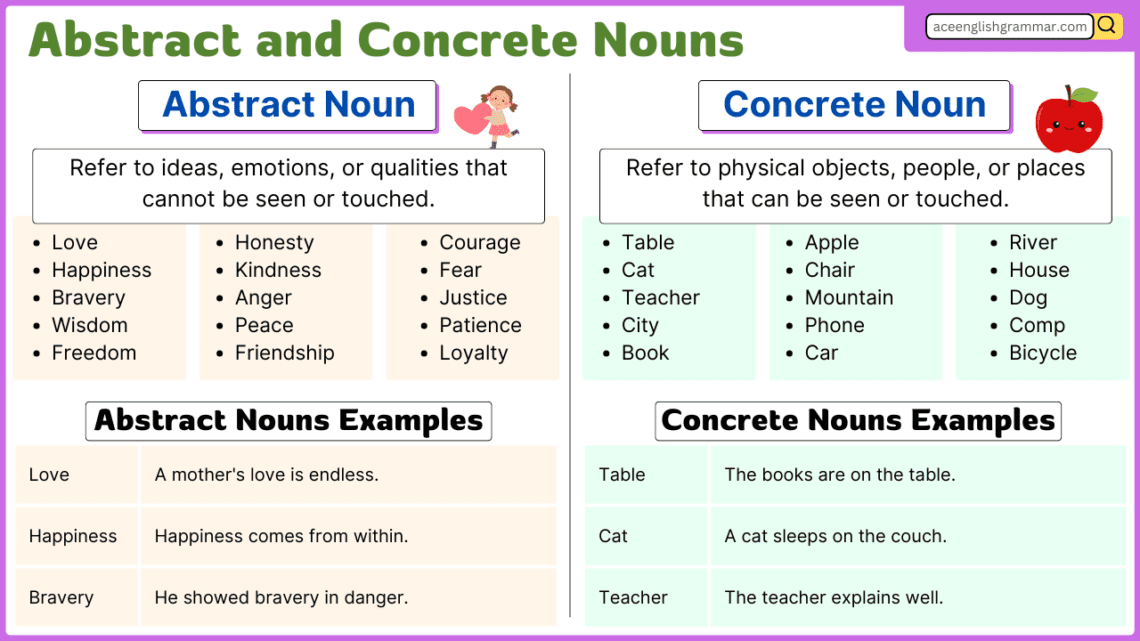
Understanding the difference between abstract nouns and concrete nouns is essential for improving both spoken and written English. Many learners struggle with these concepts, leading to confusion in sentence construction. Abstract nouns refer to intangible ideas and emotions, while concrete nouns name physical things we can see and touch. Mastering this distinction enhances clarity and precision in communication.
Table of Contents
Definition of Concrete and Abstract Nouns
A concrete noun is a noun that refers to something that can be seen, touched, heard, smelled, or tasted. It represents physical objects or things that exist in the real world.
An abstract noun refers to ideas, qualities, emotions, or states that cannot be perceived using the five senses. These nouns represent concepts rather than physical entities.
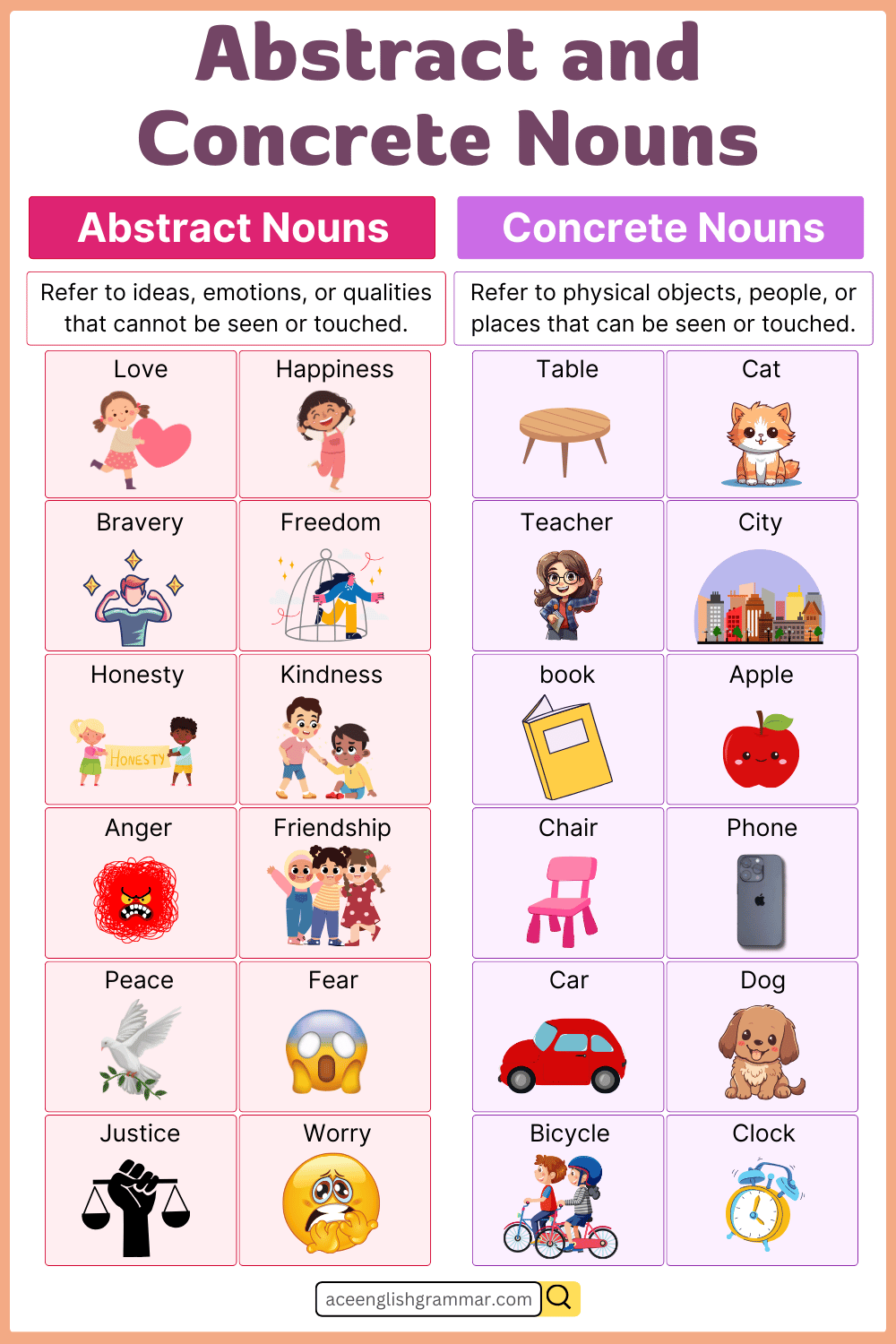
What Are Concrete Nouns?
Concrete nouns name objects or things that exist physically and can be perceived by our senses. These nouns can be categorized based on what they describe.
Types of Concrete Nouns
Common Nouns
Common Nouns are general names for people, places, or things and are not specific to any one entity.
- Teacher
- City
- Book
- Dog
Proper Nouns
Proper Nouns refer to specific names of people, places, or things and always begin with a capital letter.
- Ahmed
- Cairo
- Quran
- Toyota
Countable Nouns
Countable Nouns nouns represent objects that can be counted individually and have singular and plural forms.
- Apple
- Chair
- Bottle
- Car
Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable Nouns refer to substances or concepts that cannot be counted as separate items.
- Water
- Sand
- Air
- Milk
Collective Nouns
Collective Nouns nouns describe a group of people, animals, or things taken as a single unit.
- Team
- Flock
- Bunch
- Family
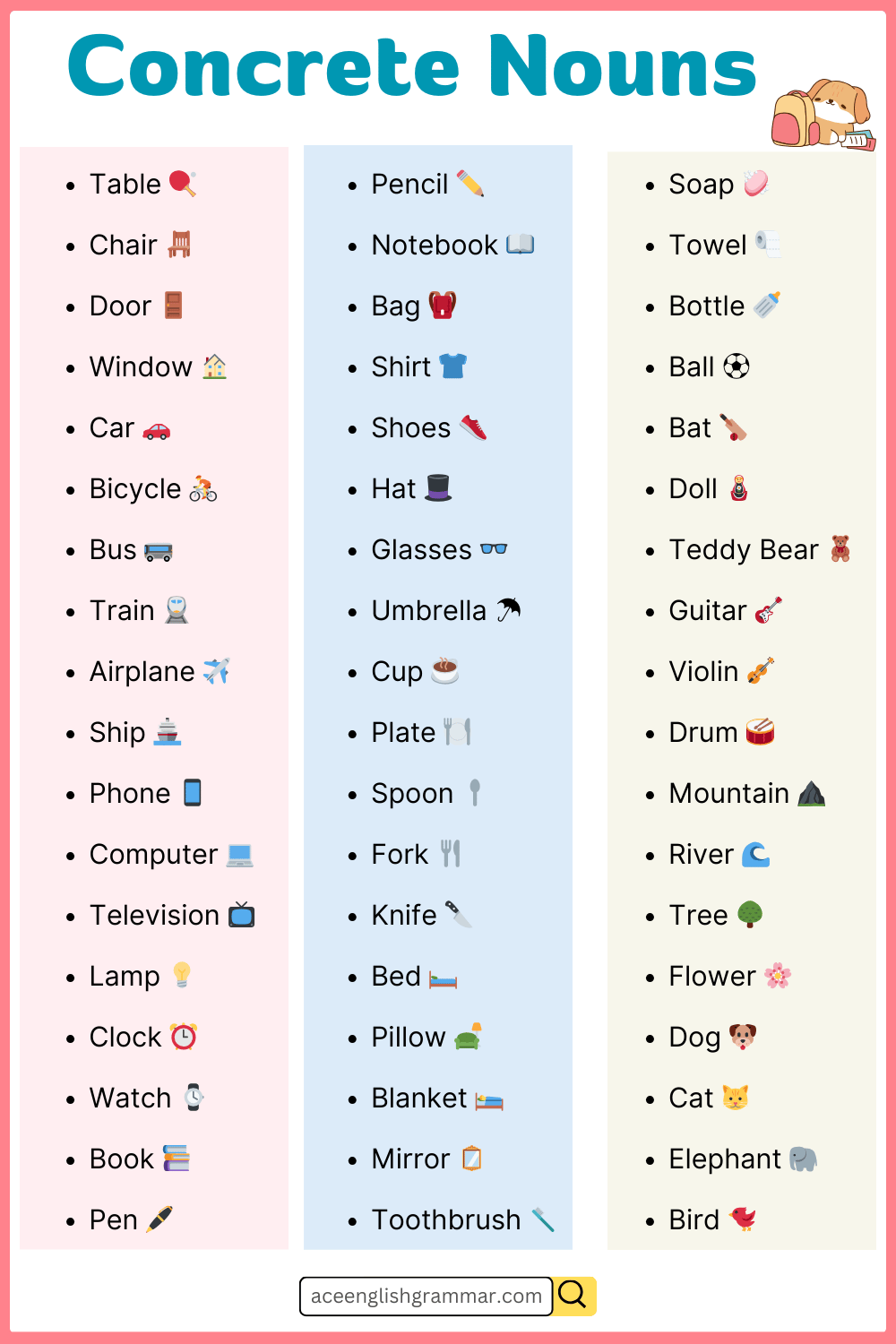
Examples List of Concrete Nouns
- Table
- Computer
- Car
- Tree
- Clock
- Mobile
- Bread
- Lamp
- Shirt
- Bicycle
- Door
- River
- Shoes
- Glass
- Pencil
- Bus
- Wall
- Fork
- Key
- Spoon
Categorical Examples of Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns refer to things we can see, touch, hear, smell, or taste. They include people, places, things, and animals. Below are categorized examples:
People-Based Concrete Nouns
- Mother
- Father
- Ali
- Hassan
- Aisha
- Omar
- Zainab
- Teacher
- Student
- Doctor
Place-Based Concrete Nouns
- Park
- Mosque
- Restaurant
- Garden
- Airport
- Library
- University
- City
- Home
- Farm
Thing-Based Concrete Nouns
- Ball
- Bottle
- Pen
- Clock
- Phone
- Mirror
- Cup
- Book
- Desk
- Chair
Animal-Based Concrete Nouns
- Dog
- Cat
- Cow
- Tiger
- Deer
- Rabbit
- Horse
- Sheep
- Monkey
- Elephant
What Are Abstract Nouns?
Abstract nouns name intangible concepts, including emotions, ideas, states, and qualities. These nouns cannot be touched, seen, or physically experienced.
Types of Abstract Nouns with Examples
Abstract nouns refer to things that cannot be physically seen or touched. They are categorized based on what they represent.
1. Descriptive Abstract Nouns
These nouns describe qualities, characteristics, or attributes.
- Beauty – Her beauty is admired by everyone.
- Bravery – The soldier’s bravery saved many lives.
- Wisdom – His wisdom helped solve the difficult problem.
- Honesty – Honesty is the best policy.
- Strength – The bridge was built with great strength.
2. Conceptual Abstract Nouns
These nouns represent ideas, beliefs, or intellectual concepts.
- Truth – The truth always prevails.
- Justice – Justice must be served for a fair society.
- Freedom – They fought for their freedom.
- Philosophy – He studied philosophy at university.
- Knowledge – Knowledge is the key to success.
3. Experiential Abstract Nouns
These nouns refer to emotions, feelings, or states of being.
- Happiness – His happiness was evident from his smile.
- Sadness – She couldn’t hide her sadness.
- Love – Love brings people together.
- Fear – He overcame his fear of heights.
- Peace – The treaty brought peace to the region.
Examples List of Abstract Nouns
- Love
- Fear
- Hope
- Knowledge
- Truth
- Patience
- Loyalty
- Beauty
- Strength
- Courage
- Justice
- Wisdom
- Determination
- Bravery
- Happiness
- Peace
- Faith
- Jealousy
- Freedom
- Friendship
Categorical Examples List of Abstract Nouns
1. Emotions
Feelings that cannot be touched but are experienced.
- Love
- Anger
- Happiness
- Fear
2. Ideas
Concepts and beliefs that shape thoughts and perspectives.
- Freedom
- Justice
- Democracy
- Knowledge
3. States
Conditions or situations that people or things experience.
- Childhood
- Sleep
- Poverty
- Chaos
4. Qualities
Characteristics or attributes of a person, thing, or idea.
- Honesty
- Kindness
- Bravery
- Intelligence
Key Differences Between Concrete and Abstract Nouns
| Feature | Concrete Nouns | Abstract Nouns |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical objects that can be sensed | Ideas, emotions, or states that cannot be physically perceived |
| Examples | Chair, river, apple, mosque | Love, bravery, freedom, wisdom |
| Usage | Used to describe tangible things | Describes intangible concepts |
Concrete and Abstract Nouns in Sentence Structure
- Concrete Noun: Fatima is reading a book.
- Abstract Noun: Patience is a valuable virtue.
Subject-Verb Agreement Rules
- Concrete nouns usually take singular or plural forms: The book is on the table. / The books are on the table.
- Abstract nouns are mostly uncountable and take singular verbs: Honesty is important in life.
How Abstract and Concrete Nouns Function in a Sentence
- Concrete noun as subject: Ahmed bought a car.
- Abstract noun as subject: Wisdom leads to success.
- Concrete noun as object: She picked up the book.
- Abstract noun as object: He appreciates kindness.
Correct and Incorrect Usage Examples
- She gave me an advices. ❌
- She gave me advice. ✅
- His braver saved the child. ❌
- His bravery saved the child. ✅
Examples of Concrete Nouns in Sentences
- Hassan placed his phone on the table.
- The dog barked loudly in the park.
- Aisha bought a new dress for Eid.
- The river flows through the valley.
Examples of Abstract Nouns in Sentences
- Honesty is the best policy.
- Sara showed great courage in the competition.
- Friendship is more valuable than gold.
- Patience leads to success in life.
Importance of Understanding Abstract and Concrete Nouns
Knowing the difference between abstract and concrete nouns helps in clear communication. Concrete nouns describe physical things we can see, touch, hear, smell, or taste, making descriptions more vivid. Abstract nouns express emotions, ideas, and qualities, helping to convey thoughts and feelings effectively. Understanding both improves vocabulary and makes writing and speech more precise.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Using plural forms for uncountable abstract nouns
- She gave me some knowledges. ❌
- She gave me some knowledge. ✅
- Confusing abstract nouns with adjectives
- She is honesty. ❌
- She is honest. ✅
FAQs
Concrete nouns refer to physical objects, while abstract nouns describe ideas, emotions, or states that cannot be sensed physically.
Yes, some nouns can function as both depending on context. “Light” can be concrete when referring to a lamp but abstract when referring to enlightenment.
Most abstract nouns are uncountable, such as “happiness” and “wisdom,” but some, like “idea” or “decision,” can be countable.
Distinguishing these noun types improves clarity in writing and speaking, making communication more effective.
Yes, when an abstract concept gains a physical representation, like “freedom” symbolized by a flag, it takes a concrete form.
Conclusion
Understanding abstract nouns and concrete nouns is essential for effective communication. Concrete nouns provide clear descriptions of tangible things, while abstract nouns help express emotions, states, and ideas. Mastering their usage improves both writing and speech, making sentences clearer and more meaningful.
Download PDF
This PDF provides a clear explanation of abstract and concrete nouns, their differences, and examples to help learners understand how to use them correctly in English. A great resource for improving grammar skills. Download now for easy learning!
Read More