In English grammar, prepositional phrases are a fundamental part of sentence structure, providing additional details about time, location, direction, and relationships between objects. Understanding how to use prepositional phrase correctly will enhance both your writing and speaking skills, helping you form more precise and meaningful sentences.
Table of Contents
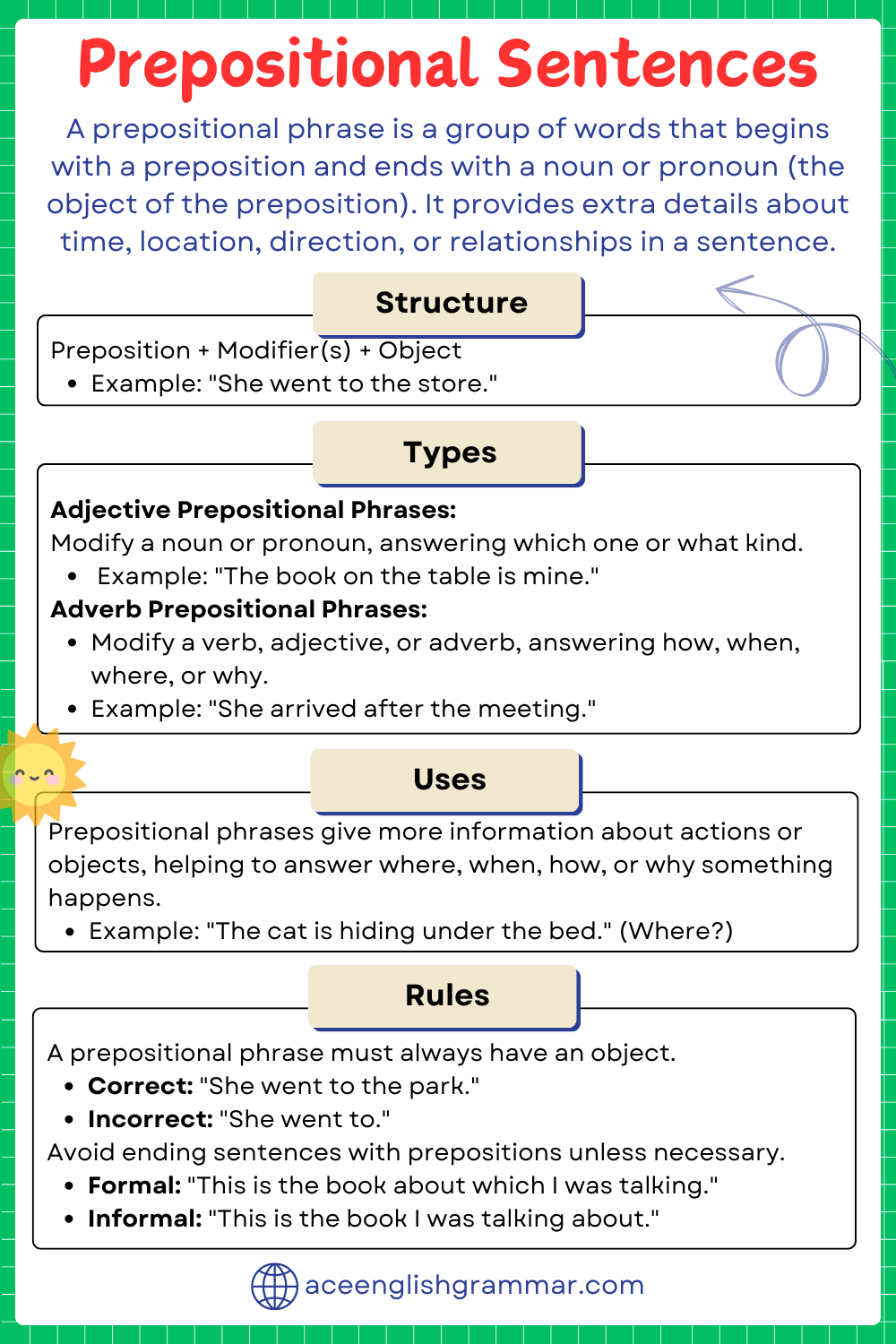
What is a Prepositional Phrase?
A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition followed by a noun or pronoun (the object of the preposition), along with any modifiers. Prepositional phrases add context to sentences by answering questions like where, when, how, and why.
Example:
“The book is on the table.”
- Preposition: on
- Object of the preposition: the table
In this example, the prepositional phrase on the table describes the location of the book.
Structure of a Prepositional Phrase
The basic structure of a prepositional phrase follows this pattern:
- Preposition + Modifier(s) + Object
The preposition shows the relationship between the object and another element in the sentence, while the modifier provides additional detail about the object.
Example:
“She went to the store.”
- Preposition: to
- Object: the store
Types of Prepositional Phrases
Prepositional phrases can be categorized into two main types based on the function they serve in a sentence:
1. Adjective Prepositional Phrases
These phrases modify a noun or pronoun, answering questions like which one or what kind.
- “The book on the shelf is mine.”
(The phrase on the shelf modifies the noun book.)
2. Adverb Prepositional Phrases
These phrases modify a verb, adjective, or adverb, answering questions like how, when, where, or why.
- “She arrived after the meeting.”
(The phrase after the meeting modifies the verb arrived.)
Common Prepositions Used in Prepositional Phrases
Here are some common prepositions often seen in prepositional phrases:
- Location: on, in, at, between, among, beside
- Direction: to, toward, into, from, through
- Time: after, before, during, since, until
- Other Relationships: about, for, with, without, concerning
Rules for Using Prepositional Phrases
Keep Prepositions Connected to Objects
A prepositional phrase must always have an object, and the preposition should directly relate to it.
- Incorrect: She went to.
- Correct: She went to the park.
Avoid Dangling Prepositions
Try to place prepositions with their objects and avoid leaving them at the end of the sentence unless necessary.
- Acceptable: This is the book I was talking about.
- More formal: This is the book about which I was talking.
Prepositions and Verb Agreement
Prepositions should not interfere with the subject-verb agreement. The verb should match the subject, not the object of the preposition.
- Incorrect: The box of books were heavy.
- Correct: The box of books was heavy.
How Prepositional Phrases Enhance Writing
Prepositional phrase is used to provide specific information, improve clarity, and add depth to sentences. They can describe where an action takes place, when something occurs, or why something happens.
Examples:
- “The cat is hiding under the bed.”
- “They met before the movie.”
- “He completed the project with great effort.”
Each phrase answers a different question, providing essential details.
Read More