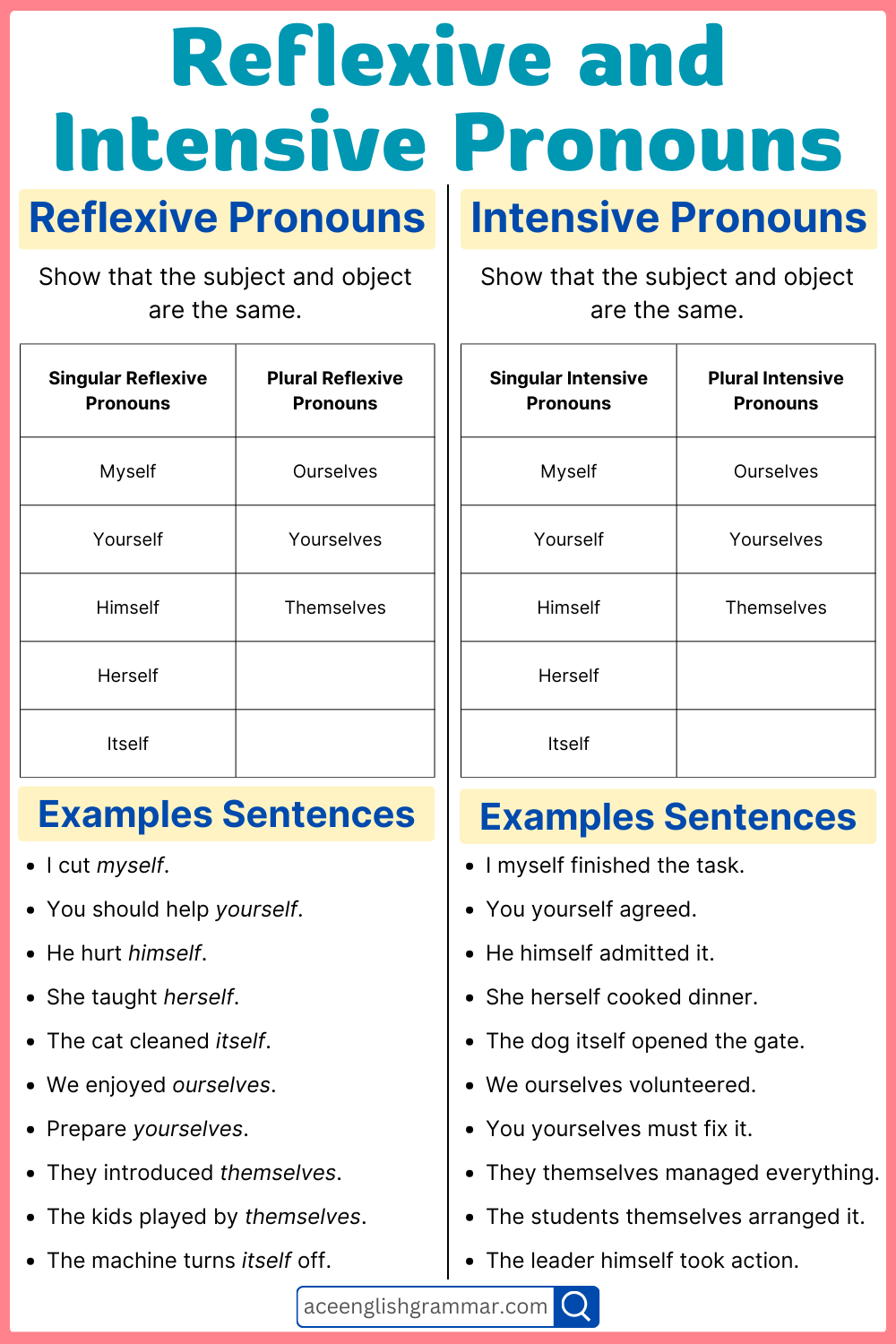
Reflexive and intensive pronouns look similar but serve different purposes. Words like myself, yourself, himself, herself, and themselves can be used to reflect back on the subject (reflexive) or to add emphasis (intensive). Many English learners struggle to distinguish between them. Understanding reflexive pronouns and intensive pronouns helps improve clarity and precision in writing. This blog post helps learn reflexive and intensive pronouns with definitions, rules, and examples for better English grammar.
Table of Contents
What is a Reflexive Pronoun?
A reflexive pronoun is used when the subject and object of a sentence are the same. It ends in -self (singular) or -selves (plural). Reflexive pronouns ensure the action reflects back on the subject.
List of Reflexive Pronouns
Singular Reflexive Pronouns:
- Myself
- Yourself
- Himself
- Herself
- Itself
Plural Reflexive Pronouns:
- Ourselves
- Yourselves
- Themselves
Usage Rules for Reflexive Pronouns
- Refers Back to the Subject: Used when the subject and object are the same person.
- Essential to Sentence Meaning: If removed, the sentence may lose its meaning.
- Used with Certain Verbs: Works with verbs like introduce, blame, teach, enjoy, hurt, perjure.
- Incorrect: He cooked for him. ❌
- Correct: He cooked for himself. ✅
What is an Intensive Pronoun?
An intensive pronoun is used to add emphasis but does not change the meaning of a sentence. If removed, the sentence still makes sense.
List of Intensive Pronouns
Singular Intensive Pronouns:
- Myself
- Yourself
- Himself
- Herself
- Itself
Plural Intensive Pronouns:
- Ourselves
- Yourselves
- Themselves
Usage Rules for Intensive Pronouns
- Used for Emphasis: Adds extra force to a noun or pronoun.
- Not Essential to the Sentence: The sentence retains meaning without it.
- Placed Near the Word It Emphasizes: Usually follows the subject or noun.
- Incorrect: The boy himself hurt. ❌
- Correct: The boy himself got hurt. ✅
Key Differences Between Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns
| Feature | Reflexive Pronouns | Intensive Pronouns |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Refers back to the subject | Emphasizes the subject |
| Sentence Meaning | Essential for meaning | Can be removed without affecting meaning |
| Position | Acts as an object | Usually follows the noun or pronoun |
| Example | She taught herself to swim. | She herself won the competition. |
Examples of Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns in Sentences
Reflexive Pronouns – Examples:
- I hurt myself while cooking.
- He taught himself to play the guitar.
- She looked at herself in the mirror.
- The cat cleaned itself after eating.
- We enjoyed ourselves at the party.
- You should take care of yourself.
- They introduced themselves to the new neighbors.
- The students prepared themselves for the exam.
- The dog entertained itself with a toy.
- She reminded herself to submit the assignment.
Intensive Pronouns – Examples:
- I myself completed the entire project.
- He himself admitted his mistake.
- She herself baked the cake for the party.
- The machine itself stopped working.
- We ourselves decorated the venue.
- You yourself should apologize for the mistake.
- They themselves built the house from scratch.
- The president himself delivered the speech.
- The author herself signed the books.
- The players themselves decided the strategy.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Using Reflexive Pronouns Incorrectly
- Incorrect: He bought a gift for myself. ❌
- Correct: He bought a gift for me. ✅
- Overusing Intensive Pronouns
- Incorrect: The manager himself will himself attend. ❌
- Correct: The manager himself will attend. ✅
- Confusing Reflexive with Intensive Pronouns
- Incorrect: She herself cut herself while cooking. ❌
- Correct: She herself cut her finger. ✅
FAQs
No, reflexive pronouns cannot be subjects. They act as objects in a sentence.
The sentence will still be grammatically correct but lose emphasis.
No, reflexive pronouns serve as objects, while intensive pronouns provide emphasis.
Yes, but it is usually placed immediately after the noun it emphasizes.
Common verbs include introduce, blame, teach, enjoy, hurt, perjure.
Conclusion
Reflexive and intensive pronouns may look alike but serve different purposes. Reflexive pronouns are necessary for sentence meaning, while intensive pronouns emphasize a subject. Understanding the distinction helps in using them accurately in writing and speech.
Download PDF
Click bellow to download this guide as a PDF for easy reference!
Read More