English learners often get confused when describing past actions that still affect the present. Do you say “I did” or “I have done”? Many misuse the Present Perfect Tense without realizing its true purpose. This blog post helps learn Present Perfect Tense with clear rules, structure, usage tips, and examples for better understanding and correct usage.
Table of Contents
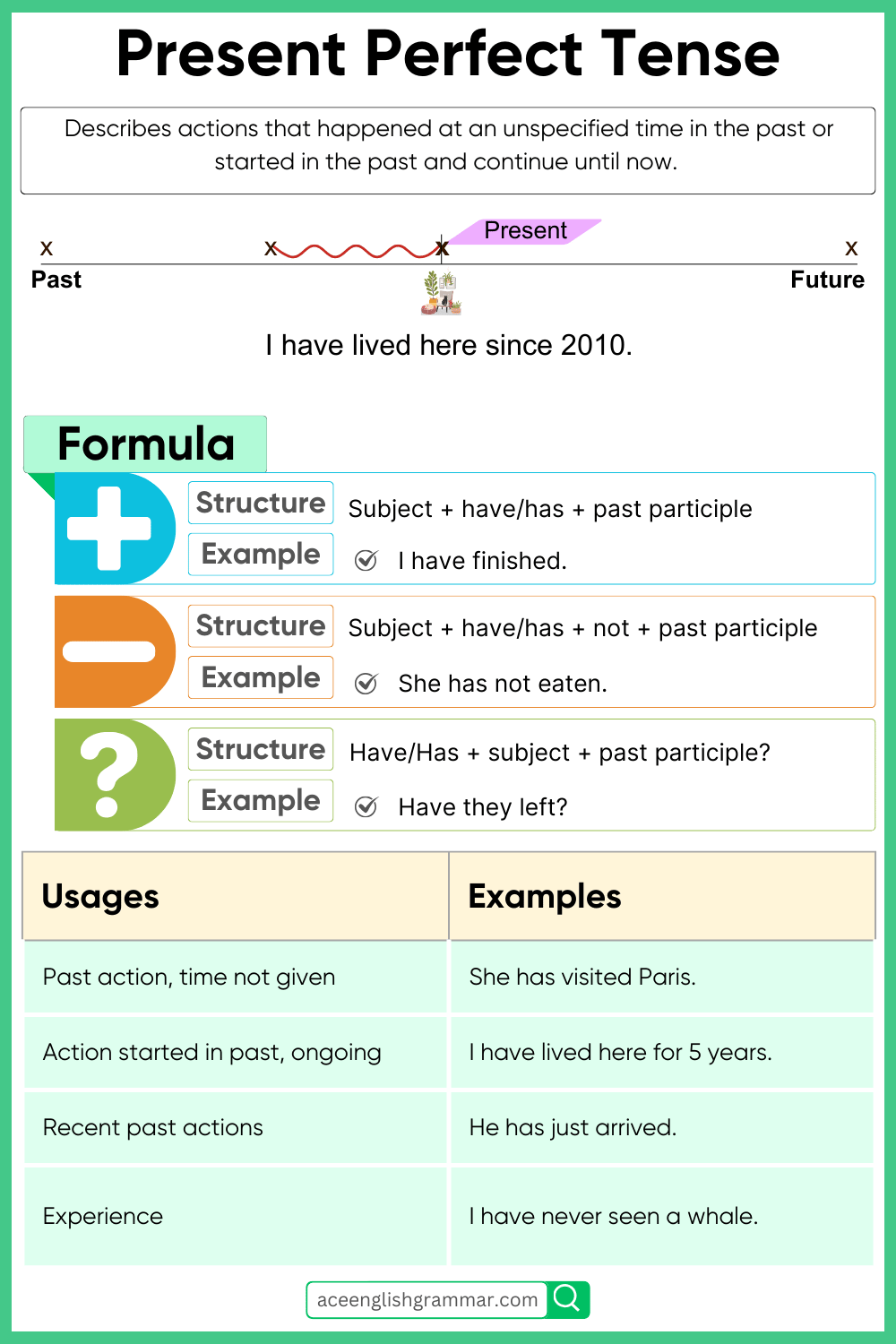
What is the Present Perfect Tense?
The Present Perfect Tense refers to actions or events that happened at some point in the past but still have importance now. It emphasizes the connection between the past and present.
I have not completed the assignment.
Structure of Present Perfect Tense
Positive Sentences (+)
The basic structure for positive sentences in the Present Perfect Tense is:
- Subject + have/has + past participle
For example:
- I have completed my homework.
- She has visited the museum.
In these examples, “have” or “has” is combined with the past participle to show that the action is completed and relevant now.
Negative Sentences (-)
In the negative form, add “not” after “have” or “has”:
- Subject + have/has + not + past participle
For example:
- I have not traveled abroad.
- He has not finished his dinner.
These examples emphasize that the action has not occurred up to the present moment.
Interrogative Sentences (?)
To ask questions, invert “have” or “has” with the subject:
- Have/has + subject + past participle?
For example:
- Have you finished your homework?
- Has she visited the Eiffel Tower?
This structure helps inquire about completed actions that are still relevant now.
Use of “Has” and “Have” in Present Perfect Tense
The choice between “has” and “have” depends on the subject of the sentence:
- “Has” is used with singular subjects such as he, she, it, and singular nouns.
- She has completed her project.
- “Have” is used with plural subjects such as I, you, we, they, and plural nouns.
- They have finished the assignment.
Rules of Present Perfect Tense
- Formation:
Use “have” or “has” + past participle.- I have studied English for two years.
- Past Participle:
For regular verbs, the past participle is formed by adding “-ed” (e.g., played, worked). Irregular verbs have their own forms (e.g., eaten, gone). - Use with Unspecified Time:
The Present Perfect Tense is often used when the exact time of the action is not mentioned or important.- She has visited New York (but we don’t know exactly when).
- Negatives and Questions:
For negatives, use “not” after “have/has.” For questions, invert “have/has” and the subject.- He has not seen the movie.
- Have they completed the task?
When Do We Use Present Perfect Tense?
1. To talk about actions that happened in the past but affect the present
- I have lost my keys. (Still lost now)
- She has broken her phone. (It’s still broken)
2. To describe life experiences (without mentioning time)
- We have travelled to Madinah.
- Amina has learned Arabic.
3. To describe repeated actions until now
- He has visited the doctor three times.
- I have called him many times.
4. To describe actions that just happened (with “just”, “already”, etc.)
- She has just arrived.
- They have already eaten.
Common Time Expressions Used
| Expression | Example |
|---|---|
| Just | She has just prayed. |
| Already | They have already finished the work. |
| Yet | Have you eaten yet? |
| Ever | Have you ever visited Makkah? |
| Never | I have never seen that before. |
| Since | I have lived here since 2020. |
| For | He has studied for 2 years. |
Examples of Present Perfect Tense
Affirmative (+)
- I have read the Quran today.
- She has written five pages.
- We have completed the task.
- Amina has cleaned her room.
- They have reached the masjid.
Negative (–)
- I have not seen the result.
- He has not replied to the message.
- They have not joined the class.
- We have not met him yet.
- Zaid has not taken the medicine.
Interrogative (?)
- Have you finished your homework?
- Has she called her mother?
- Have they visited the new house?
- Has Bilal prepared for the exam?
- Have we paid the bill?
Present Perfect vs Past Perfect Tense
Here’s a refined and clear comparison table for Present Perfect vs Past Perfect Tense, perfect for learners and visually digestible:
| Aspect | Present Perfect Tense | Past Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Describes an action that happened at an unspecified time before now or started in the past and continues. | Describes an action that was completed before another action in the past. |
| Structure | Subject + has/have + past participle (V3) | Subject + had + past participle (V3) |
| Time Reference | Connects past with present | Refers strictly to the past before another past event |
| Signal Words | just, already, yet, ever, never, since, for, recently | before, after, when, by the time, already (in past context) |
| Example 1 | Zainab has finished her homework. ✅ | Zainab had finished her homework before sunset. ✅ |
| Example 2 | They have lived in Lahore since 2020. ✅ | They had lived in Lahore before they moved to Karachi. ✅ |
| Incorrect Use | He has gone to school before I woke up. ❌ | I had seen that movie just now. ❌ |
| Usage Focus | Present result, experience, or continuity | Past completion before another past point |
Common Mistakes and Corrections
- She has went to the market. ❌
- She has gone to the market. ✅
- I have saw him today. ❌
- I have seen him today. ✅
- Has you completed it? ❌
- Have you completed it? ✅
- They have did their work. ❌
They have done their work. ✅
- We has finished the class. ❌
- We have finished the class. ✅
Present Perfect Tense Exercises
Fill in the blanks:
- She ______ (not complete) her task yet.
- ______ you ever ______ (visit) Makkah?
- They ______ (call) us already.
- He ______ (just leave) the room.
- I ______ (study) English for two years.
Answers:
- has not completed
- Have, visited
- have called
- has just left
- have studied
FAQs
Subject + has/have + past participle (V3)
Past simple is used for completed actions at a specific time. Present perfect connects past actions to the present.
No, “yesterday” refers to a finished time. Use past simple instead.
Yes. “Have been” is used for experiences or passive voice (e.g., I have been to Dubai).
Yes. Example: She has just arrived.
Read More



Leave a Comment