Personal pronouns replace specific nouns to make sentences clearer and less repetitive. Words like I, you, he, she, it, we, and they help identify people, places, or things without repeating names. Many learners struggle with subjective, objective, and possessive forms, leading to confusion. This blog post helps learn personal pronoun with definitions, types, rules, and examples to improve English grammar skills.
Personal pronouns replace specific nouns, referring to people or things without repetition.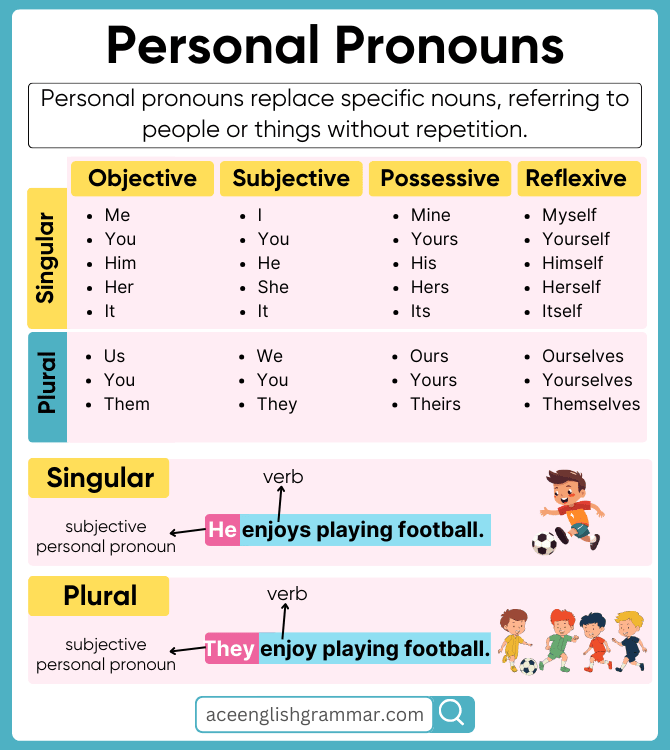
Table of Contents
List of Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are divided into three categories based on the person they refer to.
1. First-Person Pronouns (Referring to the Speaker)
- Singular: I, me
- Plural: We, us
2. Second-Person Pronoun (Referring to the Listener)
- Singular & Plural: You
3. Third-Person Pronouns (Referring to Someone or Something Else)
- Plural: They, them
- Singular: He, him, she, her, it
Rules for Using Personal Pronouns
1. Match the Pronoun with Its Antecedent
A pronoun must agree with its antecedent in number, gender, and person.
- ✅ Fatima loves her book.
- ❌ Fatima loves his book.
2. Use Subjective Pronouns as Subjects
Subjective pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, we, they) are used as the subject of a sentence.
- ✅ She is my best friend.
- ❌ Her is my best friend.
3. Use Objective Pronouns as Objects
Objective pronouns (me, you, him, her, it, us, them) function as the object of a verb or preposition.
- ✅ Ali called me yesterday.
- ❌ Ali called I yesterday.
4. Use Possessive Pronouns Correctly
Possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs) do not need apostrophes.
- ✅ This book is hers.
- ❌ This book is her’s.
5. Use Reflexive Pronouns for Emphasis or Reflection
Reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves) reflect back to the subject.
- ✅ I made this cake myself.
- ❌ I made this cake me.
Types of Personal Pronouns
Pronoun that replace specific nouns and refer to people or things. They are categorized into subjective, objective, and possessive forms.
1. Subjective Personal Pronouns
These pronouns act as the subject of a sentence.
- I like coffee.
- She is a doctor.
- They are playing football.
2. Objective Personal Pronouns
Objective personal pronouns act as the object of a verb or preposition.
- The teacher called me.
- Ahmed gave the book to her.
- We invited them to the party.
3. Possessive Personal Pronouns
These pronouns show ownership or possession and do not require an apostrophe.
- This book is mine.
- The house is theirs.
- The decision is yours.
4. Reflexive Personal Pronouns
These pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence and are used for emphasis or to indicate self-action.
- I did it myself.
- They prepared the meal themselves.
- She taught herself how to code.
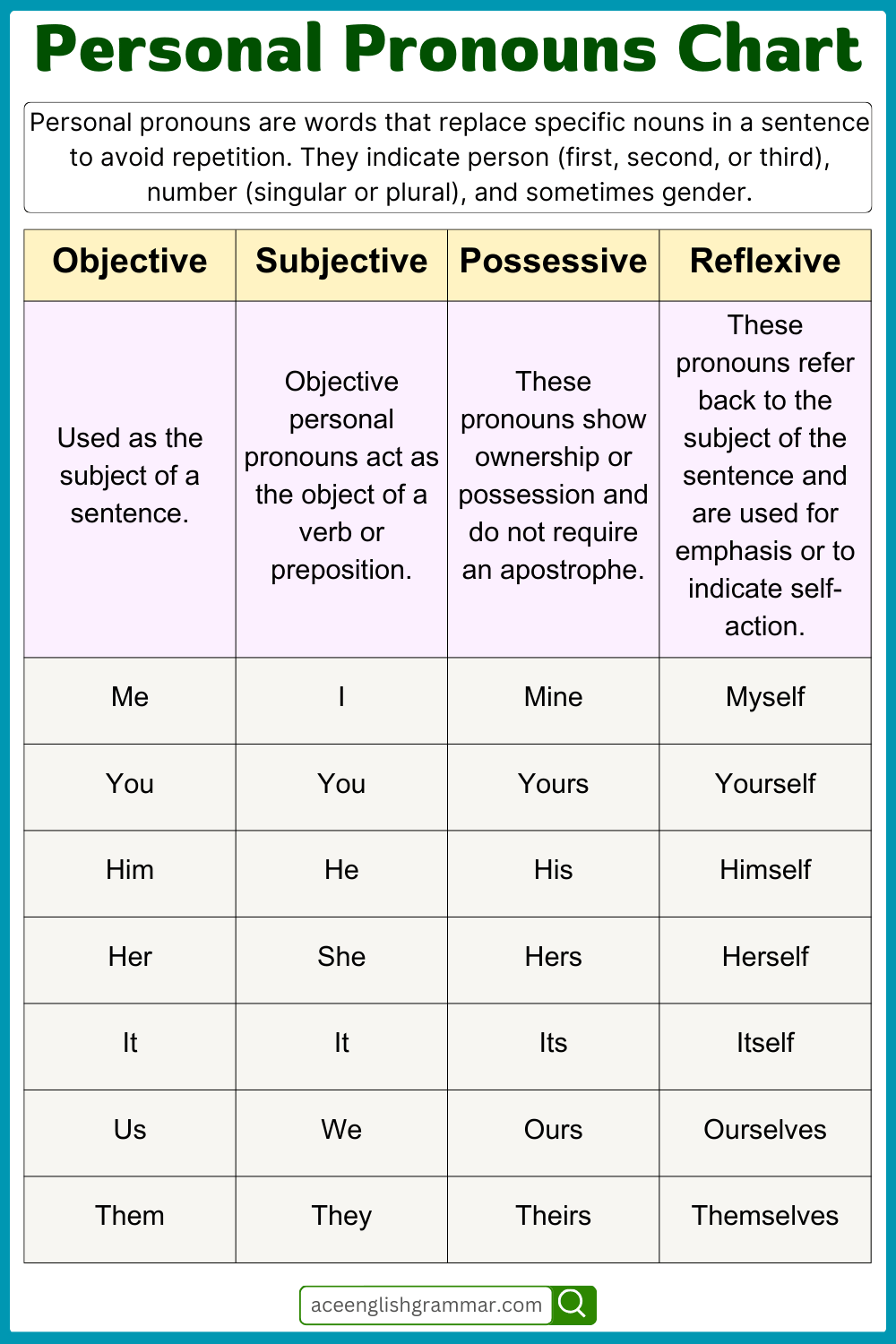
Personal Pronouns Chart with Examples
Personal pronouns are essential in English grammar as they replace nouns to avoid repetition. They are categorized into four main types: Objective, Subjective, Possessive, and Reflexive pronouns.
| Pronoun Type | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| Subjective (Used as subjects) | I, You, He, She, It | We, You, They |
| Objective (Used as objects) | Me, You, Him, Her, It | Us, You, Them |
| Possessive (Show ownership) | Mine, Yours, His, Hers, Its | Ours, Yours, Theirs |
| Reflexive (Refer back to the subject) | Myself, Yourself, Himself, Herself, Itself | Ourselves, Yourselves, Themselves |
How They Indicate Person, Number, and Gender
| Person | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| First-Person | I, me | We, us |
| Second-Person | You | You |
| Third-Person | He, him, she, her, it | They, them |
Subjective vs. Objective Personal Pronouns
| Subjective Pronoun | Objective Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| I | Me | I love reading. / The teacher called me. |
| You | You | You are my friend. / I will help you. |
| He | Him | He is studying. / She met him yesterday. |
| She | Her | She is kind. / They saw her at the park. |
| It | It | It is raining. / I found it useful. |
| We | Us | We are going to the mall. / The guide took us on a tour. |
| They | Them | They play football. / The coach trained them. |
Examples of Personal Pronouns in Sentences
- I love learning new languages.
- You are doing a great job.
- He enjoys playing football.
- She reads novels every day.
- It looks like it will rain.
- We traveled to Turkey last summer.
- They work at the hospital.
- The teacher asked me a question.
- Ahmed invited you to the party.
- Sarah helped him with his homework.
- The manager spoke to her about the project.
- Ali placed it on the table.
- The guide showed us around the city.
- The instructor advised them to study harder.
- This book is mine.
Common Errors with Personal Pronouns
Using subjective pronouns as objects:
- Me and Ali went to the park. ❌
- Ali and I went to the park. ✅
Using objective pronouns as subjects:
- Him and me are friends. ❌
- He and I are friends. ✅
Confusion between possessive pronouns and contractions:.
- Its a good idea. ❌
- It’s a good idea. ✅
Why Are They Important in English?
Personal pronoun is essential for:
- Fluent communication: They simplify sentences and avoid repetition.
- Clarity: They specify who is performing an action or receiving it.
- Grammar correctness: Using the right pronoun form ensures proper sentence structure.
FAQs
Subjective pronouns act as the subject of a sentence (I, he, she, we, they), while objective pronouns act as the object of a verb or preposition (me, him, her, us, them).
No, “it” is used for objects, animals, or abstract ideas. For people, use “he,” “she,” or “they.”
They are mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs and show ownership.
Ensure pronoun-antecedent agreement, use subjective pronouns as subjects and objective pronouns as objects, and distinguish between possessive pronouns and contractions.
“They” is commonly used as a gender-neutral singular pronoun to refer to a person when their gender is unknown or unspecified.
Conclusion
Personal pronouns are vital in English for clear, concise, and effective communication. By understanding their types, functions, and correct usage, learners can improve their grammar and fluency. Mastering personal pronoun ensures more natural and grammatically correct speech and writing.
Read More