In English grammar, modal verbs play a crucial role in expressing ideas like ability, permission, obligation, possibility, advice, and more. They are versatile and can change the meaning of a sentence depending on the context. This blog post provides an extensive list of modal verbs and their specific uses, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of how to use them effectively in everyday communication.
Table of Contents
What Are Modal Verbs in English?
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that modify the mood of the main verb in a sentence. They express various meanings, including ability, possibility, necessity, permission, and obligation.
Modal Verbs Examples
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Must
- Shall
- Should
- Will
- Would
Modal Verbs List in English
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Must
- Shall
- Should
- Will
- Would
- Ought to
- Need
- Dare
- Shall
- Will
- Would
- Must
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Need to
- Had better
- Have to
- Used to
- Be able to
- Be supposed to
- Be allowed to
- Have got to
- Be going to
- Be about to
- Be capable of
- Would rather
- Could have
- Might have
- Must have
- Shall not
- Will not
- Would not
- Should not
- Need not
- May not
- Might not
- Cannot
- Could not
- Shouldn’t
- Won’t
- Wouldn’t
- Mustn’t
- Ought not to
- Dare not
- Hadn’t better
- Had better not
- Would rather not
- Had better
- Ought to
- Have to
- Can’t
- Couldn’t
- Should
- Willing to
- Wouldn’t be able to
- Dare not
- Be expected to
- Be likely to
- Be unlikely to
- Wouldn’t mind
- Be prone to
- Wouldn’t be surprised
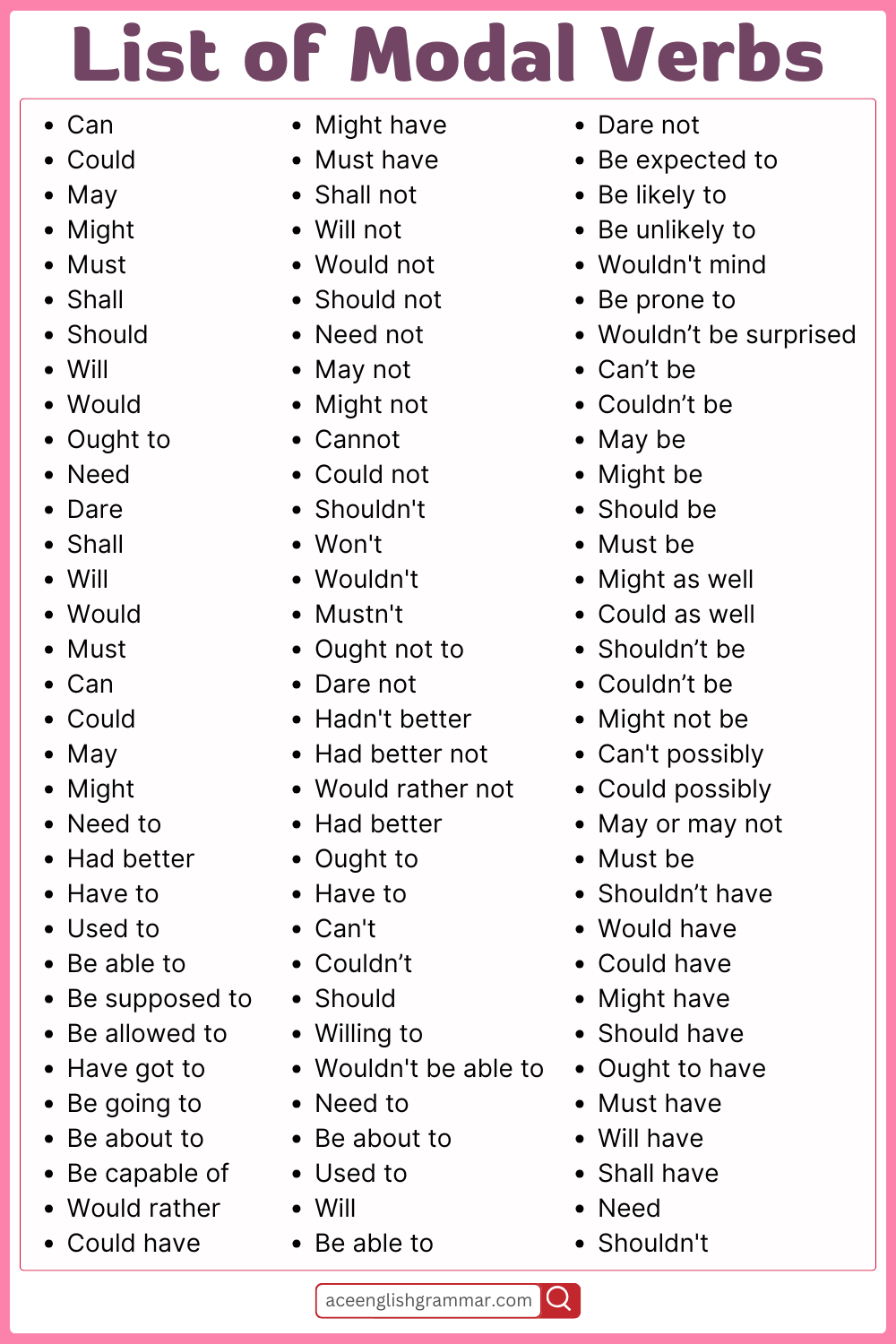
- Can’t be
- Couldn’t be
- May be
- Might be
- Should be
- Must be
- Might as well
- Could as well
- Shouldn’t be
- Couldn’t be
- Might not be
- Can’t possibly
- Could possibly
- May or may not
- Must be
- Shouldn’t have
- Would have
- Could have
- Might have
- Should have
- Ought to have
- Must have
- Will have
- Shall have
Modal Verbs List for Ability
Modal Verbs for Ability are used to express someone’s capacity or skill to do something, either in the present or past.
- Can
- Could
- Be able to
- Be capable of
- Could have
- Be good at
- Can do
Modal Verbs List for Permission
Modal Verbs for Permission are used to ask for or grant permission, or to indicate whether something is allowed or not.
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Can’t
- Couldn’t
- May not
- Might not
- Shall
- Should
Modal Verbs List for Obligation
Modal Verbs for Obligation are used to express necessity, duty, or responsibility to do something. They indicate that something is required or expected.
- Must
- Have to
- Ought to
- Should
- Need to
- Have got to
- Be supposed to
- Must not
Modal Verbs List for Possibility and Probability
Here are the modal verbs expressing possibility or probability:
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Must
- Should
- Would
- Shall
- Will
Modal Verbs List for Advice and Suggestions
Modal Verbs for Advice and Suggestions are used to give recommendations or offer guidance about what someone should or should not do.
- Should
- Ought to
- Had better
- Could
- Might
- Shall
- Would
- Can
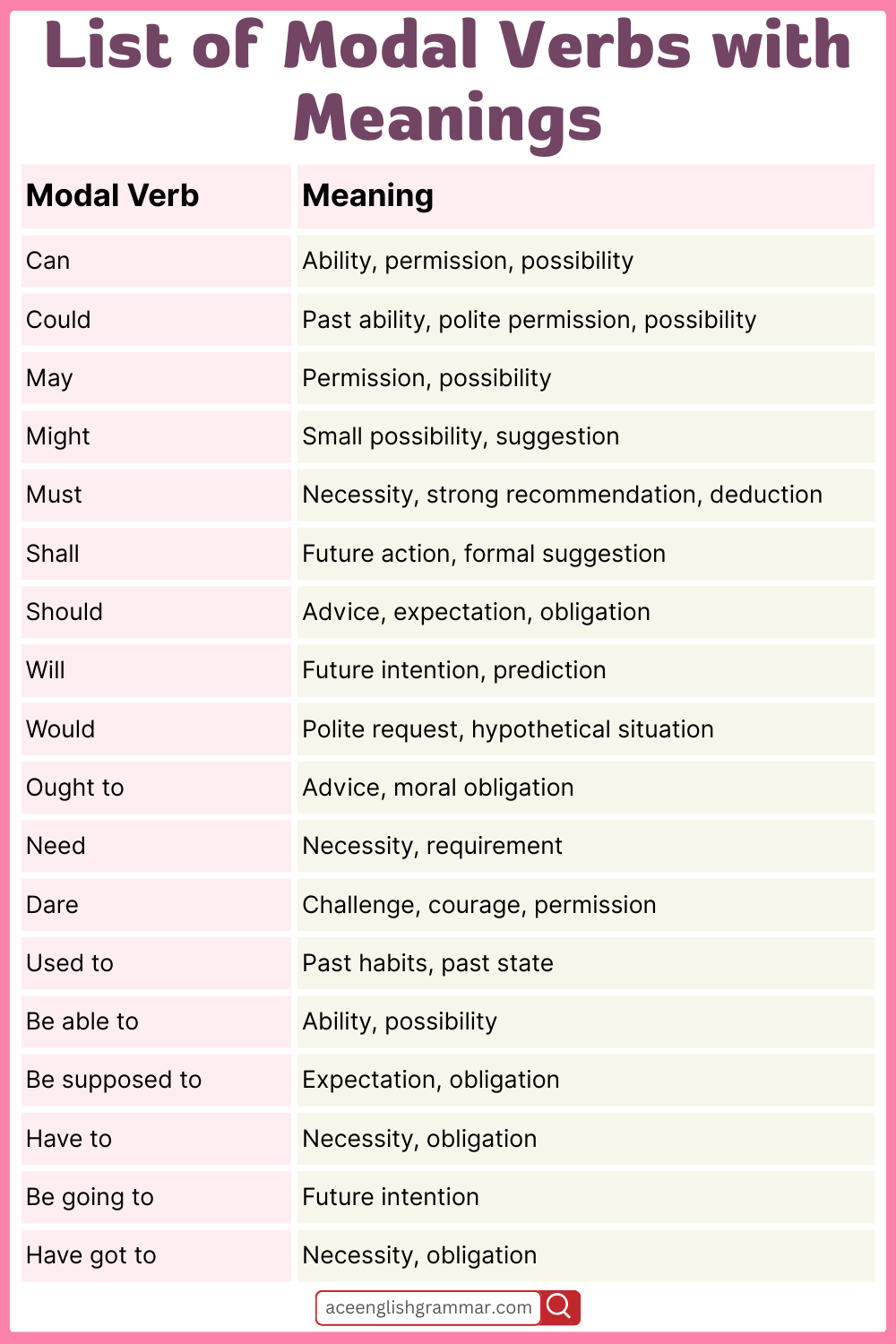
Modal Verbs with Meanings
| Modal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Can | Ability, permission, possibility |
| Could | Past ability, polite permission, possibility |
| May | Permission, possibility |
| Might | Small possibility, suggestion |
| Must | Necessity, strong recommendation, deduction |
| Shall | Future action, formal suggestion |
| Should | Advice, expectation, obligation |
| Will | Future intention, prediction |
| Would | Polite request, hypothetical situation |
| Ought to | Advice, moral obligation |
| Need | Necessity, requirement |
| Dare | Challenge, courage, permission |
| Used to | Past habits, past state |
| Be able to | Ability, possibility |
| Be supposed to | Expectation, obligation |
| Have to | Necessity, obligation |
| Be going to | Future intention |
| Have got to | Necessity, obligation |
| Had better | Advice, suggestion |
| Might as well | Suggestion, reasonable alternative |
| Could have | Past possibility or ability |
| Must have | Deduction, strong certainty |
| Shall not | Prohibition, formal negative future |
| Would rather | Preference |
| Can’t | Impossibility, prohibition |
| Shouldn’t | Prohibition, advice |
| Won’t | Future refusal |
| Wouldn’t | Hypothetical refusal, past refusal |
| Mustn’t | Prohibition, strong obligation |
| Ought not to | Prohibition, advice |
| Dare not | Lack of courage or permission |
| Hadn’t better | Strong advice with negative connotation |
| Have to | Obligation |
| Be allowed to | Permission |
| Wouldn’t be able to | Inability, future refusal |
| Can’t possibly | Strong impossibility |
| Could possibly | Small possibility |
| Must be | Strong assumption, certainty |
| Should be | Expectation, deduction |
| Might as well | Suggestion, reasonable action |
| Could as well | Suggestion, alternative |
| Must have | Deduction, certainty |
| Should have | Past advice, expectation |
| Would have | Hypothetical past |
| Might have | Possibility in the past |
| Couldn’t | Inability (past or present) |
| Should not | Prohibition, advice |
| Will have | Future certainty |
| Might not | Possibility not |
| Can’t possibly | Impossibility in any way |
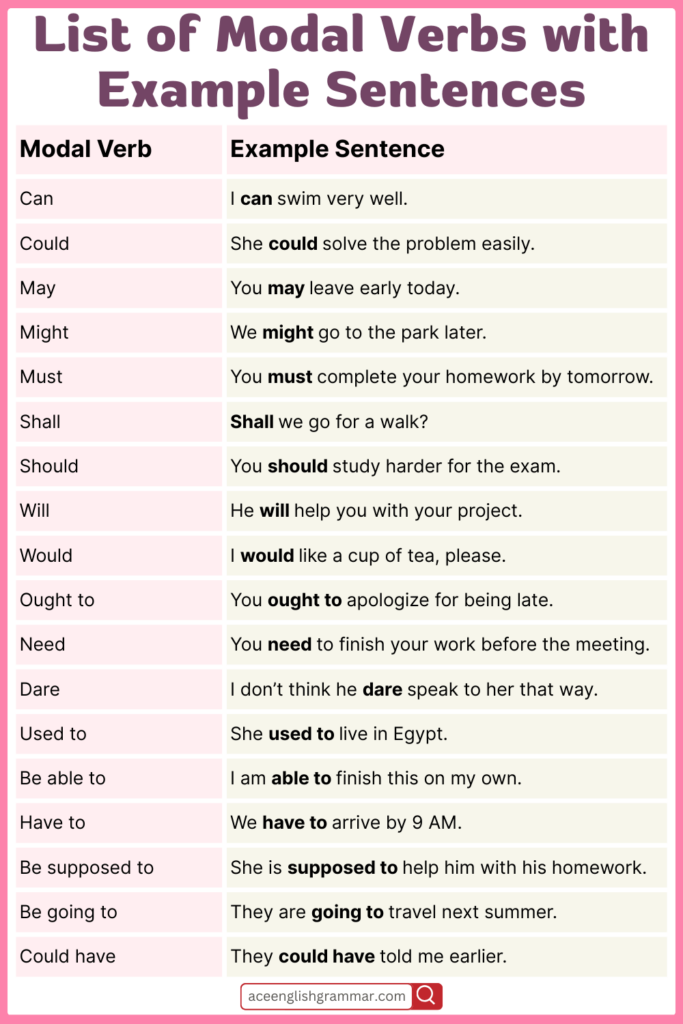
Modal Verbs in Example Sentences
| Modal Verb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Can | I can swim very well. |
| Could | She could solve the problem easily. |
| May | You may leave early today. |
| Might | We might go to the park later. |
| Must | You must complete your homework by tomorrow. |
| Shall | Shall we go for a walk? |
| Should | You should study harder for the exam. |
| Will | He will help you with your project. |
| Would | I would like a cup of tea, please. |
| Ought to | You ought to apologize for being late. |
| Need | You need to finish your work before the meeting. |
| Dare | I don’t think he dare speak to her that way. |
| Used to | She used to live in Egypt. |
| Be able to | I am able to finish this on my own. |
| Have to | We have to arrive by 9 AM. |
| Be supposed to | She is supposed to help him with his homework. |
| Be going to | They are going to travel next summer. |
| Have got to | I have got to meet him today. |
| Had better | You had better bring an umbrella. |
| Might as well | You might as well take the bus. |
| Could have | They could have told me earlier. |
| Must have | She must have forgotten about the meeting. |
| Shall not | We shall not tolerate such behavior. |
| Would rather | I would rather stay home tonight. |
| Can’t | I can’t find my keys. |
| Shouldn’t | You shouldn’t eat too much sugar. |
| Won’t | I won’t be able to attend the meeting. |
| Wouldn’t | He wouldn’t listen to anyone. |
| Mustn’t | You mustn’t cheat in the exam. |
FAQs
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs used to express ability, possibility, permission, necessity, or obligation in a sentence.
There are over 30 commonly used modal verbs in English, but some lists can include more depending on context.
Yes, could is the past tense of can, indicating past ability or polite permission.
Should is used for advice or mild obligation.
Must expresses a strong necessity or requirement.
Common modal verbs in English include can, could, will, would, shall, should, may, might, must, and ought to. These verbs are used to express ability, permission, possibility, necessity, advice, and obligation.
Ten common modal verbs are can, could, will, would, shall, should, may, might, must, and ought to. They express ability, permission, possibility, obligation, advice, and necessity in sentences.
Read More