Many learners struggle when talking about actions that were happening in the past. Was it “I watched TV” or “I was watching TV”? Mixing up past tenses causes confusion in storytelling. This blog post helps learn Past Continuous Tense with practical rules, structure, and real-life examples so you can speak and write with accuracy.
Table of Contents
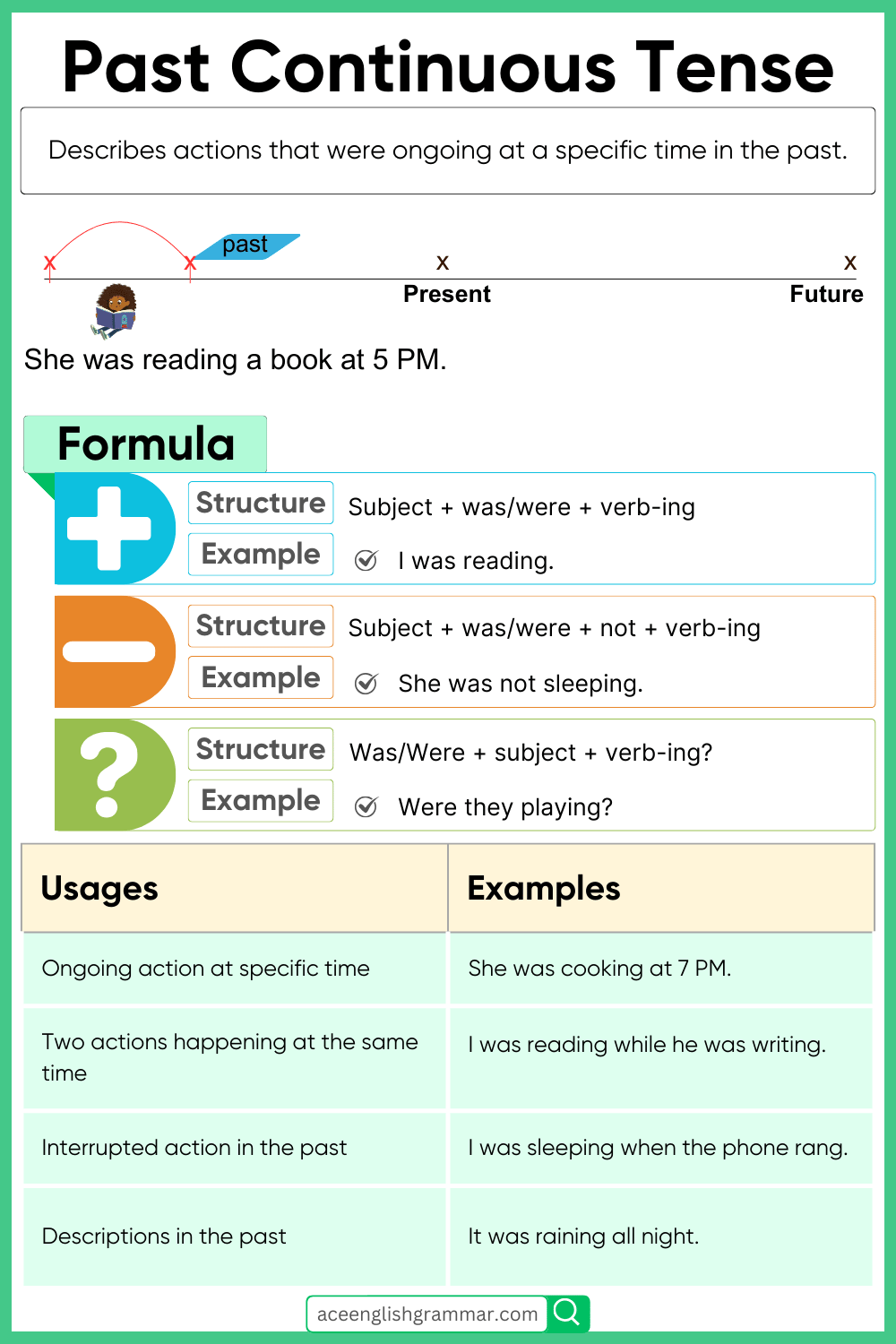
What is Past Continuous Tense?
The Past Continuous Tense (also called Past Progressive Tense) describes an action that was happening at a specific time in the past
- She was reading the Quran.
Usage of “Was” and “Were”
- Was: Used with singular subjects like I, he, she, and it.
- Example: She was reading a book.
- Were: Used with plural subjects like we, they, and you.
- Example: They were playing football.
Even with you, regardless of whether it is singular or plural, we use were.
- Example: You were studying all night.
Structure of the Past Continuous Tense
Positive Sentences (+)
To describe actions in progress in the past:
- Subject + was/were + present participle (-ing form)
Examples:
- I was reading a novel.
- They were playing football.
- She was cooking dinner.
Negative Sentences (-)
To describe actions that were not happening at a specific time:
- Subject + was/were + not + present participle
Examples:
- She was not studying for the test.
- We were not going to the party.
- They were not watching TV.
Interrogative Sentences (?)
To ask about actions in progress in the past:
- Was/Were + subject + present participle?
Examples:
- Were they playing basketball?
- Was she writing an email?
- Were you reading a book?
Negative Interrogative Sentences
To ask negative questions:
- Was/Were + subject + not + present participle?
Examples:
- Weren’t they playing in the park?
- Was she not attending the meeting?
- Were we not going to the party?
When Do We Use Past Continuous Tense?
1. To describe an action in progress at a specific time in the past
At 7 PM, I was praying Maghrib.
She was studying all night yesterday.
2. To describe two actions happening at the same time in the past
- Amina was cleaning while Ahmad was cooking.
- They were laughing while we were walking.
3. To describe a background action in a story
- I was walking to the masjid when I met Haris.
- The kids were playing when it started raining.
Common Time Expressions in Past Continuous Tense
| Expression | Example |
|---|---|
| At 5 PM | I was driving at 5 PM. |
| All evening/morning | They were studying all morning. |
| While / When | While she was cooking, I was setting the table. |
| Yesterday at [time] | He was sleeping yesterday at 10 PM. |
| During the lecture | We were talking during the lecture. |
These expressions help establish the timeframe in which the action was happening.
Rules of Past Continuous Tense
- Structure: Combine was/were with the -ing form of the main verb.
- I was studying all day.
- Negative Form: Use not after was/were to form negatives.
- They were not working yesterday.
- Questions: Invert was/were and the subject to form questions.
- Were you playing football?
- Non-Action Verbs: Avoid using this tense with non-action verbs like know, believe, or want.
Past Continuous vs Future Continuous
Here’s a short comparison table for Past Continuous vs Future Continuous:
| Aspect | Past Continuous | Future Continuous |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing action at a specific time in the past. | Ongoing action at a specific time in the future. |
| Structure | Subject + was/were + verb-ing | Subject + will be + verb-ing |
| Example | Fatima was reading at 8 PM. ✅ | Fatima will be reading at 8 PM. ✅ |
| Time Reference | Specific past moment | Specific future moment |
| Signal Words | while, when, as | at this time tomorrow, next week at 5 PM |
Examples of Past Continuous Tense
✅ Affirmative
- Bilal was walking to the mosque.
- They were playing cricket after Asr.
- I was reading a book yesterday.
- We were eating together.
- Amina was learning French.
❌ Negative
- I was not watching TV last night.
- They were not listening to the teacher.
- She was not preparing food.
- We were not coming to the event.
- Hamid was not driving fast.
❓ Interrogative
- Was she reciting the Quran?
- Were they doing homework?
- Was Ali talking on the phone?
- Were we playing too loudly?
- Was Fatima helping her mother?
Common Mistakes and Corrections
- He was play football. ❌
- He was playing football. ✅
- They was eating biryani. ❌
- They were eating biryani. ✅
- Was you coming home? ❌
- Were you coming home? ✅
- I was not go to school. ❌
- I was not going to school. ✅
- She were working late. ❌
- She was working late. ✅
Practice Exercises
Fill in the blanks:
- She ______ (sleep) when the call came.
- We ______ (not watch) TV last night.
- ______ they ______ (study) together?
- Zoya ______ (cook) while her brother ______ (read).
- I ______ (write) my essay yesterday.
Answers:
- was sleeping
- were not watching
- Were, studying
- was cooking, was reading
- was writing
FAQs
Subject + was/were + verb+ing
To describe actions that were ongoing at a specific time in the past.
No, use “was/were” instead of “did.”
Yes, it’s the correct form.
Past continuous describes ongoing past actions, while past simple shows completed past actions.
Read More



Leave a Comment