing, and soon, using phrasal verbs will feel natural!
Read More



Leave a Comment